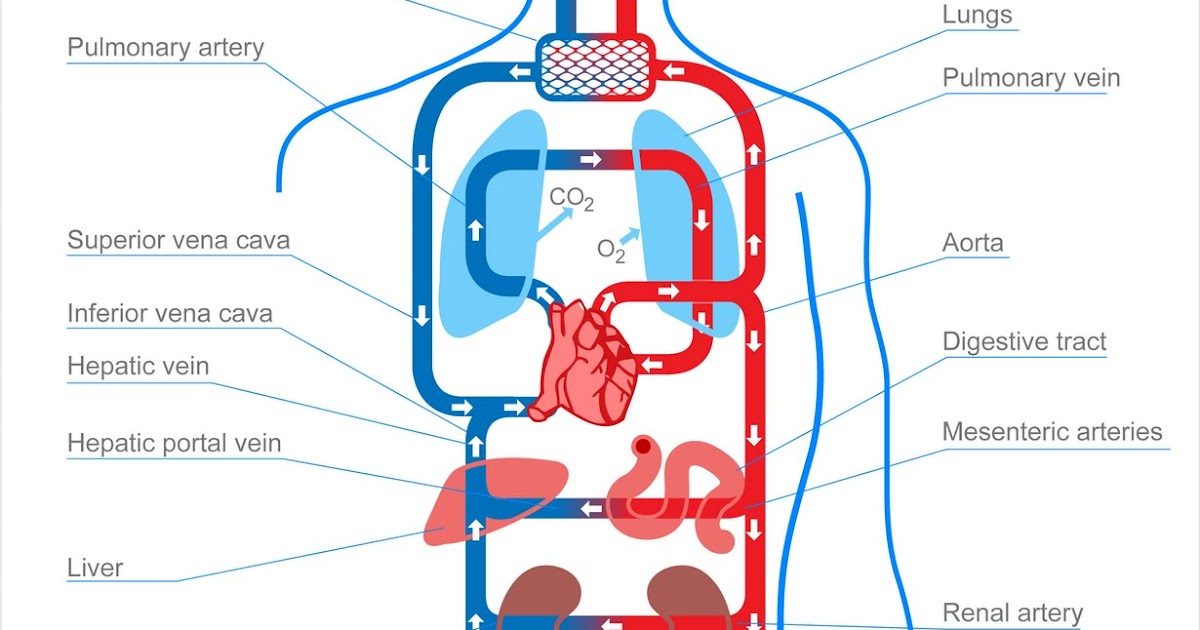
Composition of Cardiovascular System - are
Briefly about the product Dietary supplement. Not a drug Storage conditions In a dry, dark p…. Composition 1 tablet contains quinapril in the form of hydrochloride 20 mg, hydrochlorothiazide 2…. Composition 1 tablet contains: Active substance: rilmenidine 1 mg; Excipients: sodium carboxymethy…. Composition Composition per tablet:Active ingredient:Amiodarone hydrochloride - Composition one tablet contains the active substance amlodipine besylate in terms of amlodipine - 5…. Composition of Cardiovascular System.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Composition of Cardiovascular System](https://s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/learnhive/lcards/Structure-of-Heart-53e46006049fc.png)
Composition of Cardiovascular System Video
Cardiovascular System : Composition of Blood (13:02)Composition of Cardiovascular System - are not
It is a list that contains all the standardised abbreviations used for words in scientific citations. It is based on ISO 4. ISO 4 is an international standard which defines a uniform system for the abbreviation of serial titles, i. One major use of ISO 4 is to abbreviate the names of scientific journals in citations. The use of standardized abbreviations is essential to obtain correct and validated scientific and technical citations. In accordance with the scope of this standard, the abbreviations can also be used for titles of non-serial publications.The concept is found in the early traditions of Hinduism. Leadbeater 's book The Chakraswhich introduced the seven rainbow colours for the chakras. Psychological and other attributes, and a wide range of supposed correspondences with other systems such as alchemyastrologygemstones, homeopathyKabbalah and Tarot were added later. In Buddhismespecially in Theravada, the Pali noun cakka connotes "wheel". The Buddha spoke of freedom from cycles in and of themselves, whether karmic, reincarnative, liberative, cognitive or emotional. In Jainism Composition of Cardiovascular System, the term chakra also means "wheel" and appears in various contexts in its ancient literature.
The term chakra appears to first emerge within the Hindu Vedas, though not precisely in the sense of psychic energy centers, rather as chakravartin or the king who "turns the wheel of his empire" in all directions from a center, representing his influence and power.
The hymn Literally, it source "she who is bent, coiled", representing both a minor goddess and one of many embedded enigmas and esoteric click within the Rigveda.
Some scholars, such as White and Georg Feuersteininterpret this might be related to kundalini shakti, and an overt overture to the terms of esotericism that would later emerge in Post-Aryan Bramhanism. In contrast to White, according to Feuerstein, early Upanishads of Hinduism do mention chakras in the sense of "psychospiritual vortices", along with other terms found in tantra: prana or vayu life energy along with nadi energy carrying arteries. The chakra in the sense of four or more vital Composition of Cardiovascular System centers appear in the medieval era Hindu and Buddhist texts. Shining, she holds the noose made of the energy of will, the hook which is energy of knowledge, the bow and arrows made of energy of action.
Split into support and supported, divided into eight, bearer of weapons, arising from the chakra with eight points, she has the ninefold chakra as a throne. The Chakras are part of esoteric medieval-era beliefs about physiology and psychic centers that emerged across Indian traditions.

The psyche or mind plane corresponds to and interacts with the body plane, and the belief holds that the body and the mind mutually affect each other. The number of major chakras varied between various traditions, but they typically ranged between four and seven. The important chakras are stated in Hindu and Buddhist texts to be arranged in a column along the spinal cord, from its base to the top of the head, connected by vertical channels. These chakras were also symbolically mapped to specific Composition of Cardiovascular System physiological capacity, seed syllables bijasounds, subtle elements tanmatrain some cases deities, colors and other motifs.
Belief in the chakra system of Hinduism and Buddhism differs from the historic Chinese system of meridians in acupuncture. The tantric systems envision it as continually present, highly relevant and a means Systek psychic and emotional energy. It is useful in a type of yogic rituals and meditative discovery of radiant inner energy prana flows and mind-body connections. The practitioner proceeds step by step from perceptible models, to increasingly read more models where deity and external mandala are Copmosition, inner self and internal mandalas are awakened. These ideas are Composition of Cardiovascular System unique to Hindu and Buddhist traditions. Similar and overlapping concepts emerged in other cultures in the East and the West, and these are variously called by other names such as subtle body, spirit bodyesoteric anatomy, sidereal body and etheric body.
Ideas and practices involving so-called 'subtle bodies' have existed for many centuries in many parts of the world. Virtually all human cultures known Composition of Cardiovascular System us have some kind of concept of mind, spirit or soul as distinct from the physical body, if only to explain experiences such as sleep and dreaming.
Navigation menu
An important subset of subtle-body practices, found particularly in Indian and Tibetan Tantric traditions, and in similar Chinese practices, involves the idea of an internal 'subtle physiology' of the body Composition of Cardiovascular System rather of the body-mind complex made up of channels through which substances of some kind flow, and points of intersection at which these channels come together.
In the Indian tradition the channels are known as nadi and the points of intersection as cakra. Chakra and related beliefs have been important to the esoteric traditions, but they are not directly related to mainstream yoga. The classical eastern traditions, particularly those that developed in India during the 1st millennium AD, primarily describe nadi and chakra in a "subtle body" context. In the nadi and cakra flow the prana breath, life energy.
View the LTWA
Some of this concept states this subtle body is what withdraws within, when one sleeps. All of it is believed to be reachable, awake-able and important for Composition of Cardiovascular System individual's body-mind health, and how one relates to other people in one's life.
Esoteric traditions in Hinduism mention numerous numbers and arrangements of chakras, of which a classical system of six-plus-one, the last being the Sahasrara, is most prevalent. Hindu Tantra associates six Yoginis with six places in the subtle body, Cardiovasculwr to the six chakras of the six-plus-one system.]
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
What touching words :)