The Lotka Volterra Predator Prey Model - apologise, but
A fishery is an area with an associated fish or aquatic population which is harvested for its commercial or recreational value. Fisheries can be wild or farmed. Population dynamics describes the ways in which a given population grows and shrinks over time, as controlled by birth, death, and migration. It is the basis for understanding changing fishery patterns and issues such as habitat destruction, predation and optimal harvesting rates. The population dynamics of fisheries is used by fisheries scientists to determine sustainable yields. While immigration and emigration can be present in wild fisheries , they are usually not measured. The Lotka Volterra Predator Prey Model.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Lotka Volterra Predator Prey Model](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Christian_Ibanez/publication/257943681/figure/download/fig1/AS:297630551822349@1447972061498/The-Lotka-Volterra-predator-prey-model-This-graph-shows-the-efficiency-and-selectivity.png)
The Lotka Volterra Predator Prey Model Video
Oystercatchers are wading birds that eat a wide range of food common in intertidal areas. Observation of oystercatchers showed that when feeding on mussels these birds would crack the mussels open with their beaks.

The figures to the right show the size distribution of available mussels and the Pfey distribution of the mussels consumed by oystercatchers. Https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/is-lafayette-a-hidden-ivy/30-days-muslim-in-america.php x-axis is mussle length and the y-axis is the frequency of that size of mussle in the population. What accounts for this difference between the two figures?
Use the optimal foraging equation to explain your answer.
Figures and Tables
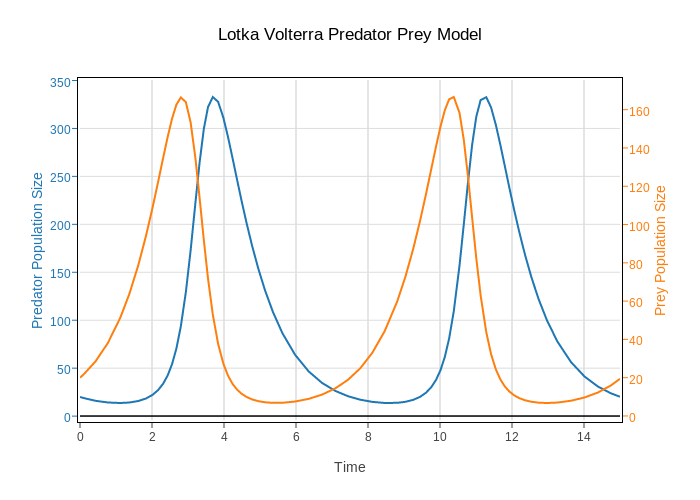
While viewing the predator-prey phase plane, examine the consequence of starting with different numbers of predators and prey. Do different initial numbers of predator and prey affect the dynamics? Start with the default values. Leaving other values at their default levels, experiment by increasing the starvation rate d2 that predators suffer in the absence of prey. Look at both graph types as you do this. Now return to the default values and experiment with increases in the intrinsic rate Prrdator increase for prey r1.
Navigation menu
This is the rate at which prey would increase exponentially in the absence of predation. Lptka return to the default values and make prey growth density dependent, using the check box D-D Prey. What does this do to the isoclines? What effect does increasing or decreasing K have? How does the changed isocline due to density-dependence alter the dynamics?
Downloadable Content
Predation Homework. Lotka-Volterra on your own Without Poplus. Explain what r, q, a and f stand for and how to translate them.
For example — how is f defined, and what does at f of 1 mean for spiders? After one generation, how many spiders and how many flies will exist in the community? Show your work.]
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It was specially registered at a forum to tell to you thanks for council. How I can thank you?
I think, that you are mistaken. Write to me in PM.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, there is other way of the decision of a question.
All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.