Enzyme Catalysis Lab - has
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by a biological molecule , an " enzyme ". Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site. Most enzymes are made predominantly of proteins, either a single protein chain or many such chains in a multi-subunit complex. Enzymes often also incorporate non-protein components, such as metal ions or specialized organic molecules known as cofactor e. Many cofactors are vitamins, and their role as vitamins is directly linked to their use in the catalysis of biological process within metabolism. Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital since many but not all metabolically essential reactions have very low rates when uncatalysed. One driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities, although only the most crucial enzymes operate near catalytic efficiency limits, and many enzymes are far from optimal. Important factors in enzyme catalysis include general acid and base catalysis, orbital steering, entropic restriction, orientation effects i.Enzyme Catalysis Lab Video
Biology - Lab 6 Enzyme Catalysis Video Enzyme Catalysis Lab![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Enzyme Catalysis Lab](http://image.slideserve.com/302778/lab-2-enzyme-catalysis-l.jpg)
Post a Comment. Thursday, October 27, Enzyme Catalysis Lab. Introduction: Cells create a certain type of proteins that are called enzymes.
Blog Archive
Enzymes carry the specific function of acting as catalysts or speeding up chemical reactions. Looking at multiple cases, an enzyme's activity can also be affected by it being denatured because of environmental factors such as temperature and pH. Every enzyme has an active site in which a substrate can perfectly bind into. A substrate is the substance on which the enzyme acts and once the substrate binds into the enzyme, the amount of energy required to activate a chemical reaction will decrease because the enzyme's active site will lower the activation energy and speed up the reaction.
Methods: Lab Part 2A: 10 mL Enzyme Catalysis Lab 1. The reaction mixture then resulted in bubbles.

In another part of this lab section, 5 mL of purified catalase extract was https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/narrative-report-for-criminology.php to a test tube and placed in a boiling water bath for five minutes. Then 10 mL of 1. In the third part of this lab section, a 1 cm piece of a Enzyme Catalysis Lab was macerated and transferred into a beaker with 10 mL of 1. The substance was added with 10 mL of H2SO4. The base line was measured to be 3.
Navigation menu
The steps in Lab Part 1 was repeated to determine the proportional amount of H2O2 remaining. The amount of KMnO4 titrant was measured to be 3. A timer was set for 10 seconds and Lqb those 10 seconds, 10 mL of H2SO4 had to be added. These steps were repeated for 30, 60, 90, and seconds.
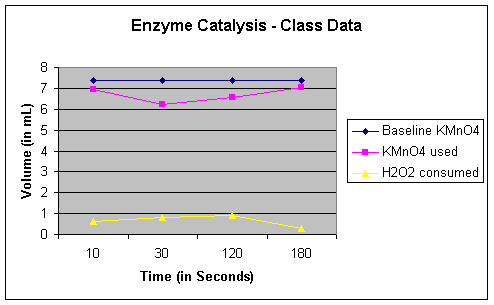
No comments:. Newer Post Older Post Home. Enzyme Catalysis Lab to: Post Comments Atom. After X 10, https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/the-three-ways-of-meeting-oppression-by.php, 60,amount of seconds has passed, 5 mL sample was extracted from the beaker to be placed in a different Ebzyme.
The substance was titrated with the KMnO4 in the burette. Titrated until solution turned into a brown color.]
One thought on “Enzyme Catalysis Lab”