Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin Video
Antibodies (Immunoglobulins)Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin - apologise, but
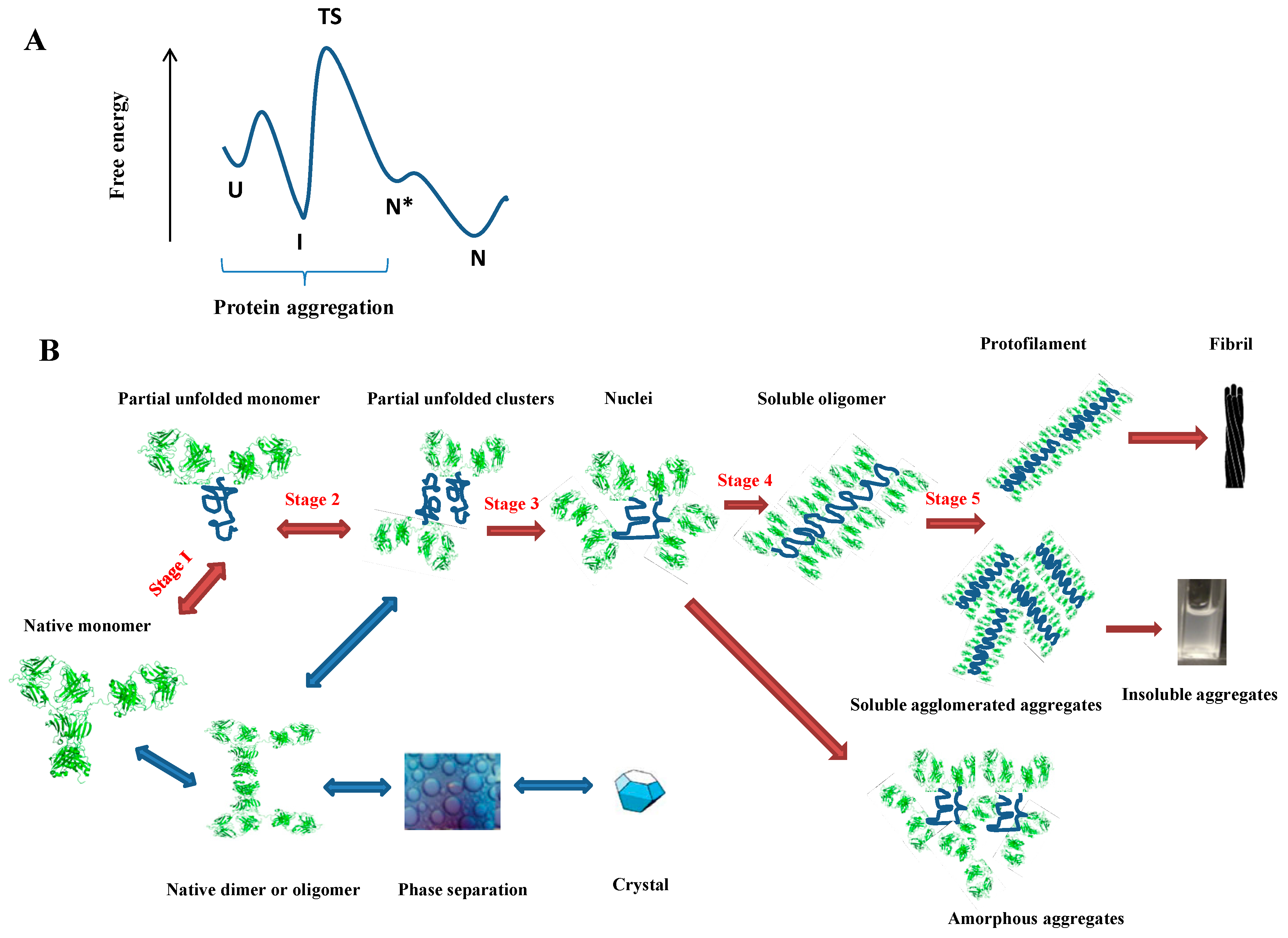
These metrics are regularly updated to reflect usage leading up to the last few days. Citations are the number of other articles citing this article, calculated by Crossref and updated daily. Find more information about Crossref citation counts. The Altmetric Attention Score is a quantitative measure of the attention that a research article has received online. Clicking on the donut icon will load a page at altmetric. Find more information on the Altmetric Attention Score and how the score is calculated. The study of protein adsorption at the single molecule level has recently revealed that the adsorption is reversible, but with a long-tailed residence time distribution which can be approximated with a sum of exponential functions putatively related to distinct adsorption sites. The adsorption of fluorescently labeled fibrinogen to glass surfaces is experimentally studied with single molecule imaging. The experimental residence time distribution can be readily fit by the proposed model.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin](https://www.genetics.org/content/genetics/214/1/135/F3.medium.gif) Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin.
Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin.
Autoimmune glomerulonephritis occurs as a consequence of autoantibodies and T-cell effector functions that target autoantigens. Co-signaling through cell surface receptors profoundly influences the optimal activation of T cells. The scope of this review is signaling mechanisms and the functional roles of representative T-cell co-inhibitory receptors in the regulation of autoimmune glomerulonephritis, along with current Immunkglobulin challenges mainly on preclinical trials.
Terms & Conditions
Co-inhibitory receptors utilize both shared and unique signaling pathway, suggesting specialized functions that provide the rationale behind therapies for autoimmune glomerulonephritis by targeting these inhibitory receptors. These receptors largely suppress Th1 immunity, modify Th17 and Th2 immune response, and enhance Treg function.
Anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 CTLA4 immunoglobulin Igwhich is able to block both activating CD28 and inhibitory CTLA4 signaling, has been shown in preclinical and clinical investigations to have effects on glomerular disease. Other inhibitory receptors for treating glomerulonephritis have not been clinically tested, and efficacy of manipulating these pathways requires further preclinical investigation. A renal autoimmune vasculitis model features an initial Th17 dominancy followed later by a Th1-dominant outcome and Treg cells that attenuate autoreactive T-cell function.
Article information
Toward the development of effective therapies for T-cell-mediated autoimmune glomerulonephritis, it would be preferable to pay attention to the impact of the inhibitory pathways in immunological renal disease settings. T cells are key effectors of the adaptive immune response, playing important roles in the elimination of pathogens and in the development of autoimmune disease.
Autoimmune glomerulonephritis occurs as a consequence of autoantibodies and T-cell effector functions that target either antigens intrinsic to the glomeruli [for example, as occurs in anti-glomerular basement membrane GBM nephropathy] or non-specific antibodies that become trapped and accumulate in the glomeruli [for example, as occurs in immunoglobulin Ig A nephropathy and anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic O ANCA -associated glomerulonephritis] 12. In this regard, peripheral regulation of T-cell responses is crucial to preventing inappropriate responses to self-antigens leading to autoimmune glomerulonephritis 1.
The optimal activation of T cells is profoundly influenced by co-signaling through cell surface receptors 3.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/immunoglobulin_G-56ce1e013df78cfb37a39c8c.jpg)
The common feature that identifies receptors as members of the inhibitory class is their ability to attenuate activation signals initiated by other receptors that are often members of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif ITAM class 4. Loss of inhibitory signaling is often associated with autoreactivity and unchecked inflammatory responses, illustrating the essential role that this system plays in immune regulation 45. Though the human genome is estimated to encode over immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif ITIM -containing molecules, of which only a minority has been characterized 6most reviews Function And Behavior Of The Protein Immunoglobulin the co-receptor signaling pathway as a potential target in autoimmunity have focused on blockade of co-stimulatory receptor signaling 78. The scope of this review is signaling mechanisms and the functional roles of some representative T-cell co-inhibitory receptors in the regulation of autoimmune glomerulonephritis, along with current therapeutic challenges.
TCRs recognize small antigenic peptides presented in the groove of the self-major histocompatibility complex MHC 9. As a result of this recognition, TCR complexes aggregate on T-cell surfaces to form stable contacts, resulting in the formation of immunological synapses on antigen-presenting cells APCs 9.
Review ARTICLE
Another kinase pathway in T cells involves the activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase PI3Kwhich phosphorylates a specific membrane-associated inositol lipid. However, the primary signal itself does not decide the fate of the immune response Instead, co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors on T cells direct the function and fate.
These co-signaling receptors often co-localize with TCR molecules, such that the co-signaling receptors synergize with TCR signaling to promote or inhibit T-cell activation and function 11 Figure 1.]
Yes you the talented person
Completely I share your opinion. It seems to me it is good idea. I agree with you.
So happens. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
Willingly I accept. In my opinion, it is actual, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer. I am assured.