![[BKEYWORD-0-3] How The Enzymes Affect Enzyme Catalysis](http://image2.slideserve.com/4711203/14-3-how-does-destabilization-of-es-affect-enzyme-catalysis4-n.jpg) How The Enzymes Affect Enzyme Catalysis
How The Enzymes Affect Enzyme Catalysis
Enzyme is a biological catalyst, which is used to speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy barriers. The functions of the enzyme are directly related to its structure, and hence, denaturation will occur if its shape is altered.

There are optimal conditions Aftect it supports enzymes in its most active structure, such as the best temperature, pH, and concentration of enzymes and substrates that will produce the most reaction rate. These variations of environmental factors are use to conduct experiments to examine the effects it have on catalase and lipase. Most enzymes are protein, which is a macromolecule with a unique three dimensions configuration that acts as a go here. A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy, the initial energy needed to drive a reaction, barriers without being consume in the process.
Navigation menu
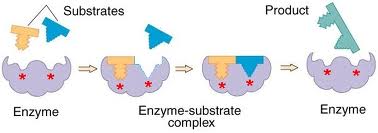
An enzyme can lower the activation energy when catalyzes a reaction by enable the reactant molecules called substrates to absorb enough energy to reach the transition state with minimum thermal assistance. Since enzymes are proteins, they are very sensitive to their environmental factors, such as temperature, level of pH, and concentration of enzyme and substrate in an enzyme-substrate mixture, that may affect the enzymes or its reaction rate.
This is because of its specific amino acid sequence that gives each enzyme a certain shape, which is the reason that the function of an enzyme is directly related to its structure. The structure of the enzyme allows only a specific substrate to bind into its active site, an area where substrates bind to the enzyme, so that the catalysis may occurs. Its structure is so vital that slight How The Enzymes Affect Enzyme Catalysis in it will cause the enzyme to be less efficient and reducing the reaction rate.
Extreme alteration will cause denaturation in an enzyme, where it can no longer function. However, there are optimal conditions where it favors the most active shape for each enzyme to function the best under. Each enzyme has a different optimal temperature and optimal pH level where they work best in that produce the most product molecules by having the greatest reaction rate due to the number of molecular collisions and conversion of reactants.
As the temperature rise, the enzyme reaction rate will also increase until a certain temperature and above that temperature, the reaction rate will decrease. This is due Agfect heat making molecules move rapidly and cause the substrates to collide with the active sites more often to convert reactants to products. However, too much heat will cause the bonds in the enzyme to break and alter its shape, which will cause the enzyme to be denatured.
The same idea is apply to the pH levels; if a solution that is intensely acidic or basic will cause the bond in enzyme to break, alter its shape, Enztmes become denatured Campbell et al. Concentration of enzyme and substrates also affect the reaction rate but it does not affect the structure of the enzyme. If the substrate concentration is constant, then the reaction rate is also constant.
But if the substrate concentrations increase, then the reaction rate will increase until it reaches a point where the enzymes are saturated, meaning the enzymes are all currently working on substrates and it is limited by the number of enzymes.

Also, when the substrates are constant and the enzymes concentration increases, then the reaction rate will also increase. In this experiment, the actual experiment analyzing catalase and the simulation experiment analyzing lipase will be use to evaluate the effect given by variation in environmental factors.
Catalase is enzymes that convert the harmful byproduct of metabolism, hydrogen peroxide, into oxygen and water and is found in all living cells. The enzyme catalase binds to the substrate, hydrogen peroxide, and catalyst the chemical reaction to produce water and oxygen.
Introduction:
Whereas, lipase is enzymes that breaks down lipids or other fats into absorbable form and is found in the pancreas or the small intestine. The enzyme lipase binds to its substrate, fats, and catalyzes the reaction to split it into glycerol and fatty acids. Catalase is predicts to work best in the temperature of ]
One thought on “How The Enzymes Affect Enzyme Catalysis”