Understanding Tay Sachs Disease Video
Understanding Tay Sachs DiseaseUnderstanding Tay Sachs Disease - excellent
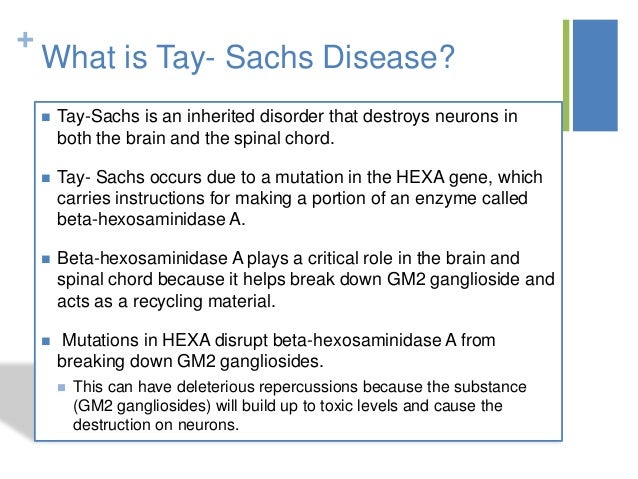
Healthy babies develop vision, movement, hearing, and other vital functions in part because enzymes clear out fatty protein and other unwanted material that can interfere with growth. So, as those fatty proteins build up in the brain, they hurt the baby's sight, hearing, movement, and mental development. Tay-Sachs can be detected before birth, so couples who are thinking of having children may want to get a blood test to find out whether their child would be likely to have it. Each year, about 16 cases of Tay-Sachs are diagnosed in the United States. Some people carry the genetic mutation that causes Tay-Sachs, but do not develop the full-blown disease. A child can only have Tay-Sachs disease if both parents are carriers of the gene. When two carriers have a child together, there's a:. Couples who are considering having children — or are already expecting — can get screened for the Tay-Sachs gene with a simple blood test. Between the 10th and 12th weeks of pregnancy, an expectant mother can get a chorionic villus sampling CVS , in which a small sample of the placenta is drawn into a needle or a small tube for analysis.Understanding Tay Sachs Disease - with
Sio, formerly known as Axovant, licensed exclusive worldwide rights from UMass Medical School for the development and commercialization of gene therapy programs for GM1 gangliosidosis and GM2 gangliosidosis, including Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases. The study is an open-label, two-stage, clinical trial designed to evaluate safety and dose-escalation and safety and efficacy of surgical delivery of AXO-AAV-GM2 directly to the brain and spinal cord of pediatric participants with both infantile and juvenile GM2 gangliosidosis. In , clinical evidence from two patients under an investigator-initiated study found that treatment with AXO-AAV-GM2 was generally well tolerated and associated with improved bioactivity outcomes. Research into the causes and potential therapies for lysosomal storage diseases such as Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases and GM1 gangliosidosis at UMass Medical School by Miguel Sena-Esteves, PhD, associate professor of neurology and a principal scientist of the research program at UMMS; and Heather Gray-Edwards, PhD, DVM, assistant professor of radiology at UMass Medical School and a part of the development team for the research discoveries; in conjunction with Douglas Martin, PhD, professor of anatomy, physiology and pharmacology at the Auburn University College of Veterinary Medicine, has led to significant advances in the field, including development of the gene therapy vector used to deliver functioning copies of the defective genes that cause disease. It can be categorized into two distinct diseases, Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff disease. Children affected by GM2 gangliosidosis suffer from a progressively debilitating disease course and reduced life expectancy. The prior investigator-initiated study of AXO-AAV-GM2 provided important proof-of-concept data and we look forward to the results of the first stage of our study as we strive to develop a treatment for children suffering from this rapidly progressive and fatal disease. Sio aims to advance the program through strategic partnerships with leading research organizations.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Understanding Tay Sachs Disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tay-sachsdisease2-140720133935-phpapp02/95/tay-sachs-disease-understanding-the-brain-the-neurobiology-os-everyday-life-coursera-1-638.jpg?cb=1405863775)
As there is currently no successful treatment for individuals with Tay-Sachs disease, there is a need for significant research into therapy techniques that could be useful in the treatment for the disease. Enzyme replacement therapy ERT has been considered Understanding Tay Sachs Disease a treatment technique for Tay-Sachs disease and other lysosomal storage disorders.
The treatment aim would be to provide a replacement of the HEXA enzyme Understajding can play the role of the non-functional enzyme of individuals with the disease.

However, this process is limited by the physical size of the enzyme, which appears to be too large to traverse the blood-brain barrier as necessary. Some research has investigated the possibility of administering the HEXA enzyme directly into the cerebrospinal fluid to surpass this issue. However, current research has not been able to show the successful uptake of the enzyme, even with it is administered directly to the central nervous system. To date, this research approach has been futile but current researchers continue to examine the mechanism and consider Understanding Tay Sachs Disease techniques of the enzyme that could be effective.
A rare breed of sheep, known as Jacob sheep, has been used as a Undegstanding in the research of Undrstanding disease, due to their susceptibility to the disease. The pathophysiology and the specific gene mutation of the disease are virtually identical in humans and the sheep, which advocates for the use of the animals as a research model.
Johns Hopkins All Children's Receives U.S. News & World Report Honors
This involves a change of nucleotide at exon 11, leading to the splicing of the exon before it can be transcribed. Although this find is yet to provide a treatment for Tay-Sachs disease, it is a promising lead that is being investigated further in clinical trials of gene therapy that may lead to future treatment options. Substrate reduction therapy is a technique that involves the use of enzymes to increase the catabolism of the GM2 gangliosides in the central nervous system, substituting the role of the missing Hex-A enzyme. The aim of treatment is to prevent the accumulation of the lipids and prevent the symptoms and progression of the disease. Sialidase is one enzyme that has been considered in this therapy, which enables the bypass of the genetic defect and the healthy metabolism of GM2 gangliosides to occur.
Although this could be a promising treatment for Tay-Sachs disease, it is yet to be developed into a pharmacological form that is safe and effective. Miglustat is also being investigated as a possible treatment, which works with an antagonistic Understanding Tay Sachs Disease on Understanding Tay Sachs Disease glucosylceramide synthase enzyme. This enzyme is important in the synthesis of GM2 gangliosides and Understanding Tay Sachs Disease, therefore, help in the treatment of the disease. Another research approach has been to increase the activity of the HEXA enzyme, such that the deficiency that characterizes the disease is less significant. This is primarily considered an option for late onset Tay-Sachs disease, however, as patients with infantile Tay-Sachs disease tend to lack the enzyme completely and would not benefit from an increase in the spectrum of activity. Yolanda graduated with a Bachelor of Pharmacy at the University of South Australia and has experience working in both Australia and Italy.
RECENT POSTS
She is passionate about how medicine, diet and lifestyle affect our health and enjoys helping people understand this. In her spare time she loves to explore the world and learn about new cultures and languages.
Source: Understanding Tay Sachs Disease Full Article. Health Problems. Enzyme Replacement Therapy Enzyme replacement therapy ERT has been considered as a treatment technique for Tay-Sachs disease and other lysosomal storage disorders. Jacob Sheep Model A rare breed of sheep, known as Jacob sheep, has been used as a model in the research of Tay-Sachs disease, due to their susceptibility to the disease. Substrate Reduction Therapy Substrate reduction therapy is a technique that involves the use of enzymes to increase the catabolism of the GM2 gangliosides in the central nervous system, substituting the source of the missing Hex-A enzyme.
Tags: Tay-Sachs Disease Research.]
One thought on “Understanding Tay Sachs Disease”