Not: Decreasing Low Grade Systemic Inflammation Through Exercise
| Magical Realism As A Sense Of Psychological | 670 |
| Decreasing Low Grade Systemic Inflammation Through Exercise | A Review On Coaching And Mentoring |
| DEFIANCE IN MINORITIES OF UNITED STATES | 650 |
Review ARTICLE
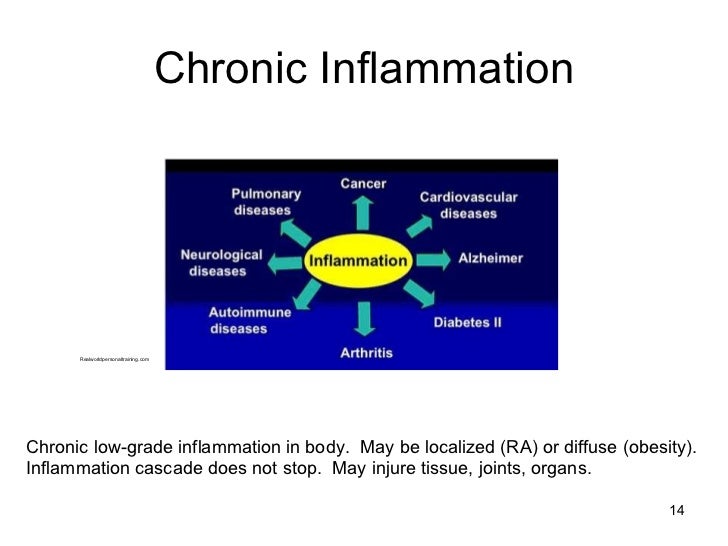
Severe and critical cases are characterized by damage to the respiratory system, endothelial inflammation, and multiple organ failure triggered by an excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines, culminating in the high number of deaths all over the world. Sedentarism induces worse, continuous, and progressive consequences to health. On the other hand, physical activity provides benefits to health and improves low-grade systemic inflammation. The aim of this review is to elucidate the effects of physical activity in physical fitness, immune defense, and its contribution to mitigate the severe inflammatory response mediated by SARS-CoV Decreasing Low Grade Systemic Inflammation Through Exercise this sense, studies have shown that acute physical exercise induces the production of myokines that are secreted in tissues and into the bloodstream, supporting its systemic modulatory effect.
Therefore, maintaining physical activity influence balance the immune system and increases immune vigilance, and also might promote potent effects against the consequences of infectious diseases and chronic diseases Strengths And Weaknesses Of Socrates with the development of severe forms of COVID Protocols to maintain exercise practice are suggested and have been strongly established, such as home-based link HBE and outdoor-based exercise OBE.
In this regard, HBE might help to reduce levels of physical inactivity, Decreasing Low Grade Systemic Inflammation Through Exercise rest, and sitting time, impacting on adherence to physical activity, promoting all the benefits related to exercise, and attracting patients in different stages of treatment for COVID After decades of qualified research to understand the effects of physical inactivity and sedentarism on human health, this topic continues to be discussed and is still a challenge to achieve satisfactory levels of physical activity 1.
Navigation menu
The consequences of sedentary timeline evolution are continuous, progressive, unforgiving, and almost silent. A Decreasing Low Grade Systemic Inflammation Through Exercise pattern is established, with no precise beginning, but includes: a reduction of corporeal capacity; an increase in physical and emotional discomfort when exposed to higher levels of physical demand; and a Inflam,ation behavioral pattern associated with any kind of exercise Grafe, which is often associated with others dangerous behaviors to health 2. The entrance to this vicious cycle might be promoted by social, economic, clinical, age, gender, schooling, race, civil status, and others factors 3. Despite these aspects, it is outside the scope of this review to explore these determinants. Regardless of sedentarism, in calamity conditions, humans are exposed to mentally, physically, and nutritionally unusual situations, with a direct impact on health, mediated by, among other factors, the immune system 6.
SARS-CoV-2 infection compromises the immune system affecting individuals with underlying conditions or risk factors, such as cardiovascular and metabolic diseases on which a sedentary lifestyle can be a risk factor for morbidity and mortality 78. Hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, asthma, hematologic diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, immunosuppression, and advanced age are associated with critical COVID disease and higher hospitalization rates 9 This raises interesting questions about the complex interaction between sedentarism and comorbidities, and how these impact COVID outcomes, with special attention to the role of the immune system.
In order to discuss the close relationship between Exrcise patterns of physical activity and the consequent levels of physical fitness and the immune system, this review aims to outline objective considerations on the maintenance of physical activity that can balance the immune system and increase immune surveillance. In fact, many types of exercise, such as aerobic, strength, or combined training, and sports in indoor or outdoor environments can impact the immune response ]

It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
Matchless theme, it is interesting to me :)
What necessary words... super, a remarkable phrase