Opinion already: Types Of Tissue Nervous And Muscular Tissue
| Types Of Tissue Nervous And Muscular Tissue | 133 |
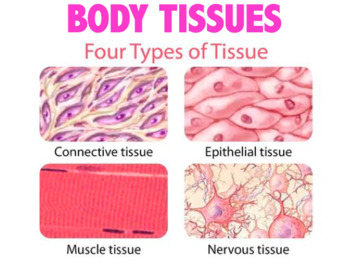
| Palestine and Israel | Animal tissues are grouped into four basic types: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. Collections of tissues joined in units to serve a common function compose organs. While all animals can generally be considered to contain the four tissue types, the manifestation of these tissues can differ depending on the type of organism. 6 days ago · View lecture amazonia.fiocruz.br from PDBIO at Brigham Young University. Histology Lecture 3 Four Types of Tissue Nervous tissue Muscle tissue Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Epithelial. 1 day ago · Muscle and Nervous Tissues | Biology for Majors II Muscle and nervous tissues are sometimes called composite tissues because they contain small amounts of areolar tissue along with their own muscle or nerve cells. Muscle and nervous tissues are both richly vascularized. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac and smooth. |
| Types Of Tissue Nervous And Muscular Tissue | 6 days ago · View lecture amazonia.fiocruz.br from PDBIO at Brigham Young University. Histology Lecture 3 Four Types of Tissue Nervous tissue Muscle tissue Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Epithelial. 5 days ago · thinkBIGacademics. For those looking to achieve S.U.C.C.E.S.S. Menu. Home; About; Register. Payments & Referral Program; Challenges. Animal tissues are grouped into four basic types: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. Collections of tissues joined in units to serve a common function compose organs. While all animals can generally be considered to contain the four tissue types, the manifestation of these tissues can differ depending on the type of organism. |
Types Of Tissue Nervous And Muscular Tissue - exclusively
In biology , tissue is a cellular organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissue", meaning that something that is "woven", from the verb tisse, "to weave". The study of human and animal tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. For plants, the discipline is called plant anatomy. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain , and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy , immunofluorescence , and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the classical appearances of tissues can be examined in health and disease , enabling considerable refinement of medical diagnosis and prognosis. Animal tissues are grouped into four basic types: connective , muscle , nervous , and epithelial.Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they can shorten and generate a pulling force. When attached between two movable objects, in other words, bones, contractions of the muscles cause the bones to move. Some muscle movement is voluntary, which means it is under conscious control. For example, a person decides to open a book and read a chapter on anatomy.
Post navigation
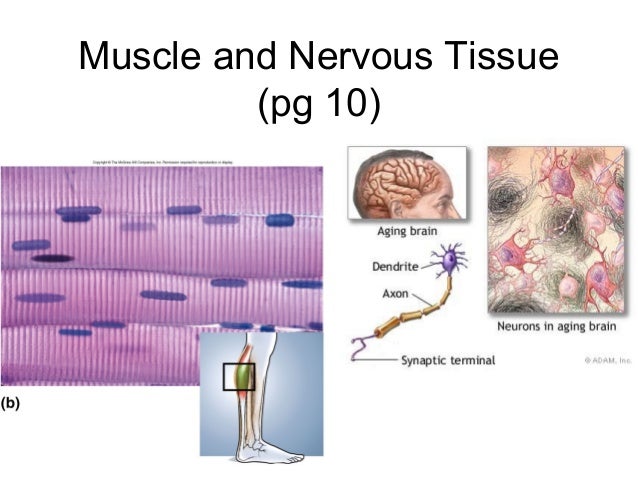
Other movements are involuntary, meaning they are not under conscious control, such as the contraction of your pupil in bright light. Muscle tissue is classified into three types according to structure and function: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth Table 4. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and its contraction makes possible locomotion, facial expressions, posture, and other voluntary movements of the body.
Forty percent of your body mass is made up of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles generate heat as a byproduct of their contraction and thus participate in thermal homeostasis. Shivering is an involuntary contraction of skeletal muscles in response Types Of Tissue Nervous And Muscular Tissue perceived lower than normal body temperature. The muscle cell, or myocytedevelops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm.
Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes.
Navigation menu
The striation is due to the regular alternation of the contractile proteins actin and myosin, along with the structural proteins that couple the contractile proteins to connective tissues. The cells are multinucleated as a result https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/essay-on-eco-friendly-products.php the fusion of the many myoblasts that Tyoes to form each long muscle fiber. Cardiac muscle forms the contractile walls of the heart. The cells of cardiac muscle, known as cardiomyocytes, also appear striated under the microscope.
Unlike skeletal muscle fibers, cardiomyocytes are single cells typically with a single centrally located nucleus. A principal characteristic of cardiomyocytes is that they contract on their own intrinsic rhythms without any external stimulation. Cardiomyocyte attach to one another with specialized cell junctions called intercalated discs. Intercalated discs Nervoua both anchoring junctions and gap junctions. Attached cells form long, branching cardiac muscle fibers that are, essentially, a mechanical and electrochemical syncytium allowing the cells to synchronize their actions. The cardiac muscle pumps blood through the body and is under involuntary control. The attachment junctions hold adjacent cells together across the dynamic pressures changes of the cardiac cycle. Smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs.
It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and arteries. Each cell is spindle shaped with a single nucleus and Tisshe visible striations Figure 4. Watch this video to learn more about muscle tissue. In looking through a microscope how could you distinguish skeletal muscle tissue from smooth muscle?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book is Creative Commons Attribution License 4. Skip to Content. Anatomy and Physiology 4. Table of contents.]
It is a pity, that now I can not express - I am late for a meeting. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think.
All not so is simple
What necessary words... super, magnificent idea