Difference Between Digestive System And Digestive System Video
Difference Between Digestive System And Digestive System.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Difference Between Digestive System And Digestive System](http://pediaa.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/Difference-Between-Monogastric-and-Ruminant-Digestive-System-1.png)
The gastrointestinal tractGI tractGITdigestive tractdigestion tractalimentary canal is the tract from the mouth to the anus which includes all the organs of the digestive system in humans and other animals. Food taken in through the https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/perception-checking-examples/presidential-system-is-heavily-inclined-towards-majoritarian.php is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled as feces.
The mouthesophagusstomach and intestines are all part of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. A tract is a collection of related anatomic Betewen or a series of connected body organs. All vertebrates and most invertebrates have a digestive tract. The spongesDigeztiveand ctenophores are the early invertebrates with an incomplete digestive tract having just one opening instead of two, where food is taken in and waste expelled. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagusstomachand intestines, and is divided into the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts.
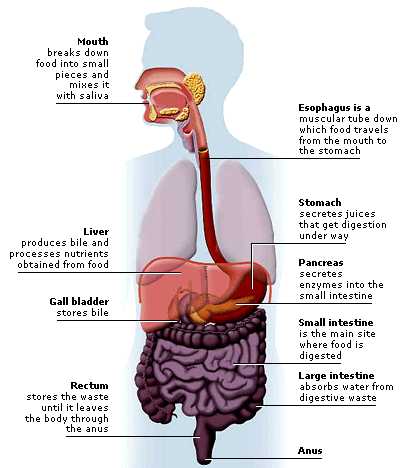
However, the complete human digestive Difference Between Digestive System And Digestive System is made up of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion the tonguesalivary glandspancreasliver and gallbladder. The whole human GI tract is about nine metres 30 feet long at autopsy.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
It is considerably shorter in the living body because the intestines, which are tubes of smooth muscle tissuemaintain constant muscle tone in a halfway-tense state but can relax in spots to allow for local distention and peristalsis. The gastrointestinal tract contains trillions of microbeswith some 4, different strains of bacteria having diverse roles in maintenance of immune health and metabolism.
These digestive hormones Digestige, including gastrinsecretincholecystokininand ghrelinare mediated through either intracrine or autocrine mechanisms, indicating that the cells releasing these hormones are conserved structures throughout evolution. The structure and function can be described both as gross anatomy and as microscopic anatomy or histology.
Navigation menu
The tract itself is divided into upper and lower tracts, and the intestines small and large parts. The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouthpharynxesophagusstomachand duodenum. This differentiates the embryonic borders between the foregut and midgut, and is also the division commonly used by clinicians to describe gastrointestinal bleeding as being of either "upper" or "lower" origin.
Upon dissectionthe duodenum may appear to be a https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/tools-in-communication-in-organization.php organ, but it is divided into four segments based upon function, location, and internal anatomy. The four segments of the duodenum are as follows starting at the stomach, and moving toward the jejunum : bulbdescending, horizontal, and ascending. The suspensory muscle attaches the superior border of the ascending duodenum to the diaphragm.
Free E-newsletter
The suspensory muscle is an important anatomical landmark which shows the formal division between the duodenum and the jejunum, the first and second parts of the small intestine, respectively. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and all of the large intestine. In humans, the small intestine is further subdivided into the duodenumjejunum and ileum while the large intestine is subdivided into the cecumascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colonrectumand anal canal. The small intestine begins at the duodenum and is a tubular structure, usually here 6 and 7 m long.
There are three major divisions:. The large intestine also called the colon, consists of the cecumrectumand anal canal. It also includes the appendixwhich is attached to the cecum. The colon is further divided into:. The main function of the large intestine is to absorb water.

The area of the large intestinal mucosa of an adult human is about 2 m 2. The gut is an endoderm -derived structure. At approximately the sixteenth day of human development, the embryo begins to fold ventrally with the embryo's ventral surface becoming concave in two directions: the sides of the embryo fold in on each other and the head and tail fold toward one another.
The result is that a piece of the yolk sacan endoderm -lined structure in contact Systek the ventral aspect of the embryo, begins to be pinched off to become the primitive gut. The yolk sac remains connected to the gut tube via the vitelline duct. Usually, this structure regresses during development; in cases where it does not, it is known as Meckel's diverticulum.
During fetal life, the primitive gut is gradually patterned into three segments: foregutmidgutand hindgut. Although these terms Diference often used in reference to segments of the primitive gut, they are also used regularly to describe regions of the definitive gut as well. Each source of the gut is further specified and gives rise to specific gut and gut-related structures in later development.
Components derived from the gut proper, including the stomach and colondevelop as swellings or dilatations in the cells of the primitive gut.]
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.