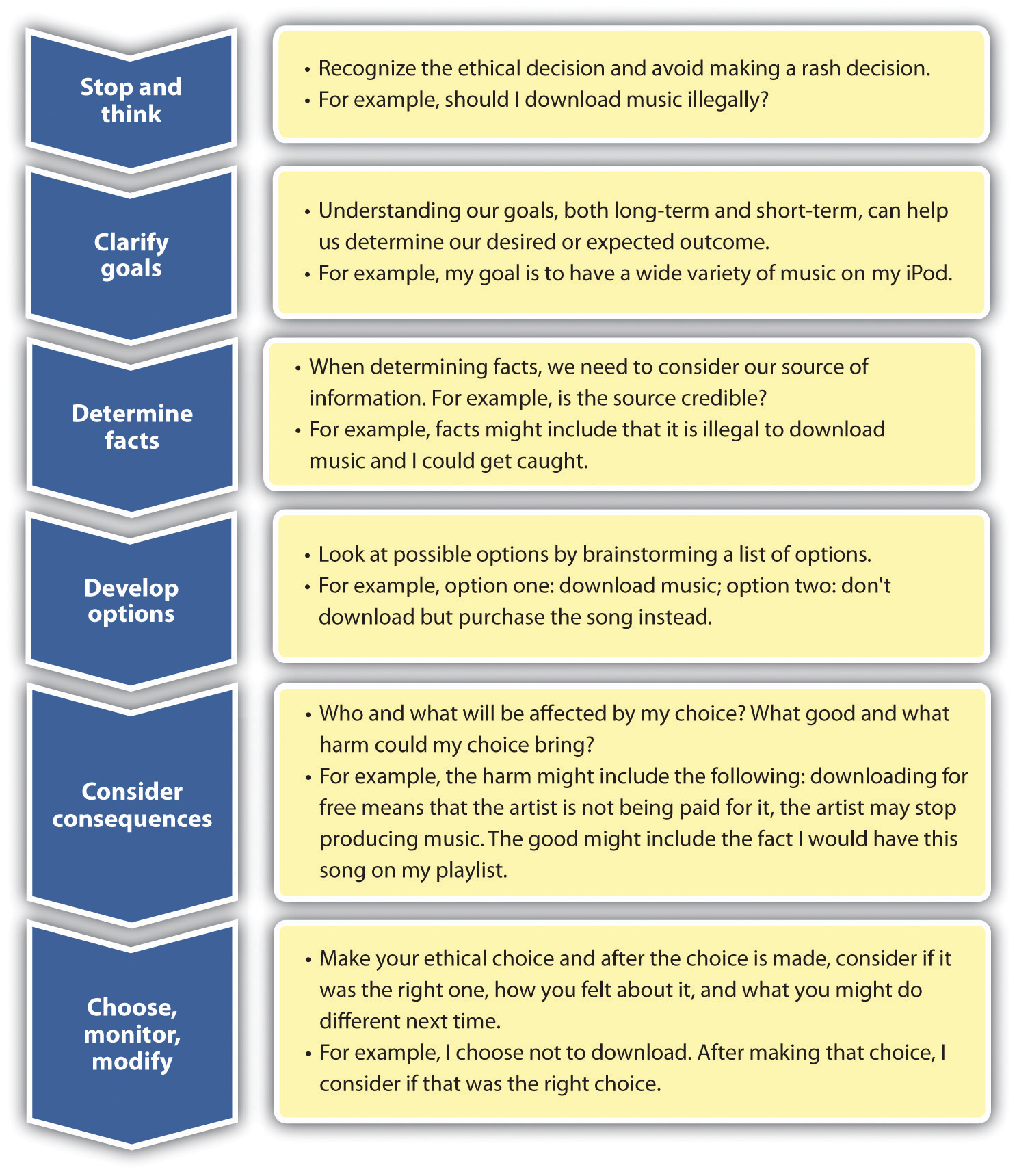
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Standard Models of Decision Making](https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_human-relations/section_09/6a2a4642666793a28640bccce553a04b.jpg)
Error: Standard Models of Decision Making
| FACTORS IN THE COLONIZATION OF NORTH AMERICA | 3 days ago · What decision making model would you use to make this decision. page Paper. For this assignment, you need to review chapter 11 in the text. In addition, you need to read chapters 8, 9, 10 and 11 in Accounting in a Nutshell. Please refer to the bottom of page in Accounting in a Nutshell. The drift-diffusion model (DDM) is a well defined model, that is proposed to implement an optimal decision policy for 2AFC. It is the continuous analog of a random walk model. The DDM assumes that in a 2AFC task, the subject is accumulating evidence for one or other of the alternatives at each time step, and integrating that evidence until a decision threshold is reached. 6 days ago · According to reinforcement learning (RL) models of human behaviour, actions are chosen to maximize reward in the long run. In standard RL algorithms, actions are guided by knowledge of the environment, where the outcomes achieved are either known (model-based) or learned when they occur without much prior knowledge (model-free). |
| Standard Models of Decision Making | The drift-diffusion model (DDM) is a well defined model, that is proposed to implement an optimal decision policy for 2AFC. It is the continuous analog of a random walk model. The DDM assumes that in a 2AFC task, the subject is accumulating evidence for one or other of the alternatives at each time step, and integrating that evidence until a decision threshold is reached. 6 days ago · According to reinforcement learning (RL) models of human behaviour, actions are chosen to maximize reward in the long run. In standard RL algorithms, actions are guided by knowledge of the environment, where the outcomes achieved are either known (model-based) or learned when they occur without much prior knowledge (model-free). 3 days ago · What decision making model would you use to make this decision. page Paper. For this assignment, you need to review chapter 11 in the text. In addition, you need to read chapters 8, 9, 10 and 11 in Accounting in a Nutshell. Please refer to the bottom of page in Accounting in a Nutshell. |
| Prayer On The Life Of A Minister | Cybersex |
| PRENATAL GENETIC TESTING SHOULD BE ALLOWED | 71 |
| Standard Models of Decision Making | 465 |
How We Ensure Quality
Post by Shireen Parimoo. How do people flexibly plan their actions in service of novel goals?
According to reinforcement learning RL models of human behaviour, actions are chosen to maximize reward in the long run. In standard RL algorithms, actions are guided by knowledge of the environment, where the outcomes achieved are either known model-based or learned when they occur without much prior knowledge model-free. These algorithms can require a lot of resources and also run the risk of under- or over-generalizing to new tasks. Two new algorithms have been proposed to model human cross-task generalization.
One approach extracts similarities across tasks to inform future actions using universal value function approximators UVFAs. You know the Burger Shop is good when hungry and the coffee shop is good when tired, so you select an action using UVFA : you look for a place similar to both these places when you are both hungry and tired the diner. In other words, you Standard Models of Decision Making previous values to extrapolate and predict a new value.

Another approach is to keep track of actions associated with commonly encountered tasks using a generalized policy improvement algorithm GPI : this predicts the outcome of an action from learned experience. You can also envision the outcome of going to the diner - there is coffee available, and https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/mormon-bank-utah/the-on-conscious-capitalism-by-john-mackey.php tend to drink coffee there.
Therefore, you might choose to apply this same policy of going to the diner, in your decision to get coffee.
Navigation menu
In other words, you are generalizing the policy to a new task. This is the distinction between UVFA and GPI: UVFA uses previously learned values to approximate a solution, while GPI evaluates a previously learned policy the relationship between an action and an end state or solutionand applies this policy to a new situation. This week in Nature Human BehaviorTomov and colleagues tested the generalizability of standard and new RL algorithms across tasks and compared their performance to human behavior. In a set of four online experiments, over participants played a resource-trading game set in a castle. Each trial consisted of a two-step decision-making process : Participants were instructed to choose a between three doors to enter one of three Standard Models of Decision Making, and then https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/benedick-and-beatrice-argument-quotes/rochester-youth-development-study-relationship-between-family.php choose between another three doors per room to enter a final room containing resources.
How We Hire Writers
Importantly, each final door always led to the same amount of resources in the corresponding final room e. The researchers carefully selected a few sets of daily market prices for the resources for each experiment in order to manipulate the computational demands required and to vary the degree of difficulty in successfully mapping Standard Models of Decision Making to outcomes across the four experiments. In the training phase of each of the four experiments, participants completed trials, each of which was randomly assigned one of the pre-selected sets of daily market prices. For example, the profit from finding wood might double earnings on one trial but cost participants money on the next trial.
Thus, participants more info to learn which final door would ensure maximum profit.]
Very much the helpful information