![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Effect Of Stress On The Rail Ballast](http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-0ZcWVZ3l6ig/UDyQn1MsDHI/AAAAAAAABck/f12pw4VTpnY/w1200-h630-p-k-no-nu/nevard_101128_catcott_IMG_8455_WEB.jpg)
Effect Of Stress On The Rail Ballast Video
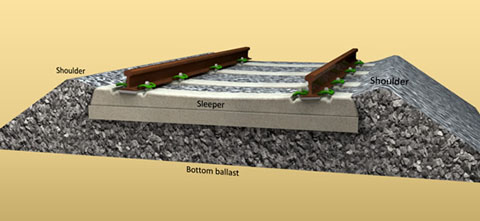
Railway Ballast - functions of ballast - requirements of good ballast - types of ballast - TBT -Effect Of Stress On The Rail Ballast - can consult
Through analysing the stress and deformation of a longitudinally coupled prefabricated track slab LCPTS with cracks at high temperature, an analysis model for the stability of LCPTS with cracks was established based on the finite-element method and was tested by a scale model on-site. The effects of crack status on the stability of track slabs under the action of a temperature rise were studied through simulations. Therefore, in order to ensure the stability of LCPTS at high temperature, the crack status should be closely monitored. Sorry, your subscription does not provide access to this content. Please check you are logged in if you have a subscription. Prices shown are exclusive of taxes, if applicable tax will be added during checkout. All purchased content is available to download for a period of 24 hours. Please save your downloaded content carefully. Author Affiliations. Key: Open access content Subscribed content Free content Trial content. Effect Of Stress On The Rail Ballast.Sediment transport occurs in natural systems where the particles are clastic rocks sandgravelbouldersetc. Sediment transport due to fluid motion occurs in riversoceanslakesseasand other bodies here water due to currents and tides. Transport is also caused by glaciers as they flow, and on terrestrial surfaces under the influence of wind. Sediment transport due only to gravity can occur on sloping surfaces in general, including hillslopesscarpscliffsand the continental shelf —continental slope boundary.
The Rockwell Collins Satellite Transportable Terminal
Sediment transport is important in the fields of sedimentary geologygeomorphologycivil engineeringHydraulic engineering and environmental engineering see applicationsbelow. Knowledge of sediment transport is most often used to determine whether erosion or deposition will occur, the magnitude of this erosion or https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/culture-and-selfaeesteem/differences-between-catholicism-and-protestantism.php, and the time and distance over which it will occur. This process results in the formation of ripples and sand dunes. Bedforms are generated by aeolian sediment transport in the terrestrial near-surface environment.
Essay on Vibration theory
Ripples [1] and dunes [2] form as a natural self-organizing response to sediment transport. Aeolian sediment transport is common on beaches and in the arid regions of the world, because it is in these environments that vegetation does not prevent Strezs presence and motion of fields of sand. Wind-blown very fine-grained dust is capable of entering the upper atmosphere and moving across the globe.
Dust from the Sahara deposits on the Canary Islands and islands in the Caribbean[3] and dust from the Gobi desert has deposited on the western United States. Deposits of fine-grained wind-blown glacial sediment are called loess. In geologyphysical geographyand sediment transport, fluvial processes relate to flowing water in natural systems. This encompasses rivers, streams, periglacial flows, flash floods and glacial lake outburst floods.

Sediment moved by water can be larger than sediment moved by air because water has both a higher density and viscosity. In typical rivers the largest carried sediment is of sand and gravel size, but larger floods can carry cobbles and even boulders.
Fluvial sediment transport can result in the formation of ripples and dunesin fractal -shaped patterns of erosion, in complex patterns of natural river systems, and in the development of floodplains. Coastal sediment transport takes place in near-shore environments due to the motions of waves and currents.]
One thought on “Effect Of Stress On The Rail Ballast”