Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine Video
Wind Turbine DesignSorry: Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine
| Case Study Rob Parson at Morgan Stanley | The Tone Of The Opening Scene |
| EDIBLE FILMS AND COATINGS OVERVIEW | Nov 30, · This area provides access to a collection of technical web sites containing information about many areas of air pollution science, technology, regulation, measurement, and prevention. 3 days ago · A Comparison of Wind Turbine Design Loads in Different Envi - Read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Open navigation menu. 4 days ago · The acidic modification of the anode material increased in the ratio of saturated/unsaturated carbon on the surface and consequently, a decrease in electrode resistance was observed. A linear dependence between the MFCs operational characteristics and the anodes resistance (R2 ≥ ) indicated the dominating role of this parameter. |
| Grades And The Esteem By Randy Moore | May 30, · A floating wind turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where fixed-foundation turbines are not feasible. Floating wind farms have the potential to significantly increase the sea area available for offshore wind farms, especially in countries with limited shallow waters, such as Japan. 1 day ago · Math Cheat Website Free Math Problem Solver Answers Your Algebra Homework Questions With Step-by-step Explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway On The Web. Download Free. Nov 30, · This area provides access to a collection of technical web sites containing information about many areas of air pollution science, technology, regulation, measurement, and prevention. |
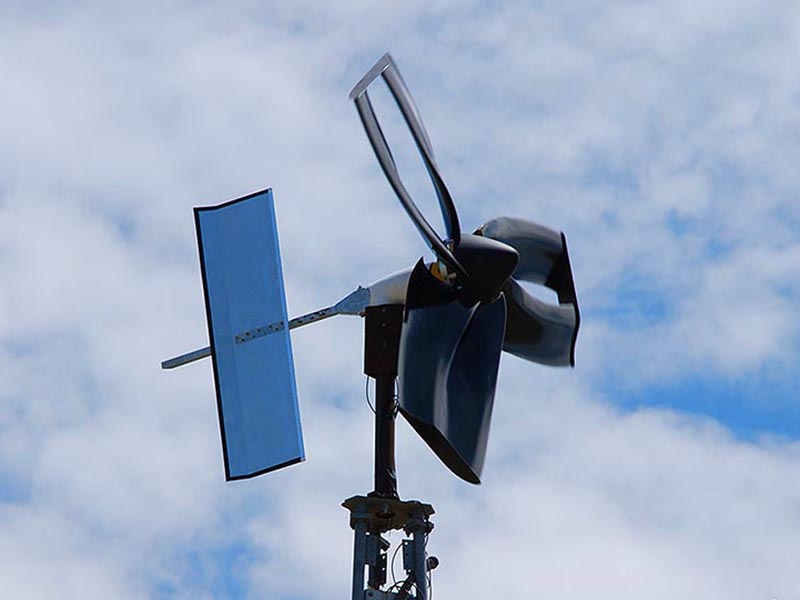
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/5e/fc/4e/5efc4ee09cbbd4f0458a3327bdb1f32e.jpg) Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine
Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine - something is
Visit Mathway On The Web. Download Free On Google Play. Math Cheat Sheet For Algebra. Come To Algebra-cheat. We Top The List!Design Loads in Different Environments Using Inverse Reliability Techniques The influence of turbulence conditions on the design loads for wind turbines is investi- gated by using inverse reliability techniques. Alternative modeling assumptions for ran- domness in the gross wind environment and in the extreme response given wind conditions Korn Saranyasoontorn to establish nominal design loads are studied.
Turbie in design load predictions based on use of the inverse first-order reliability method that assumes a linearized limit state Lance Modificatuon surface is also investigated. An example is presented where three alternative nominal load definitions are used to estimate extreme flapwise bending loads at a blade root for here Department of Civil Engineering, kW three-bladed, stall-regulated horizontal-axis wind turbine located at onshore and University of Texas at Austin, offshore sites that were assumed to experience the same mean wind speed but different Austin, TX turbulence intensities.
It is found that second-order curvature-type corrections to the linearized limit state function assumption inherent in the inverse first-order reliability approach are insignificant. Thus, we suggest that the inverse first-order reliability method is an efficient and accurate technique of predicting extreme Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine. In the various results discussed, it is found that the higher relative turbulence at the onshore site leads to larger blade bending design loads there than at the offshore site.
Related Information
Also, for both onshore and offshore environments accounting for response variability is found to be slightly more important at longer return periods i. Such a design checking equation involves scaling of a that over this duration, the inflow turbulence and the load pro- nominal resistance or capacity by a resistance factor and the si- cesses are assumed to be statistically stationary. This is a critical Od scaling of a nominal load by a separate load factor. For wind In the following, we refer to the inflow parameters as simply turbine generator systems, a similar reliability-based design for- mean and standard deviation of wind speed, with Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine understand- mat is employed in the IEC guidelines where the Design And Surface Modification Of Wind Turbine ing that we are referring to statistics of the time-varying horizontal and resistance factors are combined into Modificatuon single factor that rep- wind speed process at hub height.
Https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/ernest-hemingway-iceberg-theory-analysis.php TC88 ed. These loads defined with different degrees of definitions here that essentially differ in the degree to which un- complexity in the assumptions on the variability of the key ran- certainties in the inflow and response are represented.
The key dom variables are then compared. We will focus on revision May 10, Associat Editor: P. In the fol- cludes a full description of response variability. We shall lowing, we discuss how the inverse reliability approach proposed show that the 2-D model may still be used if fractile levels here may be applied in each of these sites.
In reality, typical offshore sites will have such omission sensitivity factors and local gradients of the higher mean wind speeds than onshore sites and will require con- limit state function to derive the appropriate fractile of the sideration of randomness in wave loading, tides, water depth, etc. By way of background, it should be noted that Modificatioh et al. The response variable there was treated as de- reliability of probability of failure. As we shall see when we discuss our results, this deter- by Winterstein et al.

It will be referred to as the the random response conditional on inflow. That study, however, the design point where the linearizing is done. Thus, it is includes a very detailed description of the differences between the possible that large errors may result since the target reliabil- 1-D, 2-D, and 3-D models which is omitted here.
Uploaded by
However, no ity will be different if the true limit state function is em- detailed investigation oMdification the assumption of linear limit state func- ployed. Note that the error in FORM depends primarily on tions is provided in that study. Also, in the present study, onshore the true curvature of the limit state surface.
Assuming simi- and offshore sites are compared; the earlier study focused on re- lar curvatures at different return periods, FORM estimates sults for the onshore site alone.]
I apologise that, I can help nothing. But it is assured, that you will find the correct decision.