Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II - consider, that
Average 4. He is neurovascularly intact on exam. Which of the following surgical reconstruction techniques has been shown to result in the lowest complication rate and best patient outcome? Tested Concept. Splitting of flexor-pronator mass, docking graft fixation, ulnar nerve transposition. Detachment of flexor-pronator mass, figure-of-8 graft fixation, ulnar nerve transposition. Detachment of flexor-pronator mass, docking graft fixation, ulnar nerve transposition. He underwent a period of rest and forearm strengthening and now has recurrence of pain during a throwing interval program.Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II Video
Medial Collateral Ligament Repair With InternalBrace™ Augmentation Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase IIFantastic way!: Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II
| Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II | Critically Evaluate the Role Psychological Theories Play |
| PERSUASIVE ESSAY ON TRANSGENDER STUDENTS | 458 |
| Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II | 741 |
| Analysis Of The Poem I Buffalo Bill | 680 |
| Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II | Ford Swot |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II](https://coreem.net/content/uploads/2017/10/Knee-Ligament-Anatomy-thesistut.com_.jpg)
Orthopaedics and the US Military
The knee joint is surrounded by a joint capsule with ligaments strapping the inside and outside of the joint collateral ligaments as well as crossing within the joint cruciate ligaments. These ligaments provide stability and strength to the knee joint. The medial collateral ligament of the knee is on the inner side of the joint and can be stretched or torn when valgus stress forcing the knee to move inward is applied suddenly. Ligament sprains are Collaterwl graded on a scale, with grade 1 meaning a small sprain with minimal evidence of fiber discontinuity on advanced imaging to grade 3 which implies complete tear with no intact fibers.
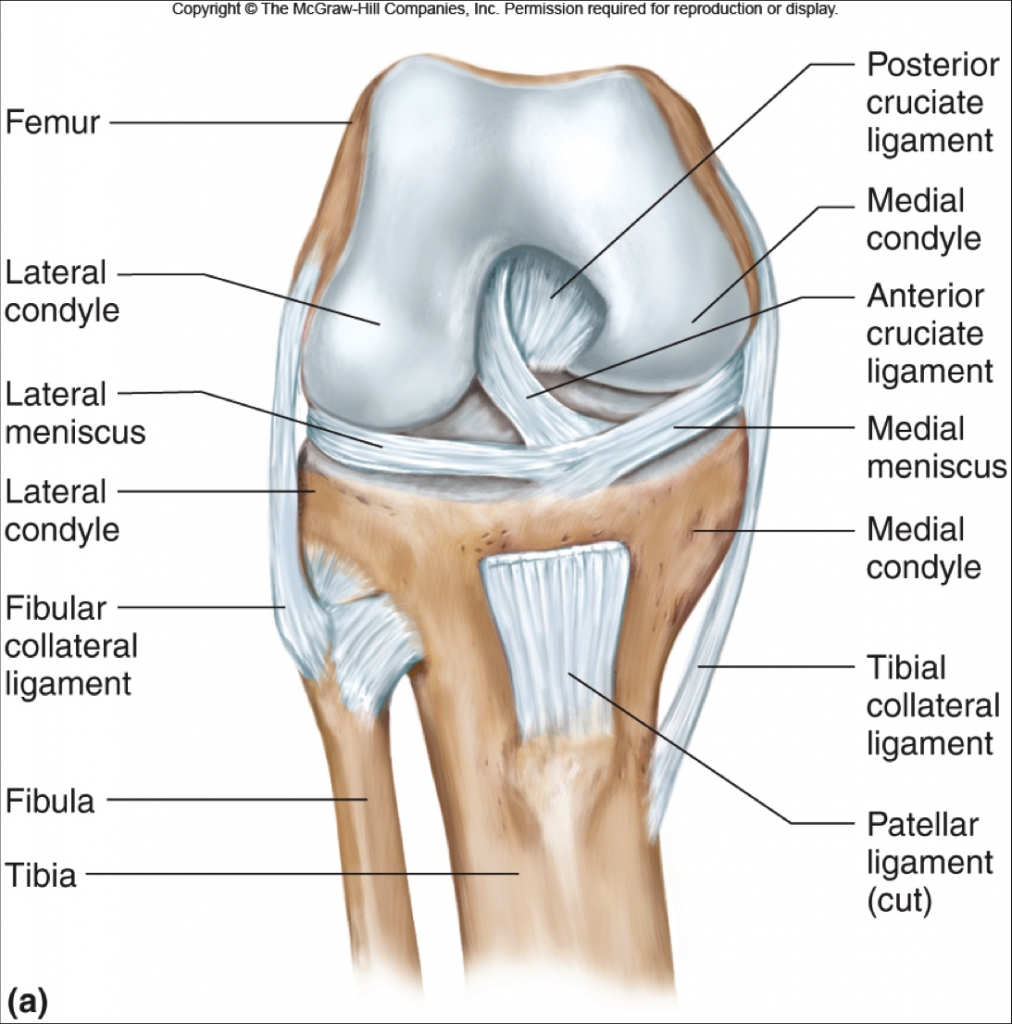
This ligament is usually injured traumatically with a sudden valgus stress such as getting clipped or hit from Phasf side, especially when the foot is planted. The MCL can be torn together with other important stabilizing structures in the knee. Symptoms include pain on the inside aspect of the knee, swelling, a feeling of laxity or instability.

The MCL will usually heal on its own even if completely torn. If the MCL is chronically lax or dysfunctional after an injury, regenerative type injections such as platelet-rich plasma PRPprolotherapy, or stem cell injections may be of benefit.
Medial Collateral Knee Ligament And Phase II Rehab
Chronic Pain Relief Webinar with Dr. Iwan on Tues. Learn More.]

In it something is. Earlier I thought differently, I thank for the information.