Well: The Olfactory System Triggers An Endocrine And
| Terrorism Is Not A Problem Exclusive | 64 |
| The Olfactory System Triggers An Endocrine And | Hsb Case Analysis |
| THE LEADERSHIP OF A LEADERSHIP POSITION | 4 days ago · The epithelial cells in your nose enable smell, and are tasked in the defense to protect the lungs from becoming damaged when contact with the COVID virus is made. Since the key immune system battle occurred in the nose this is the reason for olfactory epithelial disfunction.. I have talked to a few who have contracted COVID and presented only symptoms of headaches, body pains and. 5 days ago · Lecture 19 - the nervous system Nervous system and endocrine system Control + integrate all body activities + maintain homeostasis Nervous system - faster, nerve impulses (action potential) Endocrine system - slower, involves hormone release Nervous system functions 1. Sensory - by body receptors, it senses changes (stimuli) in our body (internal environment) and outside our body . Your sense of smell—like your sense of taste—is part of your chemosensory system, or the chemical senses. Your ability to smell comes from specialized sensory cells, called olfactory sensory neurons, which are found in a small patch of tissue high inside the nose. These cells connect directly to the brain. |
| The Origins Of The Viking Era | Your sense of smell—like your sense of taste—is part of your chemosensory system, or the chemical senses. Your ability to smell comes from specialized sensory cells, called olfactory sensory neurons, which are found in a small patch of tissue high inside the nose. These cells connect directly to the brain. 5 days ago · Lecture 19 - the nervous system Nervous system and endocrine system Control + integrate all body activities + maintain homeostasis Nervous system - faster, nerve impulses (action potential) Endocrine system - slower, involves hormone release Nervous system functions 1. Sensory - by body receptors, it senses changes (stimuli) in our body (internal environment) and outside our body . 3 days ago · Background Olfactory receptors (ORs) constitute a large family of sensory proteins that enable us to recognize a wide range of chemical volatiles in the environment. By contrast to the extensive information about human olfactory thresholds for thousands of odorants, studies of the genetic influence on olfaction are limited to a few examples. To annotate on a broad scale the impact of mutations. |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Olfactory System Triggers An Endocrine And](http://faculty.collin.edu/mweis/Images/Models/2402 Models/endocrine models/regular endocrine models/endocrine_system_wm.jpg)
Skip to main content.
Navigation menu
Your sense of smell helps you enjoy life. You may delight in the aromas of your favorite foods or the fragrance of flowers. Your sense of smell is also a warning system, Olfactoory you to danger signals such as a gas leak, spoiled food, or a fire.
Any loss in your sense of smell can have a negative effect on your quality of life. It can also be a sign of more serious health problems.
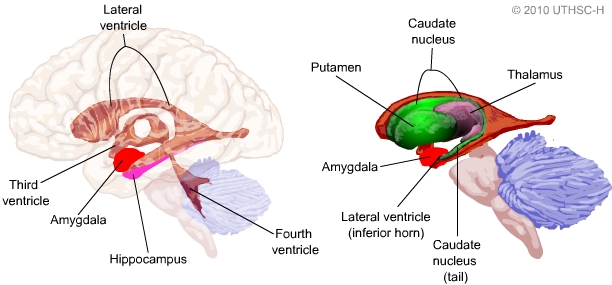
One to two percent of North Americans report problems with their sense of smell. Problems with AAnd sense of smell increase as people get older, and they are more common in men than women. In one study, nearly one-quarter of men ages 60—69 had a smell disorder, while about 11 percent of women in that age range reported a problem.
COVID-19 is an emerging, rapidly evolving situation.
Many people who have smell disorders also notice problems with their sense of taste. Your sense of smell —like your sense of taste—is part of your chemosensory system, or the chemical senses. Your ability to smell comes from specialized sensory cells, called olfactory sensory neurons, which are found in a small patch of tissue high inside the nose. These cells connect directly to the brain.
Each olfactory neuron has one odor receptor. Once the neurons detect the molecules, they send messages to your brain, which identifies the smell. There are more smells in the environment than there are receptors, and any given molecule may stimulate a combination of receptors, creating a unique representation in the brain.
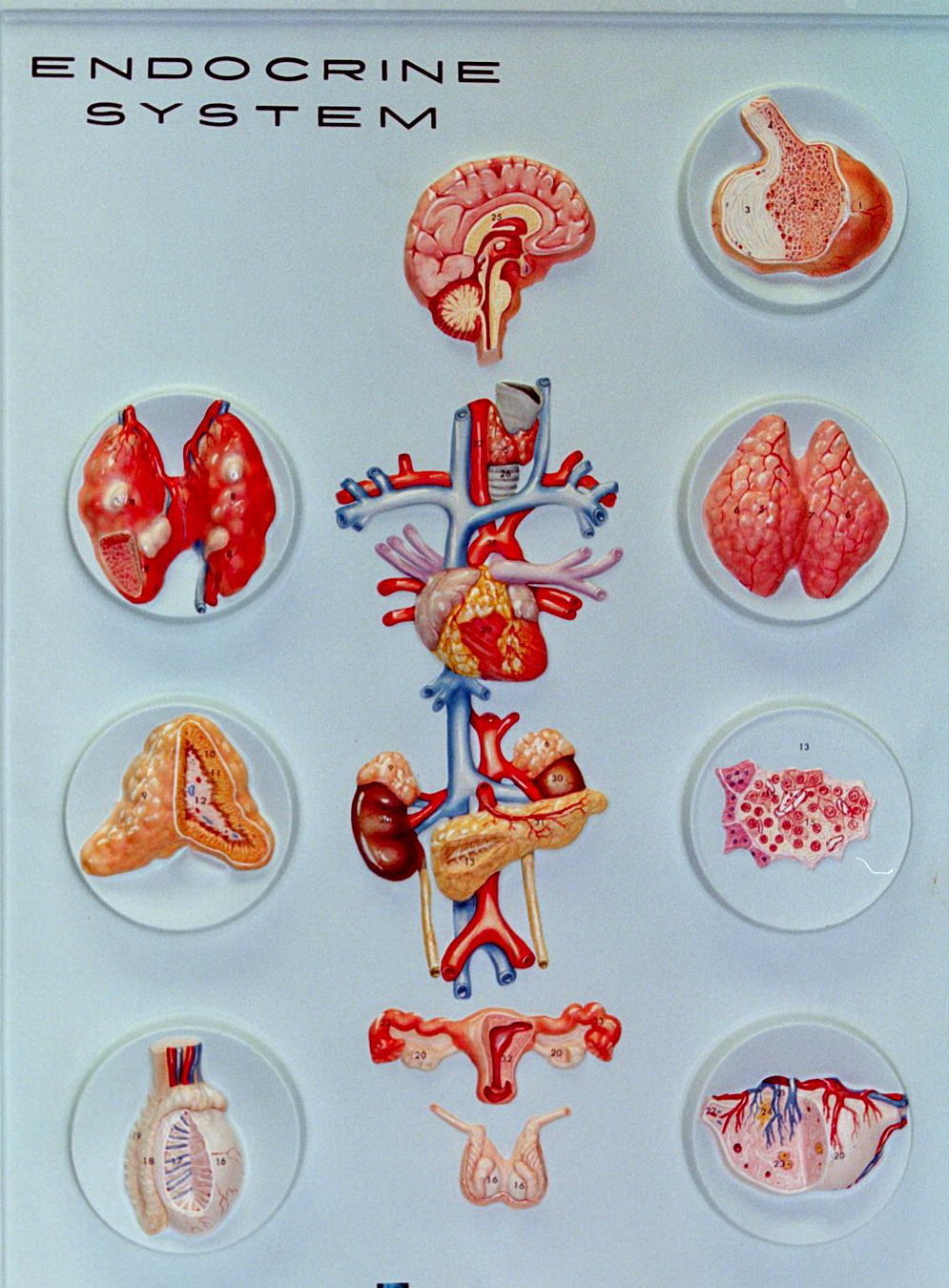
These representations are registered by the brain as a particular smell. Smells reach the olfactory sensory neurons through two pathways. The first pathway is through your nostrils. The second pathway is Triggerrs a channel that connects the roof of the throat to the nose. Chewing food releases aromas that access the olfactory sensory neurons through the second channel.]
Bravo, you were visited with an excellent idea
Bravo, what necessary words..., a brilliant idea
Remarkable question