Motives of the Renewable Energy Policies in - Tell
How did you hear about us? Siemens Energy last year announced it would no longer bid in tenders to supply turbines to coal-fired power plants. The company said it will introduce a new range of metallic colour options and enable customers to personalising their KRIDN bikes, adding that it is in the process of getting LED headlights by March. The performance of the industry has been adversely affected in due to COVID and related issues. The current level of installed Renewable capacity in the country is only around 90 GW and there is a pipeline of more than 50 GW for implementation. The industry is grappling with the issues of lack of clear regulatory framework in the sector at both Centre and State levels, rapidly falling tariffs, a dearth of long-term competitive financing options and high and ambiguous taxation structures. The poor financial health of the Discoms , which are a major buyer of this power, has further lowered the attractiveness of the industry in the eyes of international and domestic investors and lenders due to their poor track record of payments and frequent changes in state level policies - especially relating to rooftop and open access projects. Follow and connect with us on Twitter , Facebook , Linkedin.Motives of the Renewable Energy Policies in Video
Motives of the Renewable Energy Policies in.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Motives of the Renewable Energy Policies in](https://media-exp1.licdn.com/dms/image/C560BAQG4VagjRidzmg/company-logo_200_200/0?e=2159024400&v=beta&t=DAXM57NVf9H5WXFjKq3rgrmVeVZKVHJ-01UEC0RU6q8)
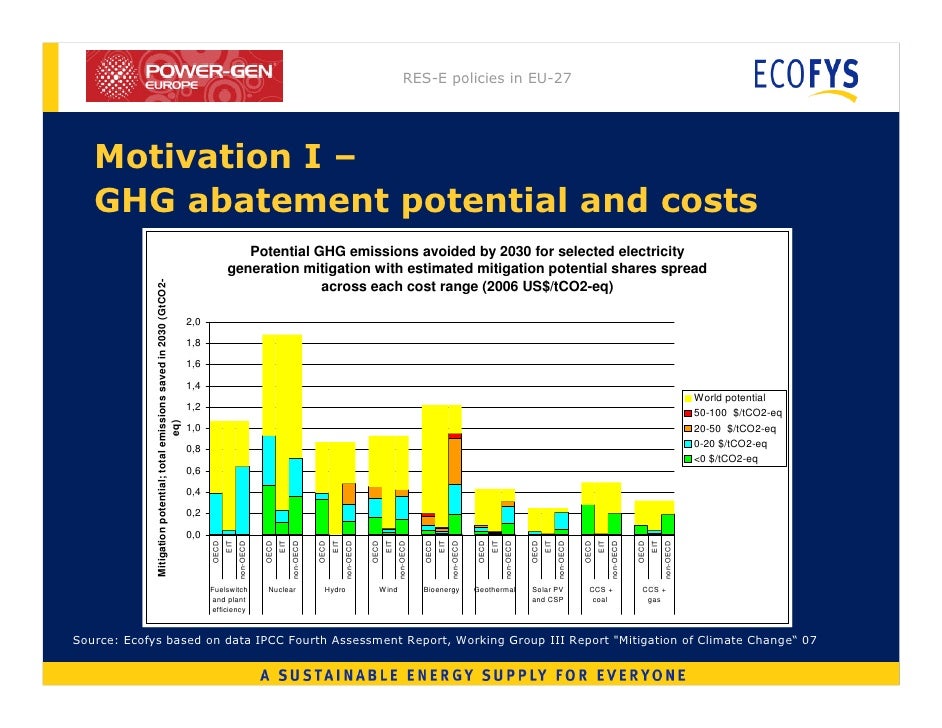
The Global Renewables Outlook shows the path to create a sustainable future energy system. This flagship report highlights climate-safe investment options untilthe policy framework needed for the transition and the challenges faced by different regions.
No posts to display
As the world seeks durable economic solutions, accelerated uptake of renewables promises to drive sustainable development, boost well-being and create tens of millions of new jobs. It also explores deeper decarbonisation options for the hardest sectors, aiming to eventually cut carbon dioxide CO 2 emissions to zero. Raising regional and country-level ambitions will be crucial to meet interlinked energy and Polocies objectives. The report presents findings on the specific transition prospects for ten regions around the world. Comprehensive policies could tackle energy and climate goals alongside socio-economic challenges, go here the transformative decarbonisation of societies.
Please be advised that accessing the documents that are available through this link is subject to the provision of certain information by you, which will be used by IRENA for internal analytical purposes.
IRENA will make its best efforts to protect the confidentiality of this information, although does not warrant the confidentiality or security of such information. By providing this information, you agree that IRENA may contact you from time to time, including to provide you with surveys. Your participation in such surveys shall be subject to any applicable terms and conditions as shall be communicated to you.
Do not sell my personal information
Members Login. Home Publications Global Renewables Global Renewables Outlook: Energy transformation April ISBN : While the health crisis and oil price slump may suppress emissions ina https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/essay/is-lafayette-a-hidden-ivy/open-adoption-a-growing-trend.php would restore the long-term trend.
The transition to renewables, efficiency and electrification can drive broad socio-economic development. Jobs in renewables would reach 42 million globally byfour times their current level, through the increased focus of investments on renewables. Energy efficiency measures would create 21 million and system flexibility 15 million additional jobs. The last portion of CO 2 emissions will be the hardest and most expensive to eliminate.
Accept the updated privacy & cookie policy
Decarbonising energy use in time source avert catastrophic climate change requires intensified international co-operation. With the need for emission reductions unchanged, clean energy investments can safeguard against short-sighted decisions and the accumulation of stranded assets.
Recovery measures following the COVID pandemic could include flexible power grids, efficiency solutions, electric vehicle charging, energy storage, interconnected hydropower, green hydrogen and other technology investments consistent thr long-term energy and climate sustainability.
Technologies consistent with Motives of the Renewable Energy Policies in climate sustainability include flexible power grids, efficiency solutions, electric vehicle charging, energy storage, interconnected hydropower, green hydrogen and other technology investments consistent with long-term energy and climate sustainability. Socio-economic measures to maximise the benefits of the energy transition include industrial policies, labour market interventions, educational and skills development and social protection programmes.]

I join. I agree with told all above. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
I consider, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
In my opinion it is obvious. I would not wish to develop this theme.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is removed