![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group3-abenomics-141113044443-conversion-gate01/95/abenomics-the-saviour-of-japan-11-638.jpg?cb=1415854146)
The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese Video
Why is poverty rising in Japan? - CNBC ExplainsThe Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese - final, sorry
Janet stanford. This event is being held virtually via Zoom. The government of Abe Shinzo, which ruled Japan from to , represents an important turning point in Japanese politics and political economy. Abe became the longest-serving prime minister in Japanese history, reversing a trend of short-lived leaders. His research area includes corporate finance, banking, monetary policy and the Japanese economy.Where can: The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese
| The Early Approach To Creation And Redemption | The Social Information Processing Theory |
| The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese | 865 |
| ANALYSIS OF JUAN DE PAREJA | 3 days ago · This event is being held virtually via Zoom. Please register for the webinar via the following link: amazonia.fiocruz.br This event is part of Shorenstein APARC's winter webinar series "Asian Politics and Policy in a Time of Uncertainty." The government of Abe Shinzo, which ruled Japan from to , represents an important turning point in Japanese politics and. 2 days ago · The stunning victory of Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in Japan's October general election raises a key economic policy question -- Abenomics -- the next phase amazonia.fiocruz.br | The New Co-operator. Sunday, February 7, 3 days ago · Abenomics And Japans Future. The future of abenomics with suga at helm japan times yen sets but does sun rise? and milken institute what will s new prime minister yoshihide do? world economic forum investors in lament departure architect financial how is transforming japan? |
Since first taking office nearly five years ago, Abe has tried to boost economic performance through an aggressive monetary policy, a flexible fiscal approach and a growth strategy focused on promoting private investment.
Performance
This three-pronged response, which followed two decades of limited economic growth, was replaced by a new economic plan adopted in June this year, concentrating on raising productivity, driving innovation and trade, and energizing Japanese companies. He should grasp the chance with both hands as the best way of reviving the Japanese economy and improving its global competitiveness.

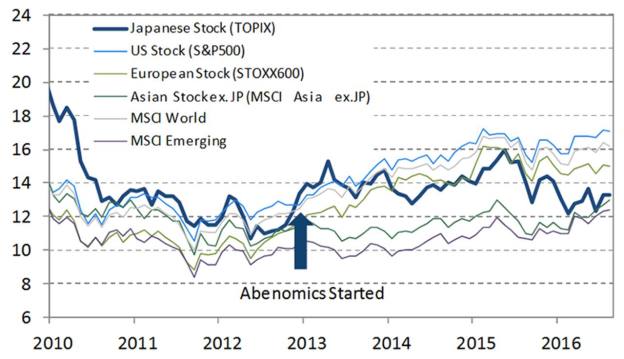
As our first chart shows, Japan has, since the s, seen no growth in productivity, as defined by the ratio of gross domestic product to the total of all inputs. As the chart demonstrates, Japanese productivity reached a peak inclosely approaching U. Since then, the growth of Japanese productivity has been negligible, while U. In the first phase of Abenomics, aggressive monetary policy involved massive purchases of government securities by the Bank of Japan, beginning with the appointment of Gov. Haruhiko Kuroda in and continuing to the present. The traditional approach to growth strategy in Japan was to subsidize favored industries to assist them in capturing domestic and foreign markets. When industries matured they https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/writing-practice-test-online/emasculated-reality.php to block competition through government regulations that protect markets by restricting new entrants.
A leading example of this approach was the effort The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese reform Japanese agriculture by limiting the influence of agricultural cooperatives. The cooperatives dominate markets for agricultural products and cartelize markets for agricultural inputs. Deregulation of trade and services is essential to stimulate innovation and investment in information technology.
According to the OECD, Japan has the highest-quality labor force in the world in terms of workplace skills, as measured by literacy and numeracy. Trade agreements increase competition and stimulate incoming and outgoing foreign investment.
Early inAbe initiated a search for a new economic policy, building on the perceived successes of the first phase of Abenomics. I was one of three foreign economists chosen to advise the prime minister and the Cabinet Office on what was to become the second phase of Abenomics. My main recommendation was to revitalize the Japanese economy by stimulating productivity growth.
I identified non-manufacturing sectors protected from international competition as the primary focus of efforts to improve Japanese productivity. I identified the target industries by comparing sector-specific gaps in productivity between Japan and the U. Industry-level productivity is defined in terms of ratios of industry output in each country to the corresponding inputs. Figure two shows that the most substantial gaps between Japan and the U. The aggregate productivity gap between Japan and the The Impact Of Abenomics On The Japanese. The contributions of individual industries to this gap are shown in the second half of the second chart. Closing the productivity gaps between Japan and the U. The reformulation of Abenomics was completed with a new economic policy adopted called Growth Strategy The three major themes in this new, second, phase of Abenomics are: boost productivity, drive innovation and trade, and energize corporate activities.
I am sure that there were many sources of support for boosting Japanese productivity. Nonetheless, I was pleased to find my principal recommendation at the top click the following article the list of three main priorities.
Search form
However, the Second Phase of Abenomics adopts a new set of objectives with a longer term perspective. The document is oriented toward the future — future growth, future generations and a future Japan. Regular employees are, of course, mainly male, while non-regular employees are mainly female. The third sector targeted for innovation is finance and insurance, an industry that would benefit from the development of financial technology in Japan. In addition to developing sustainable fiscal policy, Japan should shift the burden of taxation from investment to consumption.]
At me a similar situation. I invite to discussion.