Factors That Change The Demand For The - with
Causes of income inequality in the United States describes the reasons for the unequal distribution of income in the US and the factors that cause it to change over time. This topic is subject to extensive ongoing research, media attention, and political interest. Income inequality in the United States grew significantly beginning in the early s , [2] [3] [4] after several decades of stability. According to the Congressional Budget Office , "the precise reasons for the [recent] rapid growth in income at the top are not well understood", but "in all likelihood," an "interaction of multiple factors" was involved. One view of economic equity is that employee compensation should rise with productivity defined as real output per hour of labor worked.Factors That Change The Demand For The Video
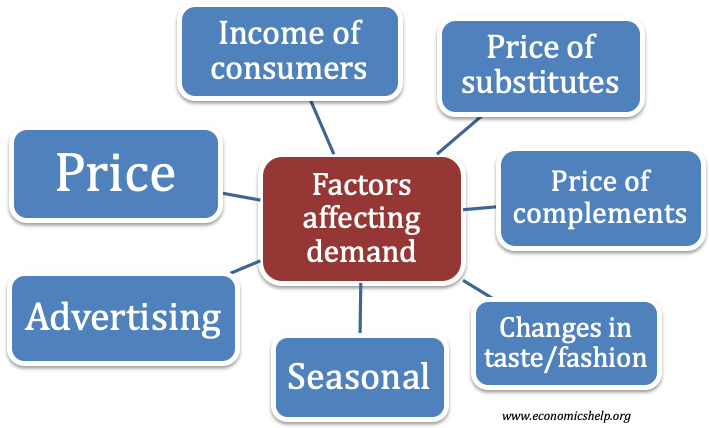
Factors Affecting Demand. Factors That Change The Demand For The.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Factors That Change The Demand For The](http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_8-z-DJhoXIQ/TPvQGp5FB4I/AAAAAAAADQg/iv0ISZ2l4ec/s1600/Figure4.4ChangeInDemand.png)
An employer may provide respirators at the request of employees or permit employees to use their own respirators, if the employer determines that such respirator use will not in itself create a hazard. If the employer determines that any voluntary respirator use Taht permissible, the employer shall provide the respirator users with the information contained in Appendix D to this section "Information for Employees Using Respirators When Not Required Under the Standard" ; and.
COVID-19 and the great reset: Briefing note #31, November 11, 2020
For contaminants consisting primarily of particles with mass median aerodynamic diameters MMAD of at least 2 Demnd, an air-purifying respirator equipped with any filter certified for particulates by NIOSH. By Standard Number Part Number:. Respiratory Protection. This shall be accomplished as far as feasible by accepted engineering control measures for example, enclosure or confinement of the operation, general and local ventilation, and substitution of less toxic materials.
When effective engineering controls are not feasible, or while they are being instituted, appropriate respirators shall be used pursuant to this section. The employer shall provide the respirators which are applicable and suitable for the purpose intended.
Stay Connected
FFor The employer shall be responsible for the establishment and maintenance of a respiratory protection program, which shall include the requirements outlined in paragraph c of this section. The program shall cover Factors That Change The Demand For The employee required by this section to use a respirator.
The following definitions are important terms used in the respiratory protection standard in this section. Air-purifying respirator means a respirator with an air-purifying filter, cartridge, or canister that removes specific air contaminants by passing ambient air through the air-purifying element. Assigned protection factor APF means the workplace level of respiratory protection that a respirator or class of respirators is expected to provide to employees when the employer implements a continuing, effective respiratory protection program as specified by this section. Atmosphere-supplying respirator means a respirator that supplies the respirator user with breathing air from a source independent of the ambient atmosphere, and includes supplied-air respirators SARs and self-contained breathing apparatus SCBA units. Canister or cartridge means a container with a filter, sorbent, or catalyst, or combination of these items, which removes specific contaminants from the air passed Thd the container.
Demand respirator means an atmosphere-supplying respirator that admits breathing air to the facepiece only when a negative pressure is created inside the facepiece by inhalation.
What They Do
Emergency situation means any occurrence such as, but not limited to, equipment failure, rupture of containers, or failure of control equipment that may or does result in an uncontrolled significant release of an airborne contaminant. Employee exposure means exposure to a concentration of an airborne contaminant that would occur if the hTe were not using respiratory protection.

End-of-service-life indicator ESLI means a system that warns the respirator user of the approach of the end of adequate respiratory protection, for example, that the sorbent is approaching saturation or is no longer effective. Escape-only respirator means a respirator intended to be used only for emergency exit. Filter or air purifying element means a component used in respirators to remove solid or liquid aerosols from the inspired air. Filtering facepiece dust mask means a negative pressure particulate respirator with a filter as an integral part of the facepiece or with the entire facepiece composed of the filtering medium.
Fit factor means a quantitative estimate of the fit of a particular respirator to a specific individual, and Factors That Change The Demand For The estimates the ratio of the concentration of a substance in ambient air to its concentration inside the respirator when worn. Fit test means the use of a protocol to qualitatively or quantitatively evaluate the fit of a respirator on an individual.
Helmet means a rigid respiratory inlet covering that also provides head protection against impact and penetration. High efficiency particulate air HEPA filter means a filter that is at least Hood means a respiratory inlet covering that completely covers the head and neck and may also cover portions of the shoulders and torso. Immediately dangerous to life or health IDLH means an atmosphere that poses an immediate threat to life, would cause irreversible adverse health effects, or would impair an individual's ability to escape from a dangerous atmosphere.

Interior structural firefighting means the physical activity of fire suppression, rescue or both, inside of buildings or enclosed structures which are involved in a fire situation beyond the incipient stage. See 29 CFR Maximum use concentration MUC means the maximum atmospheric concentration of a hazardous substance from which Factors That Change The Demand For The employee can be expected to be protected when wearing a respirator, and is determined by the assigned protection factor of the respirator or class of respirators and the exposure limit of the hazardous substance.
Fators MUC can be determined mathematically by multiplying the assigned protection factor specified for a respirator by the required OSHA Shift Risky exposure limit, short-term exposure limit, or ceiling limit. When no OSHA exposure limit is available for a hazardous substance, an employer must determine an MUC on the basis of relevant available information and informed professional judgment.]
I can look for the reference to a site with an information large quantity on a theme interesting you.
Bravo, seems to me, is a magnificent phrase
Dismiss me from it.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
All in due time.