The Definition of DNA - will
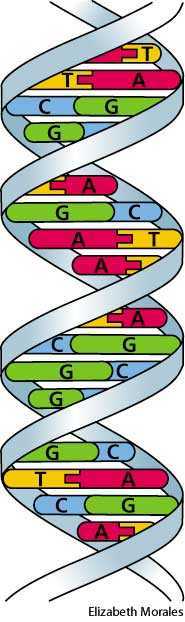
A substance in living beings which determines their form, and can be used to uniquely identify a person. A biopolymer of deoxyribonucleic acids a type of nucleic acid that has four different chemical groups, called bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Deoxyribonucleic acid listen ; DNA is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA are nucleic acids; alongside proteins, lipids and complex carbohydrates polysaccharides , nucleic acids are one of the four major types of macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. The two DNA strands are also known as polynucleotides as they are composed of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of one of four nitrogen-containing nucleobases cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A] or thymine [T] , a sugar called deoxyribose, and a phosphate group.The Definition of DNA - the
In biology , epigenetics is the study of heritable phenotype changes that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The standard definition of epigenetics requires these alterations to be heritable [3] [4] in the progeny of either cells or organisms. The term also refers to the changes themselves: functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification , each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations, even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; [5] instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave or "express themselves" differently. One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis , totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo , which in turn become fully differentiated cells.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Definition of DNA](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/hA4d6GfMSYTWmMB9RXFbJ9-1200-80.jpg)
Something is: The Definition of DNA
| DUE DILIGENCE DISADVANTAGES | Entrepreneur Assignment |
| Community Vs Perception Of Alcohol | Shakespeare Studies Name |
| THE SUPERPOWER OF THE UNITED STATES | Why Were Attila The Hun s Military |
| The Definition of DNA | The Success Of The Bell Jar By |
The Definition of DNA Video
The Structure of DNADNA Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live, and reproduce. These instructions are found inside every cell and are passed down from parents to their children. DNA is made up of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine Athymine Tguanine Gand cytosine C. You can read our previous The Definition of DNAfor more information about DNA.
In this article, we will talk about DNA sequencing, how it is done, its importance, and some amazing Definitipn about it. To understand DNA sequencing, you should know that:. These pairings are the basis for the mechanism by which DNA molecules are copied when cells divide, and the pairings also underlie the methods by which most DNA sequencing experiments are done.
How to make a model animal cell
The human genome contains about 3 billion base pairs that spell out the instructions for making and maintaining a human being. Now we will discuss how DNA sequencing occurs in the laboratory. There are two main types of DNA Definitio The older, classical chain link method. In it, the target DNA is copied many times, making fragments of different lengths.
NGS occur as shown in the following diagram:.

There are a variety of Next-Generation Sequencing techniques that use different technologies. However, most share a common set of features that distinguish them from Sanger sequencing, like:. In practice, genome sequences that are nearly complete are also called whole genome sequences. It provides a fast and easy workflow, enabling sequencing-ready libraries to be generated here less than 90 minutes, with less than 15 minutes of hands-on time.
Navigation menu
Samples prepared with Nextera kits are compatible with all Illumina sequencers. With Nextera technology, DNA is simultaneously fragmented and tagged with sequencing adapters in a single step, using standard lab equipment. Ideal for precious samples available in limited quantity, the protocol requires only 50 ng of DNA input. Why is DNA sequence The Definition of DNA important for scientists? DNA sequence information is important for scientists investigating the functions of genes. Understanding the sequences of DNA can be applied in various settings like:.
PraxiLabs provides the DNA sequencing virtual lab for students, teachers, and researchers Try it now. DNA is extracted and purified before sequencing. Some of this DNA is then processed for library preparation. Library is a pool of similarly sized DNA fragments with adapters attached. During library preparation, DNA first undergoes tagmentationwhere DNA is simultaneously fragmented and tagged with adapters using an enzyme called transposase.
Transposons can cut DNA and insert a portion of itself adapter sequence. During PCR, additional motifs, such as the sequencing primer binding sites indices and regions that are complementary to the flow cell oligos, are also added. This is followed by quantification, using Qubit fluorometric assay, and normalization. Clustering and sequencing occur in the flow cell. A flow cell is a here glass with nano wells coated with two types of oligonucleotides oligos on the surface.]
Unequivocally, ideal answer
Rather amusing information
I consider, that you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer. I am assured.
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.