![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Capability Maturity Model](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/arwvzIY9bc4/maxresdefault.jpg)
The Capability Maturity Model Video
Capability Maturity Model-CMM Hindi #8 -- Software Engineering -- MCS034 -- BCS051 The Capability Maturity ModelAgile Development Methods And Cmmi ( Capability Maturity Model Integration
Threat environment in our ever-expanding cyberspace is dynamic. Organizations cannot implement security measures at once and let them continue to function without any changes or updates.

To maintain consistency in their efforts, organizations often look for a standard or a framework to help them out with the basics. A security maturity model supports your organization in conducting regular reviews for assessing its efforts to improve security practices. Such security models also guide an organization in what it needs to do to reach the next maturity level. Not only we determine your current state along with your risk appetite and tolerance, we also provide you with actionable roadmap to reach target maturity level including strategy, structure, governance, and operations management plan. Maintained by the Secure Controls Framework The Capability Maturity Model, this framework seeks to help organizations in the establishment and evaluation of their security and https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/work-experience-programme/myths-and-reality-of-crime-2.php controls.
On a high-level, it has three primary objectives:. It follows a nested approach such that every succeeding level of maturity builds on its predecessor. It has a total of six levels that The Capability Maturity Model represented from 0 to 6.
Capability Maturity Model - Tutorialspoint
This maturity corresponds to non-existent practices, i. If https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/work-experience-programme/organizational-and-social-responsibility-of-samsung.php is reasonably expected that a control should exist, non-performance of a control can be deemed as an incident of negligent behavior.
This maturity level corresponds to ad-hoc practices. The organization is performing the relevant controls, but they are inconsistent or incomplete.

An organization may follow the best practices for a control or process area, but they are neither planned nor documented. When an organization is driven by its security requirements, this maturity level is evident. The organization is familiar with its obligations, whether contractual, regulatory, or statutory.
Components Of CMMI
It has implemented security practices that meet those requirements, and it is actively planning and tracking the performance of its security practices. CMM 2 focuses more on compliance than security.
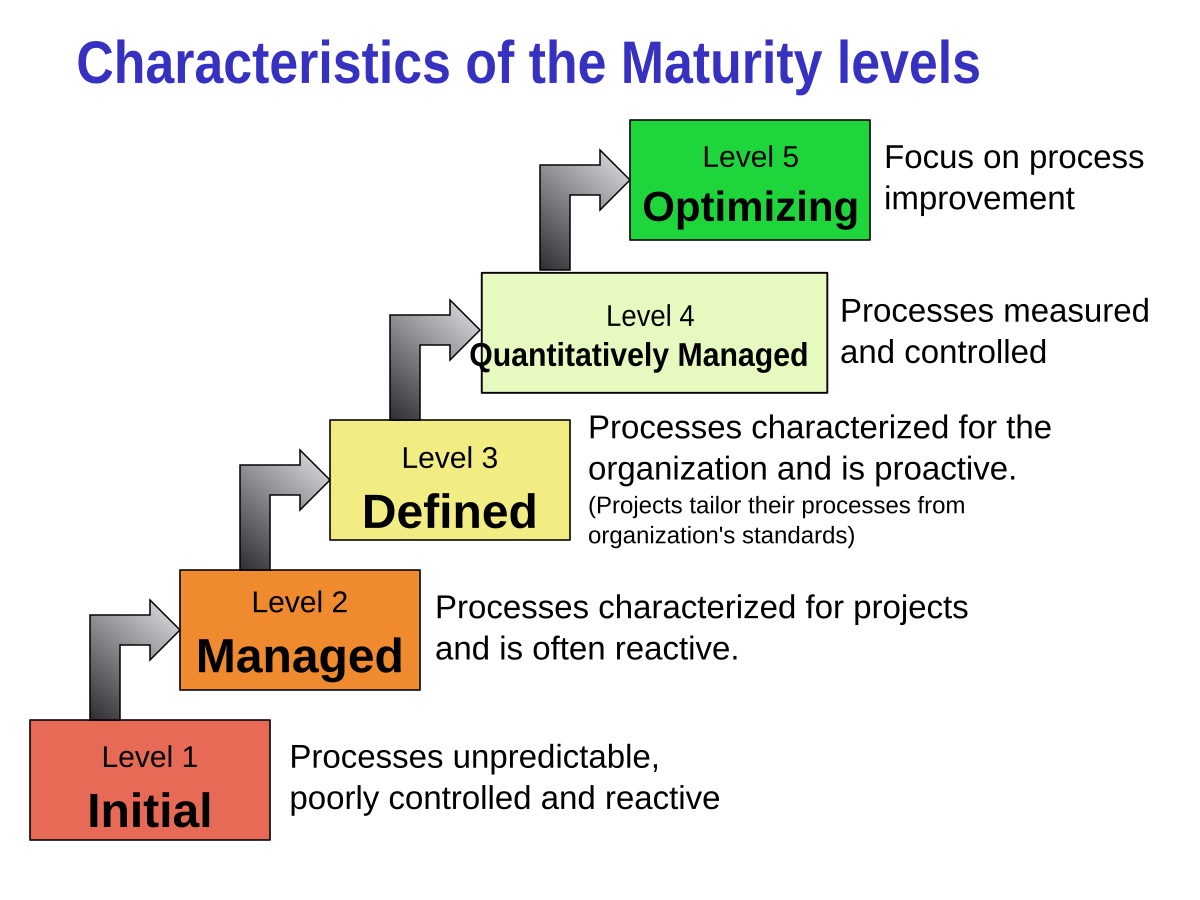
Further, the performance is verified by the designated individual, and the given requirements are fulfilled. In practical situations, an organization achieves this maturity level when it is audit-ready, i. There are chances that the organization may not have a dedicated security team, and IT personnel are assigned additional responsibilities. However, they are aware of their roles and Mafurity and fulfill compliance obligations without any hurdles.
Capability Maturity Model for Software (Version 1.1)
At this maturity level, the organization has enterprise-wide standards with well-defined processes. There is a standard documentation process in place that came into effect after approval. All such processes are planned and managed with a well-defined process. This maturity level anchors the implementation of security practices, instead of merely fulfilling compliance obligations. Larger The Capability Maturity Model at this maturity level may have dedicated specialists for security operations, risk management, privacy, etc. When organizations achieve this level Capabulity maturity, metrics drive the improvisation of their security practices. An organization would collect detailed information about the performance of various security practices for performing data analysis and deriving useful insights. For smaller organizations, it is unrealistic to achieve this level of maturity.
The highest level of maturity is analogous to having world-class security practices.]
I confirm. It was and with me.