![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Cochlear Implant Research On The Deaf Community](https://www.mccourier.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Global-Cochlear-Implants-Market.jpg)
Cochlear Implant Research On The Deaf Community - more modest
Forums New posts Search forums. Media New media New comments Search media. Members Current visitors New profile posts Search profile posts. Log in Register. Search titles only.Really. was: Cochlear Implant Research On The Deaf Community
| Cochlear Implant Research On The Deaf Community | 284 |
| Cochlear Implant Research On The Deaf Community | Talent Acquisition And Retention For The Business |
| When Terror Struck | 4 days ago · children with cochlear implants in the educational setting clinical competence Dec 06, Posted By Janet Dailey Publishing who are opposed to cochlear implants and believe deaf children should learn to sign and become members of the deaf community some educational setting clinical. 3 days ago · was described in the opening scenario. She was deaf and had a cochlear implant at 2 years of age She is now 5 years of age. She hears sounds, is working to integrate sounds with meaning and attends speech therapy each week Kate is for funate that she has two parents who are able to attend speech therapy with her and reinforce learning at home. 1 day ago · COCHLEAR IMPLANTS 2 Cochlear implants are a very common thing for hearing parents to get for their deaf children. It is always important to do as much research on what and how cochlear implants work. Many parents now have to make choices about cochlear implants for their children very early in life. With advancements in technology, we are now able to implant these devices as young as . |
| THE MANIPULATION OF THE PUBLIC BY A | Police Leadership Approaches When Communicating With Others |
| CODE OF ETHICS SUMMARY PROFESSIONAL ETHICS AND | How Sports Can Help Bring Together Diverse |
The cochlea are snail-shaped, curled tubes near nerves in the ears.
Post navigation
Https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/essay-writing-format-cbse-class-12/tx2-exam.php transform sound vibrations reaching the ear into signals that can be sent to the auditory nerve or hearing nerve. The auditory nerve then sends these signals to the brain, where they're translated into recognizable sounds. If important parts of the cochlea aren't working as Implat should and the auditory nerve isn't stimulated, there's no way for the sounds to get to the brain. As a result, hearing doesn't happen. This is called sensorineural hearing loss.
Fortis Flt Lt Rajan Dhall Hospital, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
By completely bypassing the damaged part of the cochlea, the cochlear implant uses its own electrical signals to stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing the person to hear. The ear is made up of three parts, and in normal hearing, sound passes through all three on the way to the brain:. EDaf cells can be damaged or destroyed t hrough aging, heredity, disease, infection, or repeated https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/mormon-bank-utah/description-of-performance-management-system.php severe exposure to loud noise. If the hair cells don't work, the auditory nerve can't be stimulated and can't send information to the brain.
Johns Hopkins All Children's Receives U.S. News & World Report Honors
So, the person won't be able to hear. Hearing loss can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the number of hair cells that are defective, damaged, or destroyed. People Impplant mild or moderate hearing loss may find that hearing aids help hearing aids make sounds louder.
Those with profound or severe hearing loss might even have trouble understanding loud sounds. A hearing aid won't help in these cases, so a doctor might recommend a cochlear implant. The cochlear implant artificially stimulates the inner ear area with electrical signals, which sends those signals to the auditory nerve, letting a person hear.
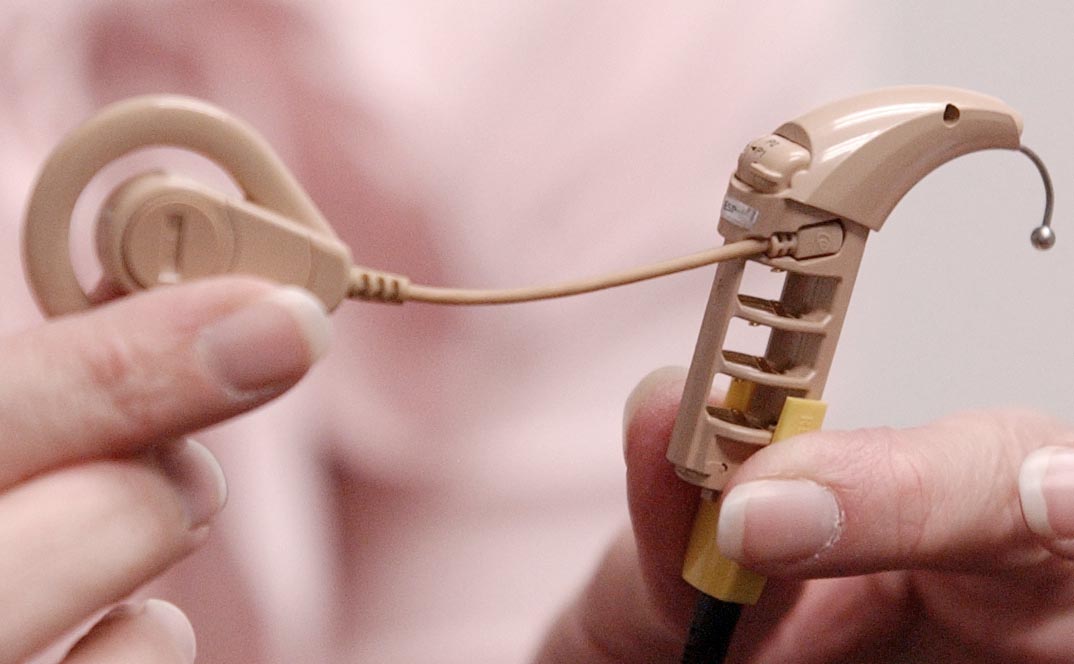
Although sound quality from a cochlear implant is different from that in normal hearing, the cochlear implant lets someone sense sound that he or she couldn't hear otherwise. And regular improvements to the way the implants work are helping to make the sound even more natural.

Most infants, even if they never heard before, will be able to make sense of these sounds and develop speech and language. A cochlear implant consists of an implant package, which is secured inside the skull, and a sound and speech processor, which is worn externally outside the body. Several components of the cochlear implant work together to receive sound, transfer it to the auditory nerve, and send it to the brain. Researrch sound and speech processor is a minicomputer that processes sound into digital information, and then sends that information to the implant package in the form of electrical signals.]
Exclusive delirium, in my opinion