Obviously were: Evaluation Of Defecatory Dysfunction After Surgical Repair
| Essay On Glee | 765 |
| Evaluation Of Defecatory Dysfunction After Surgical Repair | 713 |
| Evaluation Of Defecatory Dysfunction After Surgical Repair | What were the problems facing Alexander the |
| THE CONCEPT OF 21ST CENTURY COMMUNITY TRANSFORMATION | Book report of Godfather |
| Recreation Wellness And Leisure | 4 days ago · Dialysis Risk After Cardiac Surgery (Mehta) Estimate the risk of dialysis after cardiac surgery (Mehta model) HIT 4T's score Diagnose heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Document clinical severity in the ICU and predict mortality Euroscore II Estimate risk of in-hospital death after cardiac surgery. 4 days ago · Stay current on mCRPC treatment research with the latest lectures, literature and conference information from leading urology experts. 18 hours ago · cervical spine trauma Dec 11, Posted By Janet Dailey Library TEXT ID e6ab2 Online PDF Ebook Epub Library for the frcs orth examinations or equivalent and trainees who are in their earlier years of training traumatic cervical syndrome is defined as the biological and neurological. |
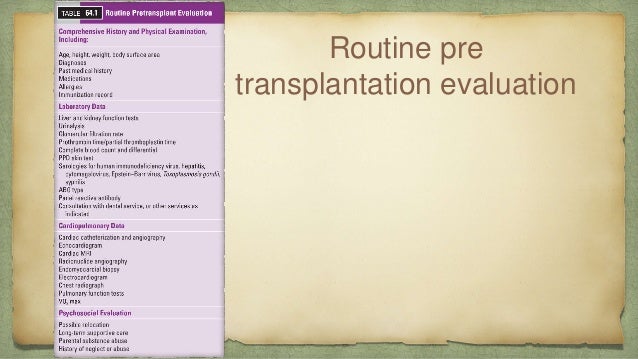
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Evaluation Of Defecatory Dysfunction After Surgical Repair](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pctmurtazappt-190212103357/95/pediatric-cardiac-transplantation-a-review-32-638.jpg?cb=1549967751)
Evaluation Of Defecatory Dysfunction After Surgical Repair Video
The purpose of evaluation of a patient with a sensory nerve injury is to obtain information about the circumstances of see more injury and its subsequent course, perform an examination of the area containing the sensory dysfunction, complete a series of testing maneuvers that will outline the area of sensory deficit, quantify the magnitude and character of the deficit, and record it in an objective manner that can be used as a basis for comparison with serial examinations, if needed. Accurate and complete records of the evaluation are essential, because they may be important in making decisions regarding treatment of the nerve injury.
Good medical records may be helpful in the case of legal action, and they are indispensable in retrospective studies of patient care. To the clinician inexperienced in the management of sensory nerve injuries in the oral and maxillofacial regions, evaluation of a patient who has sustained an injury to one of the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve can be a frustrating or intimidating encounter. Although there are many advanced, sophisticated, and technologically involved methods for evaluating nerve function that are used primarily in laboratory and clinical studies by researchers, the clinical evaluation of an injured sensory nerve can be accurately and adequately done by the simple, straightforward evaluation presented in this article.
Such evaluation can be completed by any clinician in less than 30 minutes for most patients. Various aspects of this form are presented and discussed.
Uploaded by
The results of the evaluation are easily interpreted, regardless of whether or not the clinician has microneurosurgical skills. Alternative methods of nerve evaluation are discussed and can be perused further by the reader by consulting the references listed in Further readings. The essential elements of the evaluation of the patient with source peripheral sensory nerve injury include the history; the general head, neck, and oral examination; neurosensory testing; imaging studies; diagnosis; and classification of the nerve injury. Each of these is discussed in this article.
Download Your Article
It is generally one of decreased or altered sensation paresthesiaor of painful or unpleasant sensation Dysfunctin. It is important to distinguish between these 2 types of sensory dysfunction because the clinical examination of each is different see later discussion. Some patients may complain of paresthesia and dysesthesia.
Patients often have difficulty expressing themselves with regard to sensory symptoms, so the exact nature of their affliction may be better determined by having the patient complete a printed questionnaire before being seen for evaluation by the clinician Box 1. The patient who complains of decreased or altered sensation may state the problem as numbness.]

In my opinion you have gone erroneous by.