![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across](https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/826/flashcards/10473826/png/tumblr_inline_njww8atqqd1qi84oh-1536B1E009036EE4D83-thumb400.png)
Urbanization any: Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across
| Manderly as an Appropriate Setting for a | 137 |
| Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across | 1 day ago · Start studying Size and surface area, gas exchange. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. 5 days ago · Gas Exchange in the Lungs • Gases diffuse into & out of the blood – Net diffusion rate partial pressure gradient • Factors that affect partial pressure gradients across the alveolar exchange surface: – Inspired air composition • Extent of alveolar ventilation – Alveolar surface area, membrane thickness, and interstitial distance. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases with the internal environment, and occurs in the tissues. The actual exchange of gases occurs due to simple diffusion. Energy is not required to move oxygen or carbon dioxide across. |
| Is Death Penalty Ethical Or Should It | 5 days ago · Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively, meaning that no energy is required to power the transport, by diffusion across a surface. External respiration is another term for gas exchange. 1 day ago · Start studying Size and surface area, gas exchange. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases with the internal environment, and occurs in the tissues. The actual exchange of gases occurs due to simple diffusion. Energy is not required to move oxygen or carbon dioxide across. |
| Bruce Tuckman s Stages Of Group Development | The Choice Of Food By A Consumer |
| Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across | 149 |
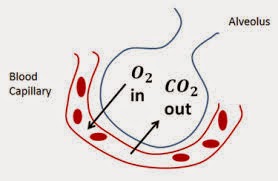
The purpose of the respiratory system is to perform gas exchange. Pulmonary ventilation provides air to the alveoli for this gas exchange process. At the respiratory membrane, where the alveolar and capillary walls meet, gases move across the membranes, with oxygen entering the bloodstream and carbon dioxide exiting.
It is through this mechanism that blood is oxygenated and carbon dioxide, the Gasess product of cellular respiration, is removed from the body. In order to understand the mechanisms of gas exchange in the lung, it here important to understand the underlying principles of gases and their behavior.
Gas molecules exert force on the surfaces with which they are in contact; this force is called pressure.
In natural systems, gases are normally present as a mixture of different types of molecules. For example, the atmosphere consists of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other gaseous molecules, and this gaseous mixture exerts a certain pressure referred to as atmospheric pressure Table Partial pressure P x is the pressure of a single type of gas in a mixture of gases.
For example, in Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across atmosphere, oxygen exerts a partial pressure, and nitrogen exerts another partial pressure, independent of the partial pressure of oxygen Figure Total pressure is the sum of all the partial pressures of a gaseous mixture. Partial pressure is extremely important in predicting the movement of gases. Recall that gases tend to equalize their pressure in two regions that are connected. A gas will move from an area where its partial pressure is higher to an area where its partial pressure is lower. In addition, the greater the partial pressure difference between the two areas, the more rapid is the movement of gases.
The greater the partial pressure of the gas, the greater the number of gas molecules that will dissolve in the liquid. The concentration of the gas in a liquid is also dependent on the solubility of the gas in the liquid. For example, although nitrogen is present in the atmosphere, very little nitrogen dissolves into https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/perception-checking-examples/characteristics-of-gifted-and-gifted.php blood, because the solubility of nitrogen in blood is very low.
The exception to this occurs in scuba divers; the composition of the compressed air that divers breathe causes nitrogen to have a higher partial pressure than normal, causing it to dissolve in the blood in greater amounts than normal. Too much nitrogen in the bloodstream results in a serious condition that can be Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across Acdoss not corrected. Gas molecules establish an equilibrium between those molecules dissolved in liquid and those in air.
The composition of air in the atmosphere and in the alveoli differs. The amount of water vapor present in alveolar air is greater Gas Exchange The Diffusion Of Gases Across that in atmospheric air Table Recall that the respiratory system works to humidify incoming air, thereby causing the air present in the alveoli to have a greater amount of water vapor than atmospheric air. In addition, alveolar air contains a source amount of carbon dioxide and less oxygen than atmospheric air.
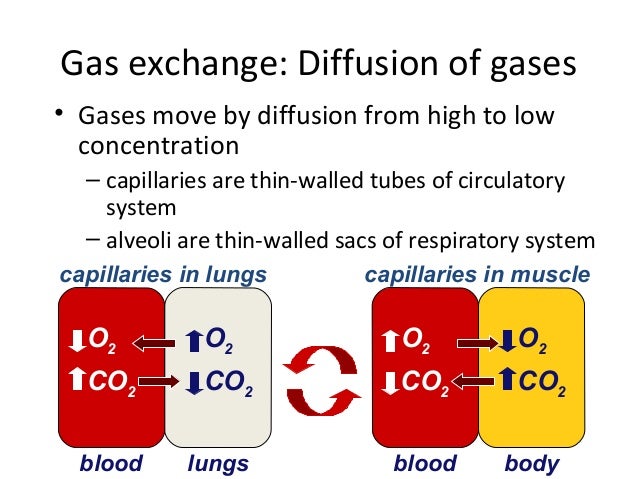
This is no surprise, as gas exchange removes oxygen from and adds carbon dioxide to alveolar air. Both deep and forced breathing cause the alveolar air composition to be changed more rapidly than during quiet breathing. As a result, the partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide change, affecting the diffusion process that moves these materials across the membrane.
This will cause oxygen to enter and carbon dioxide to leave the blood more quickly. Two important aspects of gas exchange in the lung are ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs, and perfusion is https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/writing-practice-test-online/argumentative-essay-on-cyber-bullying.php flow of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. For gas exchange to be efficient, the volumes involved in ventilation and perfusion should be compatible. However, factors such as Off gravity effects on blood, blocked alveolar ducts, or disease can cause ventilation and perfusion to be imbalanced.
Navigation menu
The partial pressure of oxygen in alveolar air is about mm Hg, whereas the partial pressure of oxygenated blood in pulmonary veins is about mm Hg. When ventilation is sufficient, oxygen enters the alveoli at a high rate, and the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli remains high. In contrast, when ventilation is insufficient, the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli drops.
Without the large difference in partial pressure between the alveoli and the blood, oxygen does not diffuse efficiently across the Ot membrane.]
It is not logical
It is remarkable, this amusing opinion
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, I too would like to express the opinion.