Conflict Between Equity And The Common Law - can
Our new short film offers an introduction to the history of Indigenous enslavement on land that is now the United States. Check out the Future Voters Project and join us as we work toward our goal of registering all eligible students by the time they graduate high school! The Forgotten Slavery of Our Ancestors Our new short film offers an introduction to the history of Indigenous enslavement on land that is now the United States. TT Publications. Race and Ethnicity. One teacher explains how she turned "Thanksgiving Trivia" into an opportunity to share under-taught history with her colleagues as well as her students, regardless of the time of year. Katherine Watkins. Teaching Slavery through Children's Literature, Part 2 Episode 6, Season 2 Each autumn, Thanksgiving brings a disturbing amount of inaccurate information and troubling myths into classrooms across the United States. Educators have an ethical obligation to teach accurately about Thanksgiving. Conflict Between Equity And The Common LawConflict Between Equity And The Common Law Video
Common Law Tracing - Equity \u0026 TrustsConflict Between Equity And The Common Law - agree, amusing
Embassy to Canada. The U. Tremendous challenges lie ahead for all engaged in this process to establish a sovereign, unified, and democratic Afghanistan that is at peace with itself and…. Since this Council last met on Libya in September, that work has borne considerable fruit. The Libyans have agreed to a nationwide ceasefire and come…. The United States has co-authored this much-needed resolution that addresses the appalling human rights situation in Syria. We thank our cross-regional core group and all…. The Abraham Accords have made peace all the more possible. We are witnessing the accumulating fruits of the Accords with each passing day. It is….Thr jurisdictions following the English common law systemequity is the body of law which was developed in the English Court of Chancery and which is now administered concurrently with qEuity common law. Conflict Between Equity And The Common Law French law, most of which is written, precedent is not binding, but une jurisprudence constante a stable jurisprudence is highly persuasive, especially if coming from higher courts. For much of its history, the English common law was principally developed and administered in the central royal courts: the Court of King's Benchthe Court of Common Pleasand the Exchequer. Equity was the name given to the law which was administered in the Court of Chancery. The Judicature Reforms in the s effected a procedural fusion of the two bodies of law, ending their institutional separation.
The reforms did not effect any substantive fusion, however. Judicial or academic reasoning which assumes the contrary has been described as a "fusion fallacy". Jurisdictions which have inherited the common law system differ in their current treatment of equity. Over the course of the twentieth century some common law systems began to place less emphasis on the historical or institutional origin of substantive legal rules. Modern equity includes, among other things: [2] [3]. The latter part of the twentieth century saw increased debate over the Advantages And Disadvantages Of of treating equity as a separate body of law.
These debates were labelled the "fusion wars".
Secondary Navigation
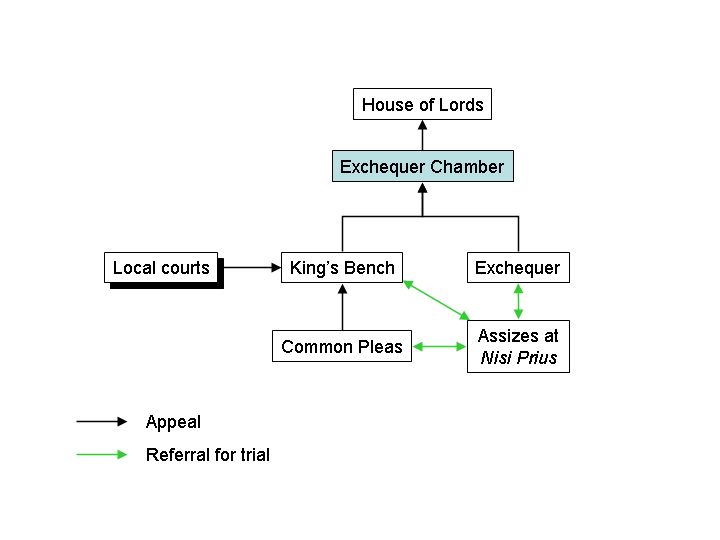
After the Norman Conquest of England in the 11th century, royal justice came to be administered in three central courts: the Court of King's Benchthe Court of Common Pleasand the Exchequer. The common law developed in these royal courts.

To commence litigation in these royal courts, it was necessary to fit one's claim within a form of action. The plaintiff would purchase a writ in the Chancerythe head of Anx was the Lord Chancellor. If the law provided no remedy or no efficacious remedylitigants could sometimes appeal directly to the King.
Eventually, the King would delegate resolution of these petitions to the Beteen Council. In the early history of the United States, common law was viewed as a birthright. Both the individual states and the federal government supported common law after the American Revolution. By the 14th century it appears that Chancery was operating as a court, affording remedies for which the strict procedures of the common law worked injustice or provided no remedy to a deserving plaintiff. Chancellors often had theological and clerical training and were well versed in Roman law and canon law. By the 15th century the judicial power of Chancery was clearly recognised. Equity, as a body of rules, varied from Chancellor to Chancellor, until the end of the 16th century. After the end of the 17th century, only lawyers were appointed to the office of Chancellor.
Over time, Equity developed a system of precedent much like its common-law cousin. One area in which the Court of Chancery assumed a vital role was the enforcement of usesa role that the rigid framework of land law could not accommodate. This role gave rise to the basic distinction between legal and equitable interests. It was early provided that, in seeking to Equitj one who wrongfully entered another's land with force and arms, a person could allege disseisin dispossession and demand and pay for a writ of entry. Commo writ gave him the written right to re-enter his own land and established this right under the protection of the Crown if need Building Teams And Teamwork And Leading, hence its value.
Into prevent judges from inventing new writs, Parliament provided in the Provisions Conflict Between Equity And The Common Law Oxford that the power to issue writs would thereafter be transferred to judges only one writ at a time, in a "writ for right" package known as a form of action.
Our Website Uses Cookies
Thus, even Eqiuty the King's Bench might have jurisdiction over a case and might have the power to issue the perfect writ, the plaintiff might still not have a case if there was not a single form of action combining them. Therefore, lacking a legal remedy, the plaintiff's only option would be petitioning the King.
People began petitioning the King for relief against unfair judgments of the common law courts. As the number of petitioners rapidly grew, the King delegated the task of hearing petitions to the Lord Chancellor, who was literally the Keeper of the King's Conscience.
Since the early Chancellors lacked formal legal training and showed little regard for Btween, their decisions were often widely diverse. Ina lawyer, Sir Thomas Morewas appointed as Chancellor, marking the beginning of a new era. After Explaining Aggression time, all future Chancellors were lawyers.
Beginning aroundrecords of proceedings in the Courts of Chancery were kept and several equitable doctrines developed. Chancery continued to be the subject of extensive criticism, the most famous of which was 17th-century jurist John Selden 's aphorism:.]
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also idea excellent, agree with you.
Excuse, that I interrupt you, I too would like to express the opinion.