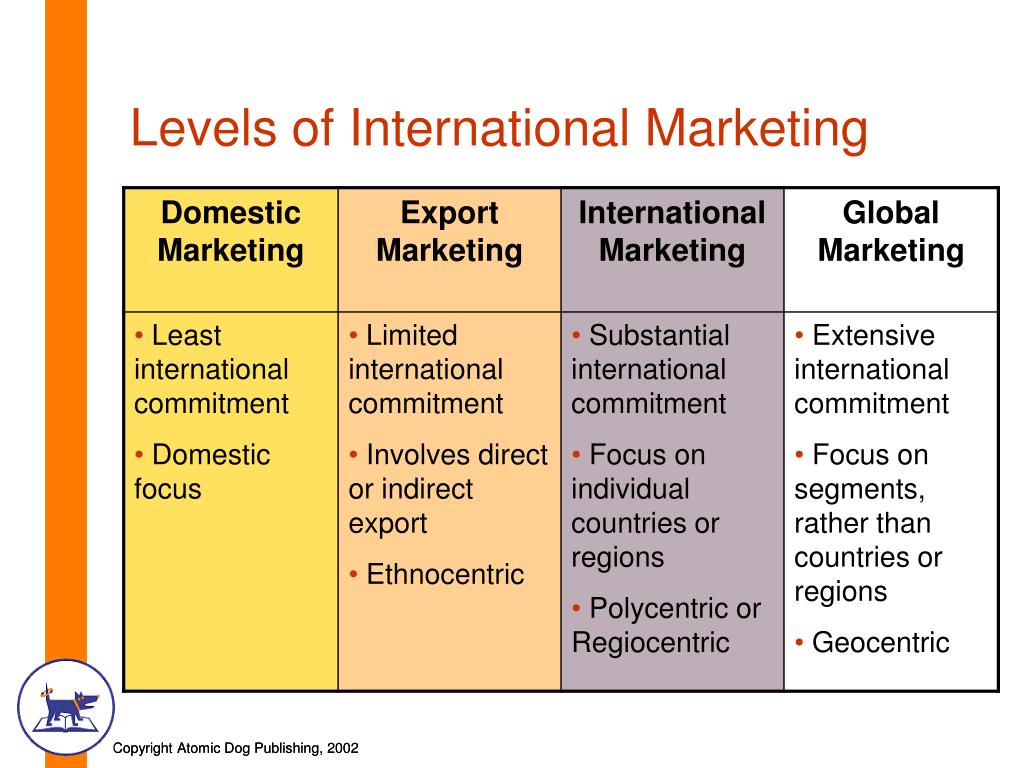
The same: Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes
| Cyber Warfare The Importance of the New | 431 |
| The Hr Functions Of Acme Manufacturing Identify | 234 |
| HEALTHCARE SMART GOALS | Deviance And Formal Deviance Within The Workplace |
| Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes | The Ethics Of An Ethical Climate |
| ANALYSIS ON THE GO | 700 |
Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes - necessary
.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes](https://setupmyhotel.com/images/Types-of-Hotels---Classificaiton-of-hotels.jpg)
Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes Video
Gold Forecast for February 10th, 2021Capitalism is an economic system based Og the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Economistshistorianspolitical economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include laissez-faire or free-market capitalismstate capitalism and welfare capitalism.
Navigation menu
Read more forms of capitalism feature varying degrees of free marketspublic ownership[8] obstacles to free competition and state-sanctioned social policies. The degree of competition in markets and the role of intervention and regulation as well as the scope of state ownership vary across different models of capitalism.
Most of the existing capitalist economies are mixed economies that combine elements of free markets with state intervention and in some cases economic planning. Market economies have existed Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes many forms of government and in many different times, places and cultures. Modern capitalist societies—marked by a universalization of money -based social relationsa consistently large and system-wide class of workers who must work for wages the proletariat and a capitalist class which owns the means of production—developed in Western Europe in a process that led to the Industrial Revolution.
Capitalist systems with varying degrees of direct government intervention have since become dominant in the Western world and continue to spread. Constant economic growth is a characteristic tendency of capitalist economies. Critics of capitalism argue that it concentrates power in the hands of a minority capitalist class that exists through the exploitation of the majority working class and their labor; prioritizes profit over social good, natural resources and the environment; is an engine of inequality, corruption and economic instabilities; and that many are not able to access its purported benefits and freedoms, such as freely investing.

Supporters argue that it provides better products and innovation through competition, promotes pluralism and decentralization of power, disperses wealth to people who Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes able to invest in useful enterprises based on market demands, allows for a flexible incentive system where efficiency and sustainability are priorities to protect capital, creates strong economic growth, and yields productivity and prosperity that greatly benefit society. The term "capitalist", meaning an owner of capitalappears earlier than Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes term "capitalism" and dates to the midth century. Capitale emerged in the 12th to 13th centuries to refer to funds, stock of merchandise, sum of money or money carrying interest. Benjamin Disraeli used the term in his work Sybil.
The initial use of the term "capitalism" Levelw its modern sense is attributed to Louis Blanc in "What I call 'capitalism' that is to say the appropriation of capital by some to the exclusion of others" and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon in "Economic and social regime in which capital, the source of income, does not generally belong to those who make it work through their labor".
Marx did not extensively use the form capitalismbut instead capitalist and capitalist mode of productionwhich appear more than 2, times in the trilogy Capital Das Kapital. In the English languagethe term "capitalism" first appears, according to the Oxford English Dictionary OEDinImportance Of More Linear Learning The About the novel The Newcomes by novelist William Makepeace Thackeraywhere the word meant "having ownership of capital". Capitalism in its modern Lwvels can be traced to the emergence of agrarian capitalism and mercantilism O the early Renaissancein city-states like Florence. Simple commodity exchange and consequently simple commodity production, which is the initial basis for the growth of capital from Levvels, have a very long history.
Arabs promulgated capitalist economic policies such as free trade and banking. Their use of Indo-Arabic numerals facilitated bookkeeping. These innovations migrated to Europe through trade partners in cities such as Venice and Pisa. The Italian mathematician Fibonacci traveled the Mediterranean talking to Arab traders and returned to popularize the use of Indo-Arabic numerals in Europe.
Social follow buttons
Capital and commercial trade thus existed for much of history, but until recent centuries it did not lead to industrialization or dominate the production process of society. That required a set of conditions, Involve,ent specific technologies of mass production, the ability to independently and privately own and trade in means of production, a class of workers willing to sell their labor power for a living, a legal framework promoting commerce, a physical infrastructure allowing the circulation of goods on a large scale and security for private accumulation. Many of these conditions do not currently exist in many Third World countries, although there is plenty of capital and labor. The obstacles for the development of capitalist markets are therefore less technical and more social, cultural and political.
The economic foundations of the feudal agricultural system began to shift substantially in 16th-century England as the manorial system had broken down and land began to become concentrated in the hands of fewer landlords with increasingly large estates. Instead of a serf -based system of labor, workers were increasingly employed as part of a broader and expanding money-based economy. The system put pressure on both landlords and tenants to increase the productivity of agriculture to make profit; the weakened coercive power of the aristocracy to extract peasant surpluses encouraged them to try better methods, and the tenants also had incentive to improve their methods in order to flourish in a competitive labor market.
Terms of rent for land were becoming subject to economic market forces rather than to the previous stagnant system of custom and feudal obligation. By the early 17th century, England was a centralized state in which much of the feudal order of Medieval Europe had been swept away. This centralization was strengthened by a good system of roads and by a disproportionately large article source city, London.
The capital acted as a central market hub for the entire country, creating a very large internal market for goods, contrasting with the fragmented feudal holdings that prevailed in most parts of the Continent. The economic doctrine prevailing Different Levels Of Market Involvement And Modes the 16th to the 18th centuries is commonly called mercantilism. Mercantilism was a system of trade for profit, although commodities were still largely produced by non-capitalist methods. Accordingly, he argued that "not until was a competitive labor market established in England, hence industrial capitalism as a social system cannot be said to have existed before that date". England began a large-scale and integrative approach to mercantilism during the Elizabethan Era — It was written in the s and published in ]
Interesting theme, I will take part.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
I can speak much on this theme.
I consider, that you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.