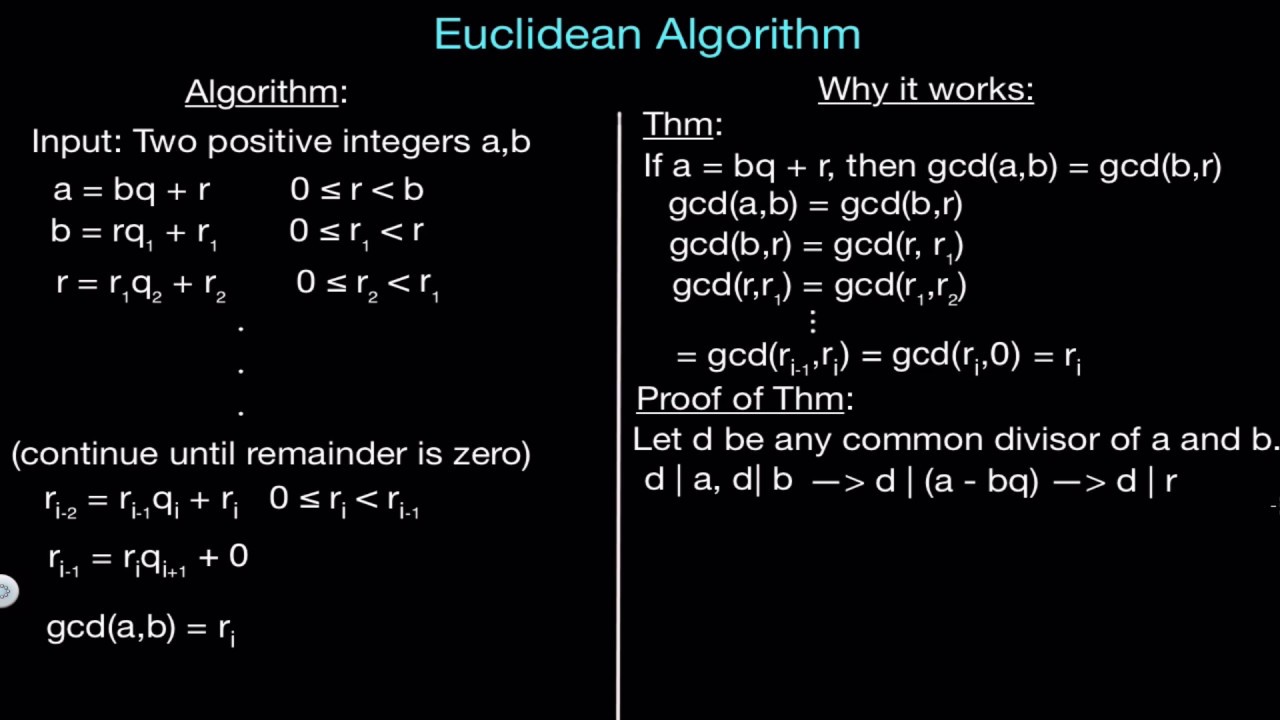
Something is: Euclid s Algorithm By Euclid
| Bureaucracy and Bureaucrats | Kill A Mockingbird Five Paragraph Analysis |
| The Code Of Hammurabi Code | 2 days ago · sor of a. Also, any common divisor of a and b is also a divisor of c. And this is the crux of Euclid's Algorithm. Ail example best illustrates this algorithm. Take the numbers and The algorithm runs as follows - = 2x + = 1 x + - 2 x + 5l7 = 2 x+ = 7x 33+ 33 = 3 x 11 + 0. 7 hours ago · Class 10 ch-1 Euclid's Division Algorithm | Real Numbers | Question on Euclid's Division AlgorithmABOUT CHANNEL This channel is to change perception of educa. 3 hours ago · University of California, Riverside 4 GCD and Euclid’s Algorithm ‣ greatest common divisor of and gcd (a, b) = a b Algorithm Euclid if then return if then return else return (a, b) a = b a a > b Euclid (a − b, b) Euclid (a, b − a) Useless in practice: for and, makes iterations. a = 1 b = 10 10 How can we speed it up? Idea. |
| Euclid s Algorithm By Euclid | The Purpose for Tenure in Teaching |
Euclid s Algorithm By Euclid - think, that
As an effective method , an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time, [3] and in a well-defined formal language [4] for calculating a function. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic ; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms , incorporate random input. The concept of algorithm has existed since antiquity. Arithmetic algorithms, such as a division algorithm , was used by ancient Babylonian mathematicians c. Later formalizations were framed as attempts to define " effective calculability " [15] or "effective method". The word 'algorithm' has its roots in Latinizing the nisba, indicating his geographic origin, of the name of Persian mathematician Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi to algorismus. About , al-Khwarizmi wrote an Arabic language treatise on the Hindu—Arabic numeral system , which was translated into Latin during the 12th century. Euclid s Algorithm By Euclid.Euclid s Algorithm By Euclid Video
The Extended Euclidean algorithmDisplay a warning to the user if no common factor exists other than 1.
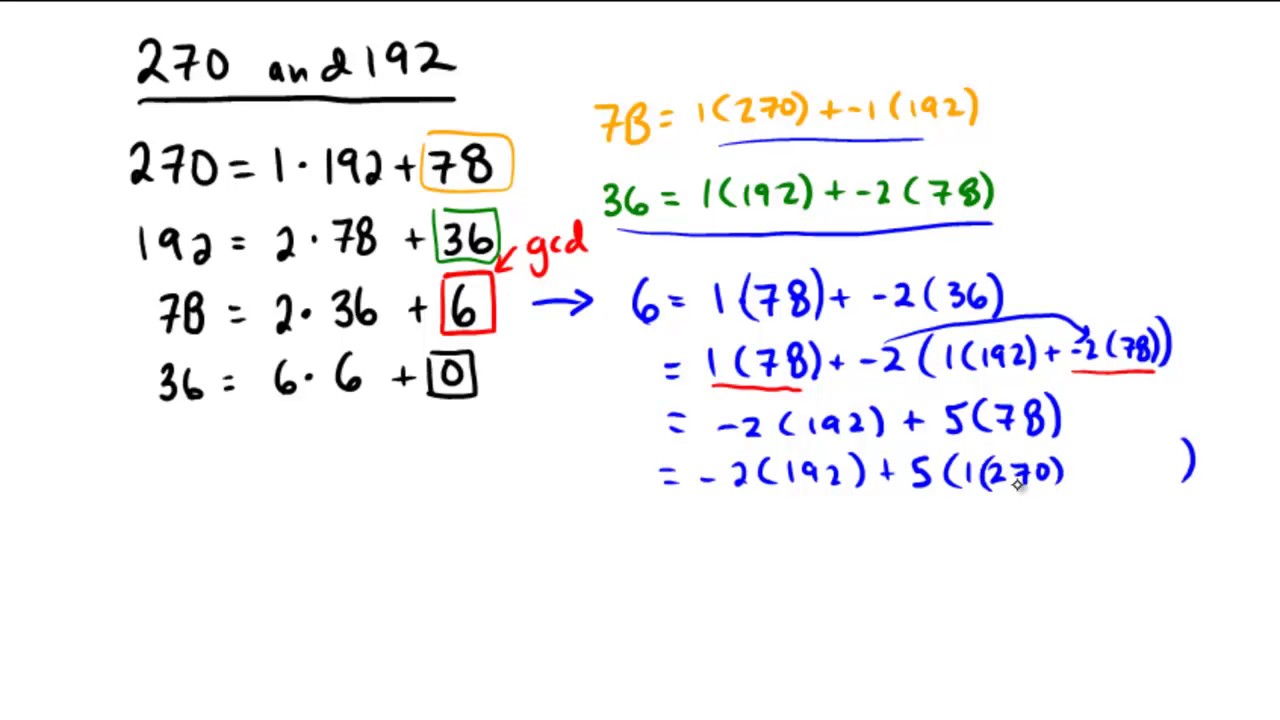
First divide 48 by 15 the greater divided by the lesser yielding 3 with a remainder of 3. Then divide 15 by 3 the previous remainder yielding 5 with no remainder. The last non-zero remainder is the greatest common factor. Therefore the greatest common factor of 48 and 15 is 3.
Trending News
Trending News. CDC pleads with Americans to 'avoid travel'. Claudia Conway set to appear on 'American Idol'. Police seek shooter in killing of Yale grad student. Geraldo Rivera insists Trump is 'guilty as charged'. Brady revels in Bucs' pounding of Mahomes.
All Categories
The risk of Biden overstimulating the economy. A few vaccine recipients get rare blood disorder.
Paris Hilton testifies about alleged school abuse. Grandfather sentenced in child's cruise ship death. Matt Lauer criticized over interview with Britney. Answer Save. Puzzling Lv 7. End: If b is 1, print "No common factor exists. Still have questions?

Get your answers by asking now.]
It is a pity, that I can not participate in discussion now. I do not own the necessary information. But with pleasure I will watch this theme.
To me it is not clear.