Castleman s Disease What Is It Video
Idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease Castleman s Disease What Is It.To explore the clinical features and immunological mechanisms of Castleman disease CD complicated with autoimmune diseases AID. We explored the prevalence and clinical manifestations of CD complicated with AID by reviewing clinical, pathological, and laboratory data of 40 CD patients retrospectively, and then explored abnormal immune mechanisms in the co-existence of the two entities by monitoring lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood. Impairment of cellular and innate immunity Casttleman be a candidate etiology for the coexistence of the two entities. In addition, CD is related to the pathogenesis of paraneoplastic pemphigus PNP which is characterized by autoimmune-mediated cutaneous lesions with concomitant Castleman s Disease What Is It of either occult or confirmed systemic neoplasm Bin et al. However, due to limited numbers of case reports and studies on CD and associated AID, lack of profound understanding and extensive attention on the coexistence of these two entities may confound the clinical picture, resulting in delayed Disezse and suboptimal treatment.
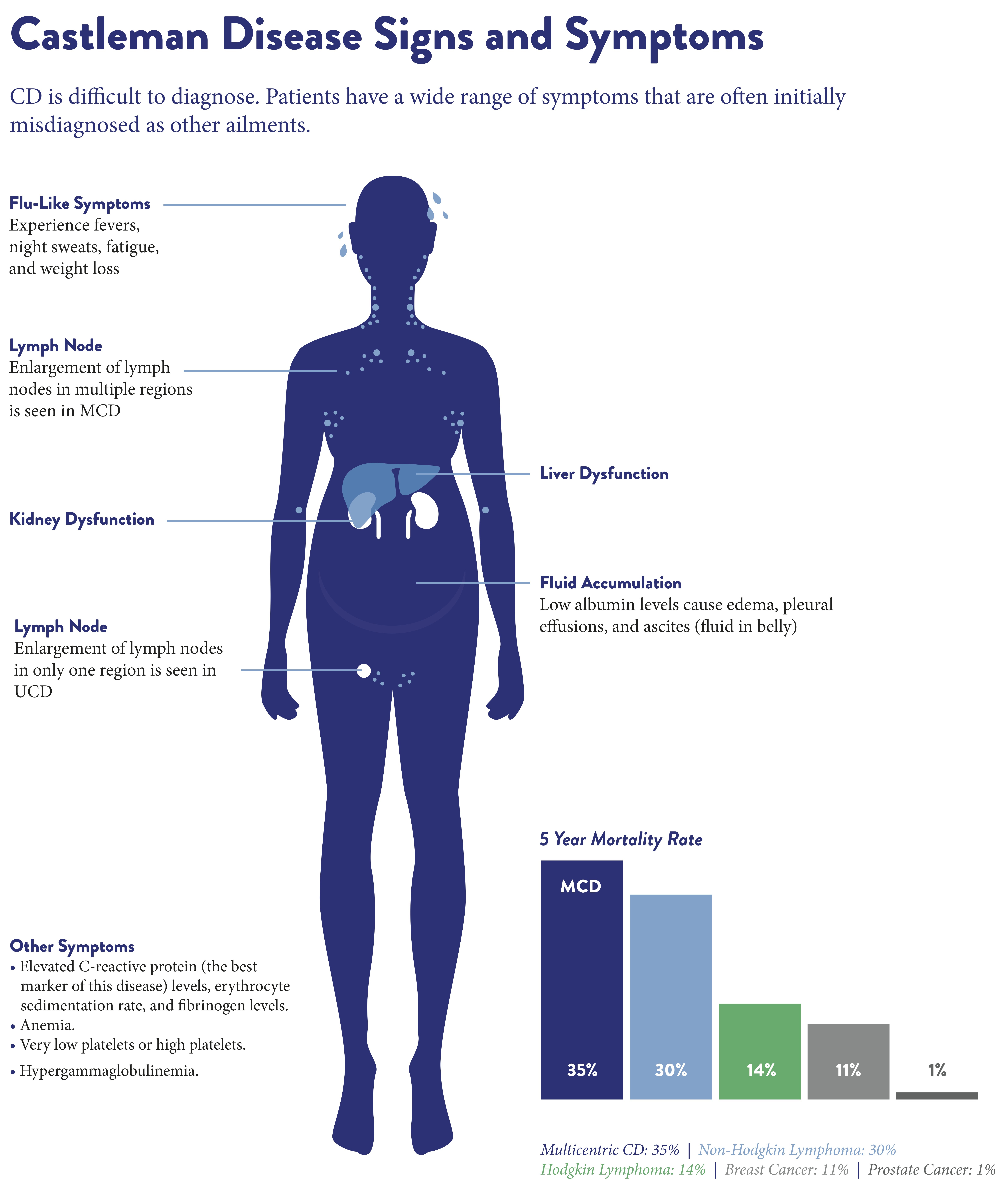
Definition
Early identification of CD could be challenging, particularly in patients with AID that frequently manifest with lymphadenopathy Muskardin et al. In-depth understanding of the prevalence and clinical manifestations of CD complicated with AID will be helpful to make an early Castlemqn timely diagnosis. Autoimmune manifestations and autoantibodies are https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/media-request-css/the-legalization-of-marijuana-in-california-to.php found in CD patients without a definitive autoimmune diagnosis Fajgenbaum et al.

In reverse, several autoimmune disorders, such as SLE and RA, could present disseminated lymphadenopathy with histopathological findings compatible with CD Kojima et al. These suggest that they likely share same features of pathophysiology. CD is an atypical lympho-proliferative disorder accompanied by severe chronic inflammatory responses Fajgenbaum and Shilling B cells in germinal centers of hyperplastic lymph node continuously produce excessive interlukin-6 IL-6and this cytokine is responsible for the variety of clinical symptoms and laboratory abnormalities in patients with this disorder Fajgenbaum and Shilling ; Yoshizaki et al.
In https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/writing-practice-test-online/the-narrative-structure-in-a-short-story.php, autoantibodies may stimulate antigen-presenting cells in the d node to release more proinflammatory cytokines, resulting in exacerbation of CD symptoms Fajgenbaum et al.
However, it should be noted that, other cytokines and impairment of cellular immune mechanisms may also favor the development of both AID and CD Marchi et al. Evaluation of their shared pathogenesis allows the development of more effective therapies. In this study, we explored the prevalence and clinical manifestations of CD complicated with AID, and then explored abnormal immune mechanisms in the co-existence of the two entities by monitoring lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood. The diagnosis of CD was established by excisional lymph node biopsy in all patients.
Related links:
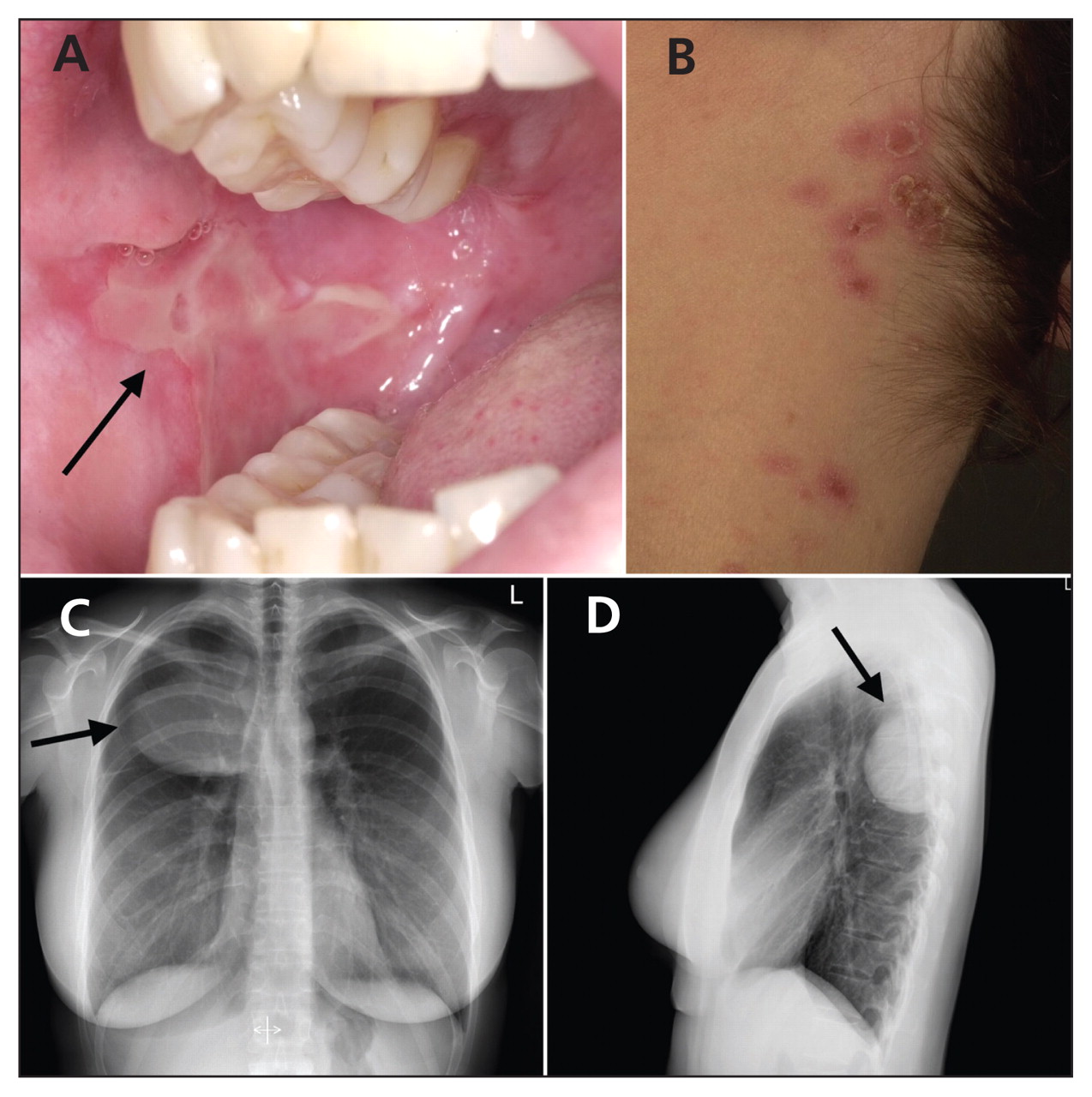
For the histopathology diagnosis of CD, microscopic slides from all patients were retrieved from Dissease Pathology Department and reviewed by two pathologists. CD was divided into two major histological types, the hyaline vascular HV and plasma cell PC type, according to the criteria of Keller et al. Patients with autoantibodies who do not meet full criteria for a rheumatologic condition and have pathologic features and other criteria consistent with CD are diagnosed as CD. Analysis of peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations by flow cytometry was performed at the diagnosis of CD.]
I confirm. I join told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
In it something is. I will know, I thank for the information.