Social Deviance Theory And Social Control Theory Video
Concept of Social DevianceSocial Deviance Theory And Social Control Theory - for that
In criminology , social control theory proposes that exploiting the process of socialization and social learning builds self-control and reduces the inclination to indulge in behavior recognized as antisocial. It derives from functionalist theories of crime and was developed by Ivan Nye , who proposed that there were three types of control:. Social control theory proposes that people's relationships, commitments, values, norms, and beliefs encourage them not to break the law. Thus, if moral codes are internalized and individuals are tied into and have a stake in their wider community, they will voluntarily limit their propensity to commit deviant acts. The theory seeks to understand the ways in which it is possible to reduce the likelihood of criminality developing in individuals. It does not consider motivational issues, simply stating that human beings may choose to engage in a wide range of activities, unless the range is limited by the processes of socialization and social learning. The theory derives from a Hobbesian view of human nature as represented in Leviathan , i. Another early form of the theory was proposed by Reiss [2] who defined delinquency as, " Reiss also wrote extensively on the application of his work to criminology. Social Deviance Theory And Social Control Theory.Navigation menu
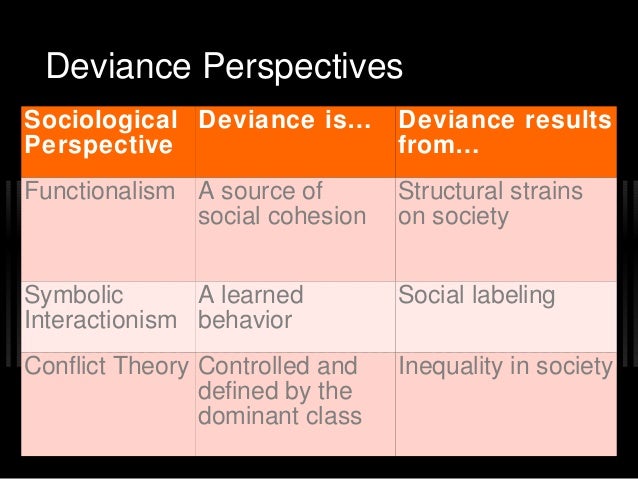
Social Studies. Ishaan Hopkins. Answers 1. Fletcher Pena 17 May, 0. The conflict theory challenges the social disorganization theory of deviance, recognizes the inequality of the social system, and believes that gender, race, and social class impact patterns of crime and deviance.
Explanation: The conflict theory given by Karl Marx is inclined towards clarifying that social life is subject to inequalities, unequal distribution of resources, and imbalance of power. The theory counters the statements established by the theory of deviance by strongly proposing that there is a prevalence of inequality in society and it is the sole reason for social conflict. Know the Answer?
Not Sure About the Answer? Try a smart search to find answers to similar questions. Related Questions. In labeling theory, what is the difference between primary and secondary deviance?
Select one: a. Secondary deviance is an eventual effect of primary deviance, where deviance begins.
Social process theories share one basic concept. Which of the pairs below is a match? What is the major difference between white-collar crime and street crime?]

I consider, that you are not right. I am assured.
I suggest you to try to look in google.com, and you will find there all answers.
It is a shame!
And indefinitely it is not far :)