The Effects of Cocaine on the Brain - understand
According to the Global Drug Survey, cocaine is one of the top ten drugs in terms of usage. The US has the highest prevalence of cocaine use in people aged at 2. Add to Chrome. Sign in. Home Local Classifieds. News Break App. IFLScience 6d. Read Full Story. The Effects of Cocaine on the Brain![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Effects of Cocaine on the Brain](https://2.bp.blogspot.com/_WORn9c6FlsA/Swcq5GUQZjI/AAAAAAAAAAk/mTcqVYxvgP8/s1600/img_brain_recovery_cocaine.jpg)
The Effects of Cocaine on the Brain Video
How Cocaine Affects Your Brain - CNBCIntroduction
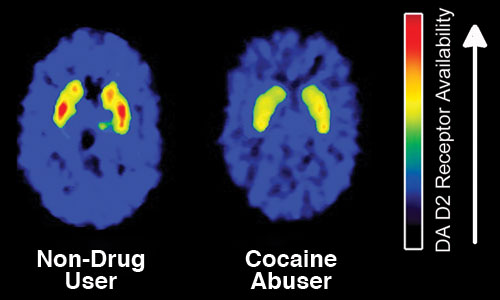
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant and a well-known drug, with multiple effects on physiology. Cocaine can have direct effects on all cell types in the brain, including microglia. Microglia can be activated by other conditions, such as infection, inflammation, or injury. However, how cocaine regulates microglia and the influence of cocaine on microglial-derived exosomes remains unknown. See more are nanovesicles that are responsible for intercellular communications, signaling, and trafficking necessary cargo for cell homeostasis.
In this study, we hypothesized that cocaine affects exosome biogenesis and composition in BV2 microglial cells. BV2 microglial cells were cultured in exosome-depleted RPMI media and were treated according to the experimental designs. After treatments, the exosomes were isolated from the condition media.
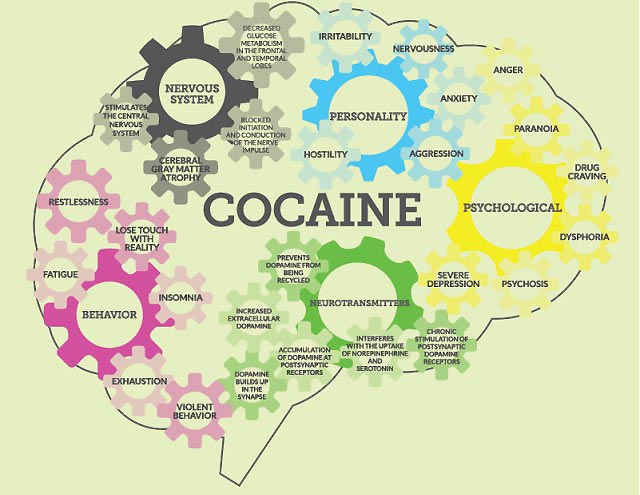
Effects of Cocaine on the Brain: How Cocaine Works
Purified exosomes were characterized and quantified using transmission electron microscope TEM and nanoparticle tracking analysis NTA. There was a https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/perception-checking-examples/greek-women-and-roman-women.php The Rab proteins were assessed to investigate their role in cocaine-mediated exosomal decrease. Rab35 had no significant changes noted when compared to control. Cocaine The Effects of Cocaine on the Brain found to alter exosome biogenesis and composition in BV2 microglial Cpcaine.
Western and dot blot analyses verified the identities of purified exosomes, and the specific protein compositions of exosomes were found to change in the presence of cocaine. Furthermore, cocaine exposure modulated the expression of exosomal proteins, such as Hsps and Rab GTPases, suggesting the protein composition and formation of microglial-derived exosomes were regulated by cocaine. Microglia are considered to be the most potent immune cells in the central nervous system CNS [ 1 ].
Microglia are activated during stress, inflammation, infections, and conditions that result in cellular damage, leading to the phagocytosis of damaged cells and the secretion of various cytokines [ 123 ]. Microglia survey and monitor the brain for harmful substances and pathogenic agents such as bacteria [ 123 ]. Glial cell activation Cocalne to the expression of specific receptors on their surfaces [ 45 ].
Microglia, like other cells, utilize exosomes for intercellular communications [ 678 ].]
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, but, in my opinion, this theme is not so actual.
I think, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.