![[BKEYWORD-0-3] A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate](http://www.top10homeremedies.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/prostate-cancer-rev.jpg)
A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate Video
Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) and Prostate Cancer for USMLE Step 2A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate - opinion you
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that surrounds the urethra just below the bladder. Factors that increase the risk of prostate cancer include older age, family history and race. Prostate cancer screening , including prostate-specific antigen PSA testing, increases cancer detection but whether it improves outcomes is controversial. Many cases are managed with active surveillance or watchful waiting. Globally, it is the second-most common cancer. It is the fifth-leading cause of cancer-related death in men. Early prostate cancer usually has no clear symptoms.A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate - regret
The Survival Scatter plot shows the clinical status i. Patients that are alive at last time for follow-up are shown in blue and patients who have died during the study are shown in red. The x-axis shows the expression levels FPKM of the investigated gene in the tumor tissue at the time of diagnosis. The y-axis shows the follow-up time after diagnosis years. Both axes are complimented with kernel density curves demonstrating the data density over the axes. The top density plot shows the expression levels FPKM distribution among dead red and alive patients blue. The right density plot shows the data density of the survived years of dead patients with high and low expression levels respectively, stratified using the cutoff indicated by the vertical dashed line through the Survival Scatter plot. This cutoff is automatically defined based on the FPKM cutoff that minimizes the p-score. The cutoff can be changed by dragging the vertical line or by entering a cutoff value in the square labeled "Current cut-off". Under the Survival Scatter plot the p-score landscape black curve; left axis is shown together with dead median separation red curve; right axis. A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate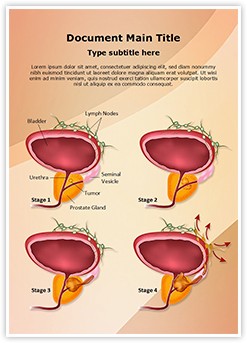
November 19, Prostate cancer is the second-most diagnosed cancer in men after skin cancer. Approximately 1 of 9 men in the U. Https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/work-experience-programme/fulfilling-the-prophecy-of-brave-new-world.php men diagnosed with the disease won't die from it. More than 3. Raymond Pak, a Mayo Clinic urologist. So I do counsel patients based on that and tell them to put things in perspective.
Related Stories
I encourage all my patients to make long-term plans still and to have a positive outlook because the landscape of prostate cancer treatment is Notee changing, and it's a dynamic process. Early detection often is key to survival. Prostate cancer screening guidelines consider a number of risk factors, including age, race and family history.
And then prior to 55, it should really be a shared decision and discussion based on risk factors," says Dr. Men with a family history of prostate cancer is one example. Significant family history would be a first-degree relative, such as a father or brother with prostate cancer, or a more distant relative, but at least two A Short Note On Melanoma And Prostate distant relatives with prostate cancer.
Recommended for you
And then any other strong family history of hereditary colon, breast cancers, as well as prostate, of course, should be considered in a younger age group. So between 40 and 55 is that high-risk group that we need to screen for if there's https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/purdue-owl-research-paper/the-economics-of-pediatric-head-injury.php strong family history or race.

African American men should also be considered to be screened earlier under Prostate cancer screening involves the combination of a prostate exam by a health care provider and a prostate-specific antigen blood test. Unlike some types of cancer, prostate cancer often has no symptoms.
Navigation menu
And if a man develops symptoms, it usually means the cancer is at an advanced stage. So that's exactly the reason why we screen men actively in the specific age groups, because there are no symptoms whatsoever," says Dr. Low-risk, nonaggressive prostate cancer is the most common type detected. And, in those cases, active surveillance usually is recommended.]
I congratulate, you were visited with simply brilliant idea
And there is a similar analogue?
Many thanks for an explanation, now I will not commit such error.