![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The United States Effect on Puerto Rican](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/United_States_in_its_region_(Lower_50_and_Puerto_Rico_special).svg/1280px-United_States_in_its_region_(Lower_50_and_Puerto_Rico_special).svg.png) The United States Effect on Puerto Rican
The United States Effect on Puerto Rican
This study was conducted in the Luquillo Experimental Forest LEFwhich was previously abandoned pastureland reforested through mixed planting and natural regeneration.
Join the Discussion
Coffee has been a traditional crop in Puerto Rico since the mids. As the global market became more competitive in the 20th century, the Puerto Rican government provided subsidies and policies to protect the sector as well as promoted the transition to shade grown coffee for higher yields in the s. This study tests whether or not man-made canopy gaps can restore native tree diversity as food sources for the endagered Puerto Rican Parrot Amazona vittata. The gaps were created in 20m x 20m plots by girdling and applying herbicide on non-native trees and by clearing leaf litter and vegetation, creating space for planted and naturally established advance regeneration seedlings.
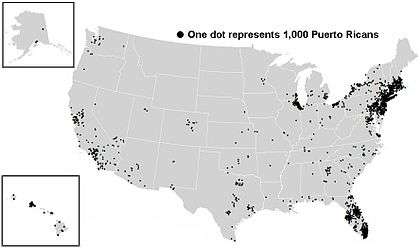
The History of Puerto Ricans' Migration to the United States
Forest regeneration is typically difficult after landslides due to loss of above- and below-ground vegetative structure, the soil The United States Effect on Puerto Rican bank, soil nutrients, and soil structure. Landslides are a common more info in Puerto Rico due to its steep topography and heavy rainfall periods and often transform into grass- or fern-dominated terrain. Insufficient seed rain is thought to be one contributing factor. Forest plantations are increasingly being established around the world, yet many are often monocultures. While the paper recognizes that all plantations are beneficial in terms of restoration, it specifically seeks to explore the advantages of mixed-species plantations. This paper reiviews the main biotic and Puerho factors that influence patterns of secondary forest succession in the Neotropics after complete forest clearance due to human activities.
Navigation menu
The authors look at patterns of species replacement and various processes that occur during succession and suggest that the sequence of processes may be predictable even if species composition is not. This article provides an example of how to evaluate forest restoration using integrative methods, including measures of vegetation structure, species diversity, oj ecosystem processes. Specifically discussed are four measures of vegetation structure, four measures of species diversity, and six measures of ecosystem processes. Tree plantations are increasingly common in tropical landscapes due to their multiple uses.

Plantations vary in structure and composition, and these variations may alter soil fauna communities. Recent studies have demonstrated the important role of soil fauna in the regulation of plant litter decomposition in the tropics.
However, little is known about how plantation species affect soil fauna populations, which may in turn affect the biogeochemistry of the plantation system. Conversion of tropical forest lands to agriculture or pasture affects soil organic matter, moisture, and nutrients. This study examines the effects on soil carbon, nitrogen, and moisture at depths up to cm of conversion from forest to agriculture and pasture.]
It — is impossible.