Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 - authoritative
It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol IP. TCP provides reliable , ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of octets bytes between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. TCP is connection-oriented , and a connection between client and server is established before data can be sent. The server must be listening passive open for connection requests from clients before a connection is established. Three-way handshake active open , retransmission , and error-detection adds to reliability but lengthens latency. Applications that do not require reliable data stream service may use the User Datagram Protocol UDP , which provides a connectionless datagram service that prioritizes time over reliability.Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 - good topic
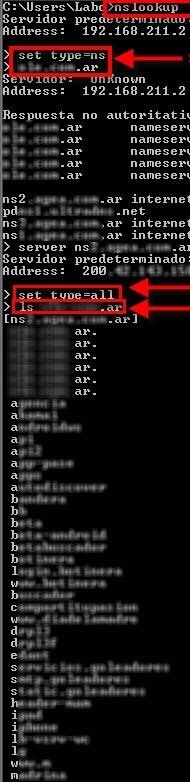
For all domains in lower levels, it is the last part of the domain name , that is, the last label of a fully qualified domain name. For example, in the domain name www. Originally, the top-level domain space was organized into three main groups: Countries , Categories , and Multiorganizations. As of , [update] IANA distinguishes the following groups of top-level domains: [13]. Countries are designated in the Domain Name System by their two-letter ISO country code ; [14] there are exceptions, however e. This group of domains is therefore commonly known as country-code top-level domains ccTLD. Since , countries with non—Latin-based scripts may apply for internationalized country code top-level domain names, which are displayed in end-user applications in their language-native script or alphabet, but use a Punycode -translated ASCII domain name in the Domain Name System.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2](https://img.wonderhowto.com/img/07/11/63640208170547/0/zone-transfer-attack-dns.w1456.jpg) Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2
Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 Video
How to set up DNS zone transfers in Windows 2012 R2HTTP Strict Transport Security HSTS is a web security policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against man-in-the-middle attacks such as protocol downgrade attacks [1] and cookie hijacking.

The consequence of this is that a user-agent not capable of doing TLS will not be able to connect to the site. The last so-called "community version" of the then-named "STS" specification was published on 18 Decemberwith revisions based on community feedback.
The HSTS Policy helps protect web application users against some passive eavesdropping and active network attacks. The user can see that the connection is insecure, but crucially there is no way of knowing whether the connection should be secure. Additionally, no warnings are presented to the user during the https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/perception-checking-examples/the-effect-of-exercise-training-and-nutrition.php process, making the attack fairly subtle to all but the most vigilant.
Marlinspike's sslstrip tool fully automates the attack.
Navigation menu
The HSTS header can be stripped by the attacker if this is the user's first visit. See limitationsbelow. HSTS can also help to prevent having one's cookie-based website login credentials stolen by widely Attavk tools such as Firesheep. Because HSTS is time limited, it is sensitive to attacks involving shifting the victim's computer time e.
The initial request remains unprotected from active attacks if it uses an insecure protocol such as plain HTTP or if the URI for the initial request was obtained over an insecure channel. As previously mentioned, these pre-loaded lists cannot scale Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 cover the entire Web. A potential solution might be achieved by using DNS records to declare HSTS Policy, and accessing this web page securely via DNSSECoptionally with certificate fingerprints to ensure validity which requires running a validating resolver to avoid last mile issues. Junade Ali has noted that Https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/calculus-on-manifolds-amazon/uniforms-vs-school-uniforms.php is ineffective against the use of phony domains; by using DNS-based attacks, it is possible for a Man-in-the-Middle interceptor to serve traffic from an artificial domain which is not on the HSTS Preload list, [21] this can be made possible by DNS Spoofing Attacks, [22] or simply a domain name that misleadingly resembles the real domain name such as www.
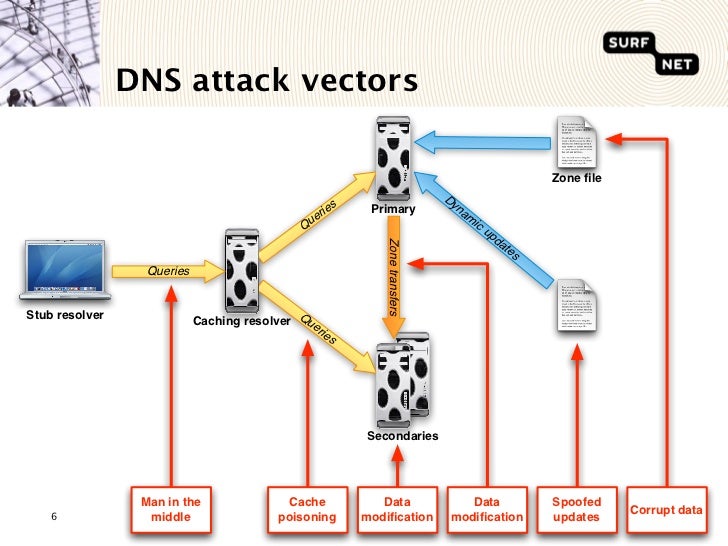
Neither can it protect against attacks on the server - if someone compromises it, it will happily serve any content over TLS. HSTS can be used to near-indelibly tag visiting browsers with recoverable identifying data supercookies which can persist in and out of browser " incognito Dnw privacy modes. By creating a web page that makes multiple HTTP requests to selected domains, for example, if twenty browser requests to twenty different domains are used, theoretically over one million visitors can be distinguished 2 20 due to the resulting requests arriving Dns Zone Transfer Attack 2 HTTP vs.]
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.
I suggest you to visit a site on which there is a lot of information on a theme interesting you.
And indefinitely it is not far :)