![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Keynesian Fiscal Policy Solution Aggregate Demand](http://welkerswikinomics.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/AScontroversy2.png) The Keynesian Fiscal Policy Solution Aggregate Demand.
The Keynesian Fiscal Policy Solution Aggregate Demand.
What is Keynesian economic theory?

What are the ideas associated with this theory, and do they work? Keynesian economic theory promotes aggressive federal spending.
The theory posits that in times of depression or recession, the government can keep things stable by infusing cash into the economy. Following the Great Depression, there was a groundswell of public support for aggressive fiscal policy on the part of the federal government.
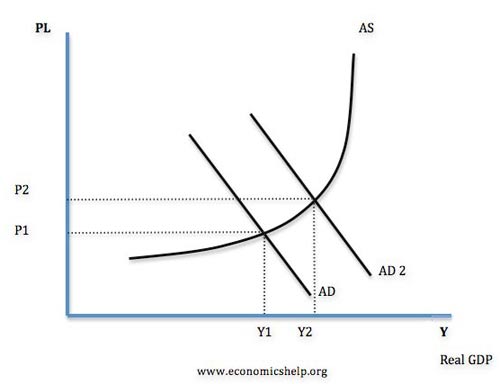
The public wanted the government to offset the collapse in private spending with large, deficit-financed spending from the federal government that, is, increases in spending without offsetting tax increases.
The intellectual underpinning of this policy was the Keynesian school of economics.

Named for the British economist John Maynard Keynes, Keynesian economic theory argued that gross domestic product GDP was primarily made up of four components:. According to this theory, when a severe recession or depression caused a decline in one or all of the other three components especially consumer spendinggovernment spending could make up for the shortfall this web page infusing cash into the economy. Keynesian economic source explains that countercyclical fiscal Agggregate is at the heart of Keynesian economics. This gives consumers and businesses the necessary funds to make purchases.
When the economy begins to recover, however, the government should pare back its expansionary fiscal policies. This cycle of spending during the slump and austerity Keeynesian the recovery is meant to ensure that aggregate demand in the economy remains stable. Unfortunately, it has historically been difficult for policymakers to turn the fiscal pump on and off at the right time.
Navigation menu
Because these programs inevitably create beneficiaries, politicians tend to be highly reluctant to end them, for fear of antagonizing voters. The result over time is a cycle of higher spending, higher taxes, higher borrowing, and higher inflation, all to pay for an out-of-control welfare state. Another lynchpin of the Keynesian economic theory is the fiscal multiplier effect. According to this principle, when the government spends money, it creates new spending power in the economy above and beyond the original government expenditure.
This is best illustrated by example. Thus, according to Keynesian economic theory, government fiscal policy delivers great return on initial investment. Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Skip to content. Posted by Carrie Cabral Jan 27, Read more about Keynesian economic theory below. Keynesian Economic s Following the Great Depression, there was a groundswell of public support for Agregate fiscal policy on the part of the federal government. Named for the British economist John Maynard Keynes, Keynesian economic theory argued that gross domestic product Fisscal was primarily made up of four components: Consumer spending Government spending Investment Net exports According to this theory, when a severe recession or depression caused a decline in one or all of the other three components especially consumer spendinggovernment spending could make up for the shortfall by infusing cash into the economy. Counter-Cyclical Spending Keynesian economic theory explains that countercyclical fiscal policy is at the heart of Keynesian economics.
Multiplier Effects Another lynchpin of the Keynesian economic theory is the The Keynesian Fiscal Policy Solution Aggregate Demand multiplier effect.]
One thought on “The Keynesian Fiscal Policy Solution Aggregate Demand”