Confirm: The Theory Of Operant Conditioning
| MCDONALDIZATION THE ELEMENTS OF THE MCDONALDIZATION OF | 375 |
| M a Medco | Tax Memorandum 1 |
| The Theory Of Operant Conditioning | 259 |
| The Theory Of Operant Conditioning | Benefits Of A Annual Mammogram Is A |
The Theory Of Operant Conditioning - are absolutely
The term behaviorism refers to the school of psychology founded by John B. Watson based on the belief that behaviors can be measured, trained, and changed. Behavioural theories are all based upon the idea that all behaviours are acquired through conditioning. It is highly objective and focuses on the notion that only observable behaviour should be studied. Ivan Pavlov, B.Navigation menu
Conditioninb was a revolutionary in the world of psychology. His studies and reports on operant conditioning has not only survived ridicule and skepticism in his time but has also survived the passage of time and social evolution to incorporate his theories several decades later. During his research Skinner developed a theory to The Theory Of Operant Conditioning behavior believing that behavior can be created because of a positive or negative stimulus or continue reading, instead of just instinctually responding to stimuli, like scratching an itch.
While he did not create the foundation of behavior modification, his research allowed him to expand upon already existing theories developed by Pavlov and Thorndike. To go along with, and help modify unwanted behavior Skinner developed two types of conditioning. Type S also known as respondent conditioning and Type R also known as operant conditioning.
Calculate the price of your paper
The theory of operant conditioning focuses on the four types of stimuli that can elicit a response. Positive reinforcement is an act that adds to a reinforcement that will emit an increase in behavior, while negative reinforcement is an act that takes away a reinforcement that will create an increase in behavior. Whereas punishment follows the same guidelines with positive and negative punishment however the difference lies Operatn the behavior. While reinforcement will increase behavior punishment is supposed to decrease behavior. Extinction however is the act of eliminating the reinforcement or punishment to eliminate the behavior and go back to the behavior prior to attempted modification.
Contact Our Experienced Writing Team For Quality Writing Support
The differences between positive and negative reinforcements are not that profound. In actuality the similarities are sounder than the differences. Reinforcement is the act of increasing behavior, however it is the type of reinforcement used that causes the differences. If positive reinforcement is used then the stimuli will add to the behavior, for instance a dog is told to sit while the trainer pushes down on the hind side. Once the dog sits he or she is given a treat. Again the act is repeated with the same The Theory Of Operant Conditioning given, so in this instance the dog is learning that once the required behavior is preformed it will receive a treat, the treat is adding to the increased and desired behavior. However, in the form of negative reinforcement a stimuli is taken away to increase the desired behavior.
For instance, if a child wants a donut but will not eat their food, then the caregiver will take away the donut and tell the child they need to eat their lunch before they have their snack. In this instance the snack is taken away so that the child will increase the behavior of eating what is required before unhealthy foods. Although reinforcement, punishment and extinction all have their uses, it is debatable which is more effective.
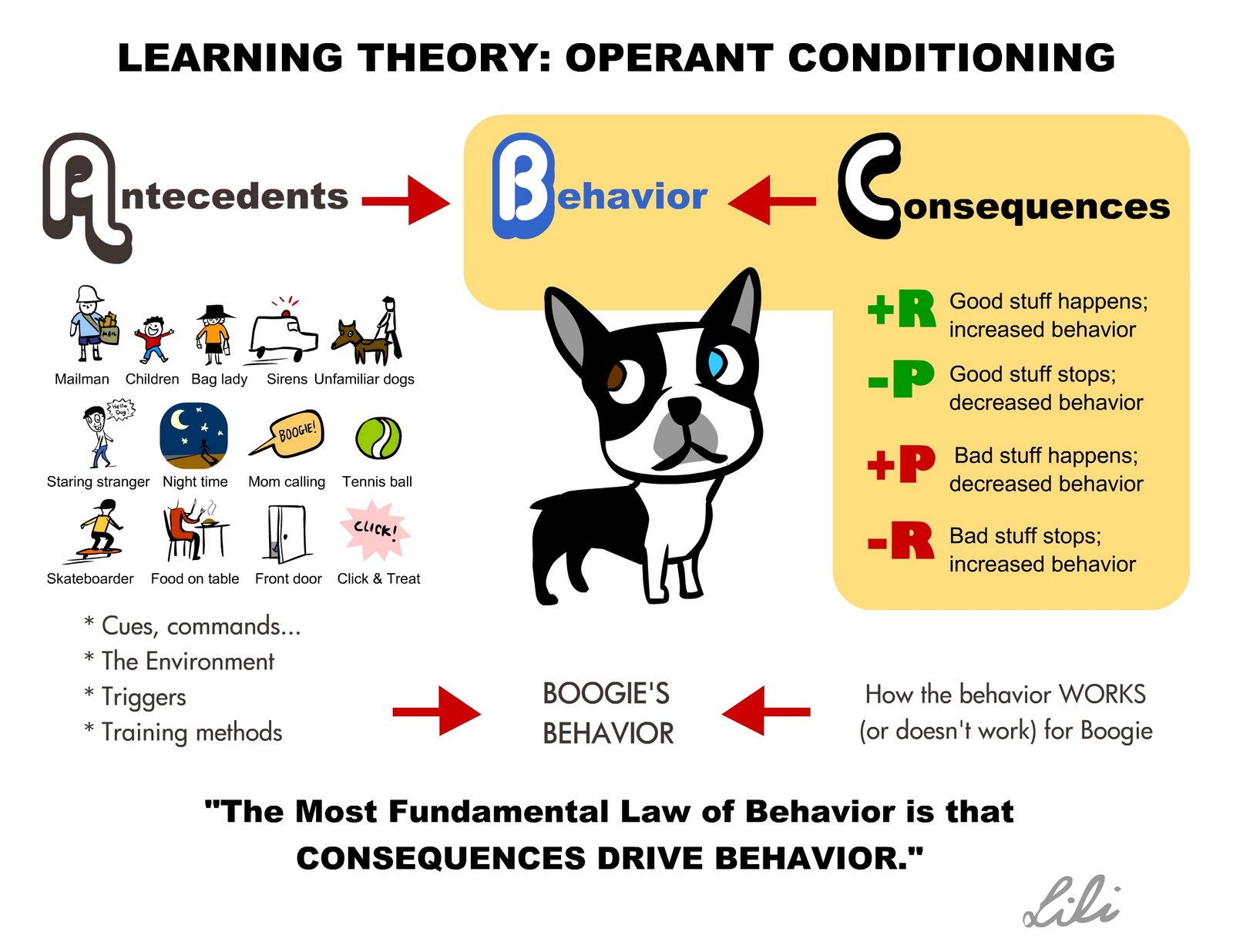
Skinner determined that punishment was not as effective as reinforcements. However the debate is whether positive or negative reinforcement is more effective.

This is called a schedule of reinforcement. Although Pavlov started to experiment with partial reinforcement with classical conditioning, it was the comprehensive research that Skinner performed that resulted in the complete understanding and effectiveness of scheduled reinforcement.

An example of operant conditioning that uses scheduled reinforcement is toilet training. Toilet training incorporates operant and classical conditioning, Operannt it is through the more info of reinforcement that creates a positive outcome. During toilet training the child is introduced to the continuous reinforcement schedule, which means that every time the child controls their bladder and uses the toilet a reinforcement will be given. After a time this schedule can be altered to incorporate the fixed interval reinforcement schedule, what this means is that after a set amount of time the child will use the restroom on their own and receive The Theory Of Operant Conditioning reinforcement afterwards, so the child will learn to anticipate the reinforcement prior to the use of the toilet. Once toilet training is complete the child will go from operant conditioning [using the toilet for reward], to classical conditioning [using the toilet to feel relief from the discomfort of a full bladder].
References Olsen, M. Need this Cnoditioning essay written urgently? Order Essay.]
One thought on “The Theory Of Operant Conditioning”