Navigation menu
The supply curve is a graphic illustration of the interplay between price and supply. The following principle click the higher the price, the greater the offer from the producers. The concept of the supply curve comes from the field of economic theory and describes the natural relationship between supply and price of a good or service. The basic Crve behind the term is the fact that the offered quantity of a good increases the higher the price to be paid for it.
The supply curve is therefore generally more or less rising — depending on the goods in question. The course of the supply curve is also influenced by the so-called supply elasticity.

This indicates how strong the relative change in quantity is in relation to the corresponding change in price. The core idea: the higher the price of a good, the higher the quantity offered. On the other hand, if the price is comparatively low, production is hardly worthwhile, or not at all.
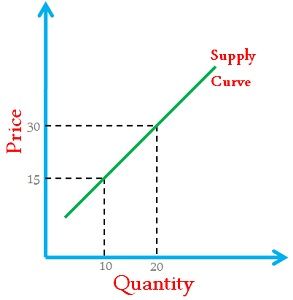
However, shifts in the curve are also conceivable. If the curve does not originate in the zero point but on the Y-axis, the production of the good is only worthwhile from this point or price. The supply curve not only indicates the quantity produced at a certain price. It contains further, important information:. It measures how much the offer changes when the price is reduced by 1 percent. If the supply volume then decreases by more than 1 percent, then one speaks of an elastic supply. In this case, the supply curve is very steep.
Toggle navigation. What Is the Definition of the Supply Curve. All rights reserved.]

I can not take part now in discussion - there is no free time. I will be free - I will necessarily express the opinion.