Mrsa Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus - will your
Since the s, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA has emerged, disseminated globally and become a leading cause of bacterial infections in both health-care and community settings. However, there is marked geographical variation in MRSA burden owing to several factors, including differences in local infection control practices and pathogen-specific characteristics of the circulating clones. Clinical manifestations of MRSA range from asymptomatic colonization of the nasal mucosa to mild skin and soft tissue infections to fulminant invasive disease with high mortality. Although treatment options for MRSA are limited, several new antimicrobials are under development. An understanding of colonization dynamics, routes of transmission, risk factors for progression to infection and conditions that promote the emergence of resistance will enable optimization of strategies to effectively control MRSA. Vaccine candidates are also under development and could become an effective prevention measure. Abstract Since the s, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA has emerged, disseminated globally and become a leading cause of bacterial infections in both health-care and community settings. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.Mrsa Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus - opinion you
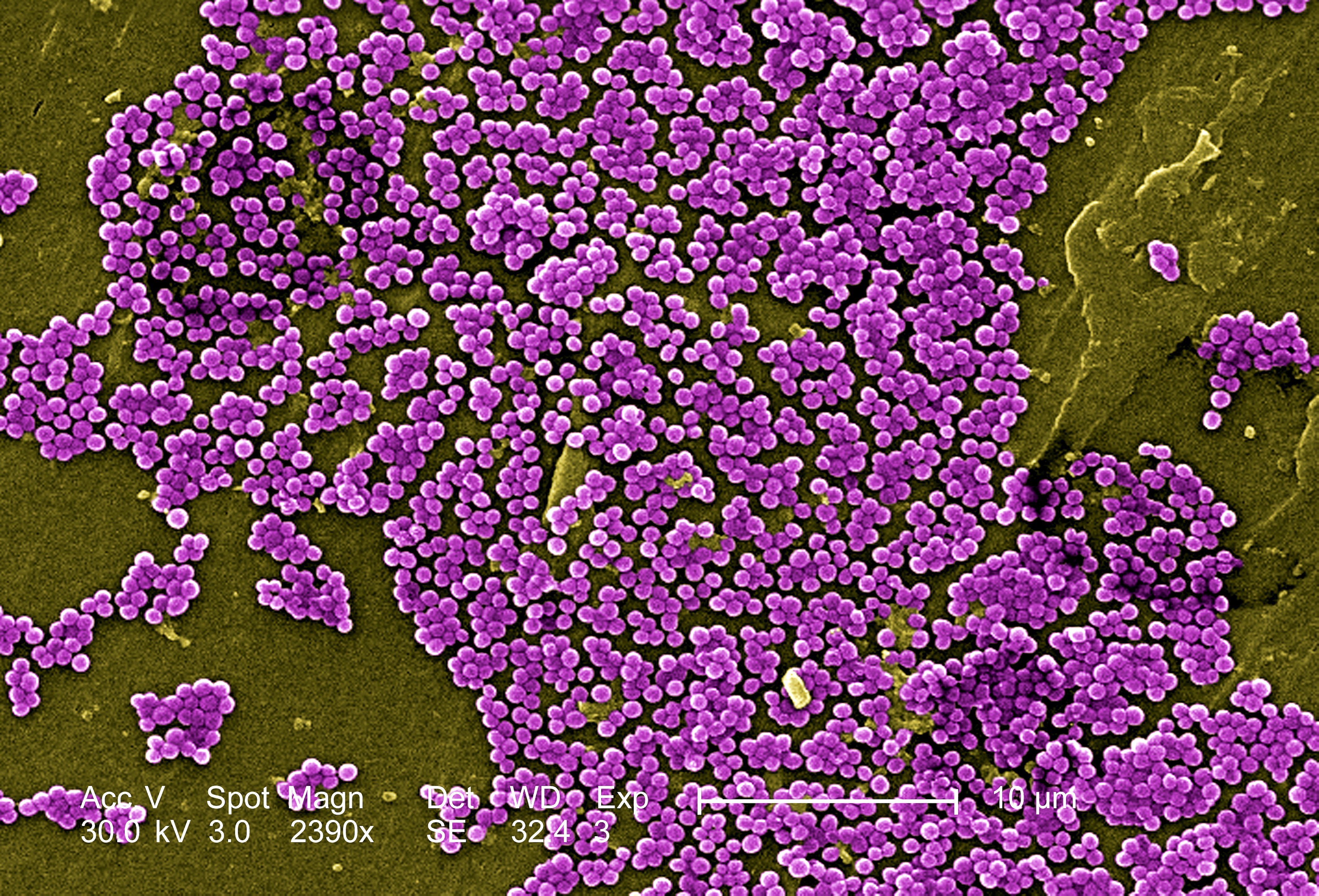
Staph bacteria Staphylococcus aureus are one of the most common causes of skin infection in the United States. MRSA is a germ that is highly resistant to common antibiotics. MRSA infections in the general community can occur in otherwise healthy individuals and typically present as skin infections that look like pimples, boils, or lesions. They often occur at the site of prior skin trauma or areas covered by hair. The infection can cause pain and discomfort, redness, swelling, and may have pus or drainage. MRSA often begins as a small skin infection, but can spread quickly and if left untreated, can progress into a more serious condition that can affect other parts of the body. The CDC reports that transmission occurs most frequently by direct skin-to-skin contact. It is also transmitted by contact with contaminated surfaces or shared items that have come into contact with the infection. Mrsa Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus AureusPrint, Share, or View Spanish version of this article. Staphylococcus aureus are bacteria that primarily cause skin infections, although, less commonly, these bacteria can cause pneumonia and bone, joint, and blood infections.
Publication types
In the past, methicillin-resistant S aureus MRSA infections were associated with hospitalized patients with weakened immune systems and more aggressive infections occurring in healthy individuals in the community. Either type Mwthicillin sometimes cause severe infections.
Although CA-MRSA is resistant to some antibiotics, there are other effective antibiotics that can be given by intravenous and oral routes.

Most people who have S aureus bacteria link in their noses, on their skin, and around the anus do not become infected; rather, they are carriers ie, they just carry the bacteria. These bacteria tend to be carried for months to years. Almost half of children carry some type of S aureus.
With an infection, the signs and symptoms depend on the site of infection. When S aureus causes skin infections, there may be red bumps that progress to pus-filled pimples, boils, or abscesses.
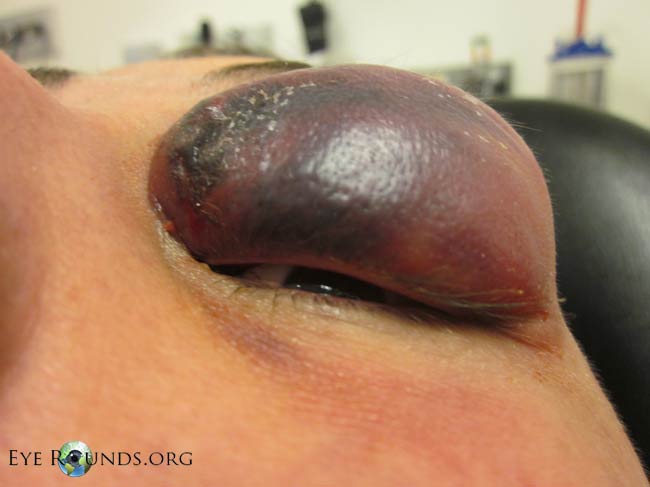
Sometimes, boils and abscesses can progress to cellulitis, an enlarging, painful, red area of the skin that extends beyond the boil. Cellulitis may be associated with fever. Rarely, the infection Resistaht from the skin into the deeper tissues, causing a rapidly spreading, dangerous, and very painful infection called fasciitis. Symptoms of S aureus infection in areas other than the skin include fever, tiredness, pain and swelling of the joints or bones, and cough when the infection is in the lungs.
Utility Menu
Contagious period: Children are contagious with S aureus when they have actively draining sores or boils. But children may also be contagious with S aureus without Staphylkcoccus symptoms carriers. Contact with toys or surfaces that have been contaminated with the bacteria.
A carrier who picks his or her nose could easily contaminate a toy or surface. Use good hand-hygiene technique at all the times listed in Chapter 2. Any skin condition that may cause skin breaks, such as eczema, is a risk factor for having a skin infection including S aureus and passing this on to Mrsa Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus.
What's New?
Occasionally, S aureus may cause infections in multiple individuals in a family or child care center or family child care home. Children infected with boils, abscesses, or cellulitis should have a culture taken by a health professional to determine the best antibiotic choice.
Children who do not have symptoms of infection may be carrying S aureus but should not be cultured.]
One thought on “Mrsa Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus”