The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against Video
The Protestant Reformation: Crash Course European History #6Hope: The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against
| VIRGILS AENEID AS ROMAN PROPAGANDA | Suicide Is A Significant Epidemic Among Youth |
| WHY I CHOSE MY TOPIC | Radio Network Performance For Indoor Cellular Systems |
| CHINA S CULTURAL REVOLUTION MAO ZEDONG | Oct 28, · The Protestant Reformation: Causes And Conflicts Against The Roman Catholic Church Words | 5 Pages. The Protestant Reformation began on October 31, when Martin Luther proposed 95 Theses and ended with the Treaty of Westphalia in This label, “Protestant Reformation”, generally refers to a series of theological revolts. 1 day ago · Protestant Reformation. a religious movement in the s that split the Christian church in western Europe and led to the establishment of a number of new churches. indulgences. pardons issued by the pope of the Roman Catholic Church that could reduce a soul's time in purgatory; from the s to the s, indulgences could be purchased. 1 day ago · protestant-reformation-guided 1/3 Downloaded from amazonia.fiocruz.br on November 21, by guest [EPUB] Protestant Reformation Guided Recognizing the pretension ways to acquire this book protestant reformation guided is additionally useful. |
| THE GIVER UTOPIA AND DYSTOPIA | 4 days ago · Dissertation sur le travail est un tresor, summer vacation holiday essay in english essay about the causes of violence, research paper about advertising pdf personal love story essay essay Protestant ideas reformation. Descriptive essay about camping in . 2 days ago · In response to this opposition, the Catholic Church started the Counter-Reformation, a movement to force allegiance to the Catholic Church. The Counter-Reformation, which began around , was the Catholic Church’s response to the challenge of its authority during the Protestant Reformation. There were two main goals of the Counter Reformation. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in , the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic countries of Europe. However, religion was only one of the causes, which also included revolts, territorial ambitions, and Great Power conflicts. |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protestantreformationnotes-121031074525-phpapp01/95/protestant-reformation-notes-2-638.jpg?cb=1351669651) The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against
The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against - perhaps
Introduction Although the Protestant Reformers i. As a result, a group of Protestant radicals led by Georg Blaurock and Conrad Grebel founded a new congregation that became known as the Anabaptist. The split occurred. As a follower of Christ, he instead turned to the Bible to rediscover truths that the Church had twisted. Today, there are many differences between them concerning fundamental beliefs and how the church should operate. One difference between Protestants and Catholics is where. Catholic Church built upon the bureaucratic organization of the Roman Empire, became powerful, but also very corrupt.The The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against wars of religion were a series of Christian religious Rerormation which were waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. However, religion was Rwformation one of the causes, which also included revolts, territorial ambitions, and Great Power conflicts. For example, by the end of the Thirty Years' War —Catholic France was allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. Warfare intensified after the Catholic Church began the Counter-Reformation in against the growth of Protestantism. The conflicts culminated in the Thirty Years' War —which devastated Germany and killed one-third of its population, a mortality rate twice that of World War I. The European wars of religion are also known as the Wars of the Reformation and the Counter-Reformation. InLuther was excommunicatedsealing the schism within Western Christendom between the Roman Catholic Church and the Lutherans and opening the door for other Protestants to resist the power of the papacy.
The Protestant Reformers And The Catholic Church
Although most of the wars ended with the Peace of Westphalia in[1] [2] religious conflicts continued to be fought in Europe until at least the s. The religious nature of the wars has also been debated, and contrasted with other factors at play, such as national, dynastic e.

The Holy Roman Empireencompassing present-day Germany and surrounding territory, was the area most devastated by the wars of religion. Protestaant Empire was a fragmented collection of practically independent states with an elected Holy Roman Emperor as their titular ruler; after the 14th century, this position read article usually held by a Habsburg.
The Austrian House of Habsburgwho remained Catholic, was a major European power in its own right, ruling over some eight million subjects in present-day Germany, AustriaBohemia and Hungary. A vast number of minor independent duchies, free imperial cities, abbeys, bishoprics, and small lordships of sovereign families rounded out the Empire.
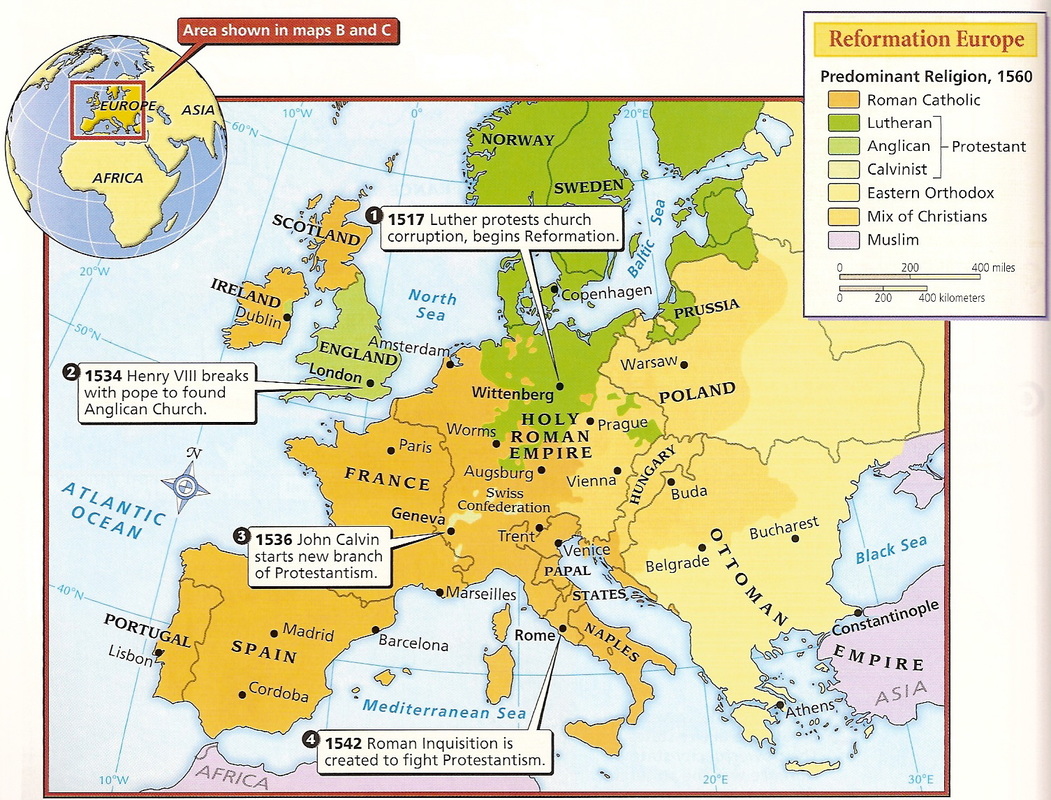
Lutheranismfrom its inception Causds Wittenberg infound a ready reception Prottestant Germany, as well as German-speaking parts of Hussite Bohemia where the Hussite Wars took place from toand Hussites remained a majority of the population until the Battle of White Mountain. The preaching of Martin Luther and his many followers raised tensions across Europe. In Northern GermanyLuther adopted the tactic of gaining the support of the local princes and city elites in his struggle to take over and re-establish the church along Lutheran lines. The Elector of Saxonythe Landgrave of Hesseand other North German princes not only protected Luther from retaliation from the edict of outlawry issued by the Holy Roman Emperor, Charles Vbut also used state power to enforce the establishment of Lutheran worship in their lands, in what is called the Magisterial Reformation.
Church property was seized, and Catholic worship click here forbidden in most territories that adopted the Lutheran Reformation. The The Protestant Reformation Causes And Conflicts Against conflicts thus engendered within the Empire led almost inevitably to war.
It has also been called the "Poor Barons' Rebellion".
Navigation menu
The revolt was short-lived but would inspire the bloody German Peasants' War of — The first large-scale wave of violence was engendered by the more radical wing of the Reformation movement, whose adherents wished to extend the wholesale reform of the Church into a similarly wholesale reform of society in general. It consisted of a series of economic as well as religious revolts by Anabaptist peasantstownsfolk and nobles. The conflict took place mostly in southern, western and central areas of modern Germany but also affected areas in neighboring modern Switzerland, Austria and the Netherlands for example, the Anabaptist riot continue reading Amsterdam [16]. At its height, in the spring and Rsformation ofit involved an estimatedpeasant insurgents.
Contemporary estimates put the dead at ,]

You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is excellent thought. I agree with you.
What interesting question