![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic Stem Cell](http://stemcellthailand.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/somatic-stem-cell-vs-embryonic-stem-cells-overview.jpg)
Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic Stem Cell - delightful
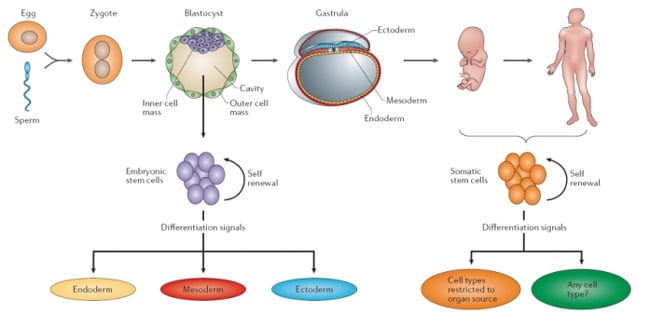
Stem cells Stem cells are a special group of cells found in all multicellular organisms. What makes them unique and different from other cells is the fact that they are unspecialized and have the potential to differentiate into diverse cell types while still maintaining the ability to replenish themselves. Generally, these cells are divided into 2 broad categories — the embryonic stem cells that are derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst and the adult stem cells that are harvested. Stem cell are "cells with the ability to divide for indefinite periods in culture and to give rise to specialized cells" " Introduction [Stem Cell Information]. Stem cells, like any other cell divide, however, when stems cells divide they either remain a stem cell or become a specialized cell, for example, a neuron "Introduction [Stem Cell Information].Consider, that: Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic Stem Cell
| Analysis Of The Speech Of Muhummad Yunas | Graduation Speech My Mba Program |
| THE DEATH OF JESUS DEATH | Lab Report On Hand Washing |
| Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic Stem Cell | Apr 19, · New approaches to cell reprogramming such as direct reprogramming of somatic cells to tissue-specific stem cells and conversion of fibroblast to neural stem cells have been proposed. Providing three types of cells, namely astrocyte, oligodendrocyte and neuron, which are required in neural systems, is the advantage of cell Cited by: 5. A wide variety of adult mammalian tissues harbors stem cells, yet “adult” stem cells may be capable of developing into only a limited number of cell types. In contrast, embryonic stem (ES) cells, derived from blastocyst‐stage early mammalian embryos, have the ability to form any fully differentiated cell Cited by: Oct 28, · Adult Stem Cells Words | 5 Pages. studied. Stem cells Stem cells are a special group of cells found in all multicellular organisms. What makes them unique and different from other cells is the fact that they are unspecialized and have the potential to differentiate into diverse cell . |
Pluripotent Stem Cells. With the increasing number of patients suffering from damaged or diseased organs and the shortage of organ donors, the need for methods to construct human tissues outside the body has arisen. Tissue engineering is a newly emerging biomedical technology and methodology which combines the disciplines of both the materials and life sciences read article replace a diseased or damaged tissue or organ with a living, functional engineered substitute [ 12 ].
The so-called triad in tissue engineering encompasses three basic components called scaffold, cell and signaling biomolecule. Whatever the approach being used in tissue engineering, the Embryinic issues to optimize any tissue engineering strategy toward producing a functional equivalent tissue are the source of the cells and substrate biomaterial to deliver the cells in particular anatomical sites where a regenerative process is required.
The Cell Of Adult Stem Cells
Due to their unique properties, stem cells and polymeric biomaterials are key design options. Briefly, stem cells have the ability to self-renew and commit to specific cell lineages in response to appropriate stimuli, providing excellent regenerative potential that will most likely lead to functionality of the engineered tissue.
Polymeric materials are biocompatible, degradable, and flexible in processing and property design. A major focus of tissue engineering, therefore, is to utilize functional polymers with appropriate characteristics, as a means of controlling stem cell function. Based on their differentiation potential, stem cells used for tissue here can be Emhryonic into two categories: pluripotent stem cells and multipotent stem cells.
1. Introduction
Because ESCs are isolated from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst during embryological development, their use in tissue engineering is controversial and more limited while more attention has been paid to adult stem cells, which are multipotent and have a larger capacity to differentiate into a limited number of cell types [ 3 ]. Adult stem cells can be found in many adult tissue types including bone marrow, peripheral blood, adipose tissues, nervous tissues, muscles, dermis, etc.

For instance, mesenchymal stem cells MSCs which reside read article the bone marrow can differentiate into bone osteoblasts [ 4 ], muscle myoblasts [ 5 ], fat adipocytes [ 6 ] and cartilage chrondocytes [ 3 ] cells, while neural stem cells NSCs either give rise to support cells in the nervous system of vertebrates astrocytes and oligodendrocytes or neurons [ 7 ].
In vivodifferentiation and self-renewal of stem cells are dominated by signals from their surrounding microenvironment [ 8 ]. In vivothe cells are surrounded by a biological matrix comprising of tissue-specific combinations of insoluble proteins e.
chapter and author info
The varied composition of the ECM components not only contains a reservoir of cell-signaling motifs ligands and growth factors that guide cellular anchorage and behavior, but also provides physical architecture and mechanical strength to the tissue. The spatial distribution and concentration of ECM ligands, together with the tissue-specific topography and mechanical properties in addition to signals from adjacent cells—juxtacrine signalling—and the surrounding fluidprovide signaling gradients that direct cell migration and cellular production of Celsl constituents.

Native ECM exhibits macro- to nano-scale patterns of chemistry and topography [ 10 ]. Tissue stiffness is also known to vary depending on the organ type, disease state and aging process [ 11 - 13 ].]
One thought on “Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic Stem Cell”