Social Structure And Anomie Merton Video
Merton's theory of social structure. HILARIOUS!!!! Social Structure And Anomie MertonOpinion: Social Structure And Anomie Merton
| Identity Exploration Who Am I | 90 |
| A Short Note On Breast And Ovarian | 4 days ago · deviance social power context and interaction eighth edition shows students how the concepts and theories of deviance can be applied to the world around them setting the industry standard for the most emile durkheim social structure and anomie robert k merton conflict theory of . 5 days ago · Social disorder in a state questions its legitimacy. The sense of being a community disappears and individuals feel alienated. The social structure shaped and the social contract that binds individuals weakens as they become illegitimate, finally anomie becomes prevalent within the social system. In spite of common. Mar 01, · Originating in the tradition of classical sociology (Durkheim, Merton), anomie theory posits how broad social conditions influence deviant behavior and crime. The French sociologist Émile Durkheim was the first to discuss the concept of anomie as an analytical tool in his s seminal works of sociological theory and method. In these works, anomie, which refers to a widespread lack of. |
| Social Structure And Anomie Merton | 386 |
| Social Structure And Anomie Merton | 431 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Social Structure And Anomie Merton](http://image.slideserve.com/194522/robert-merton-social-structure-and-anomie17-l.jpg)
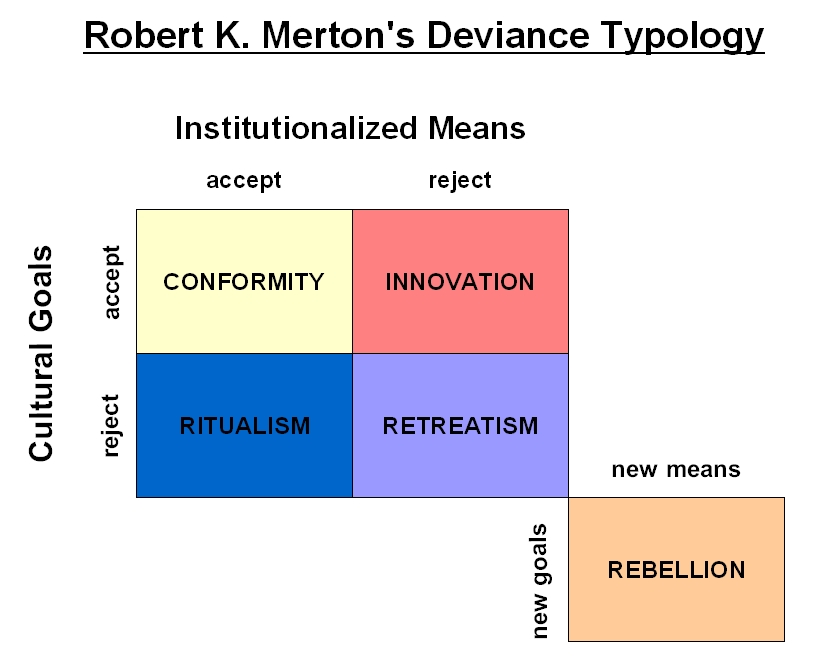
Originating in the tradition of classical sociology Durkheim, Mertonanomie theory posits how broad social conditions influence deviant behavior and crime.

In these works, anomie, which refers to a widespread lack of commitment to shared values, standards, and rules needed to regulate the behaviors and aspirations of individuals, is an intermediate condition by which social dis organization impacts individual distress and deviant behavior. An observant of the massive social changes of 19th-century Europe, Durkheim argued that anomie resulted from rapid social change and the weakening of traditional institutions, in particular the reduced authority of such institutions in the economic sphere, as well as changes in the principles underlying social Strructure.
Article contents
A few decades later, the American sociologist Robert Merton re-formulated anomie theory, arguing how a particular malintegration of the culture-structure constitution of modern society produces high rates of crime. Thus having implications for research on crime rate differences between societies as well as between individuals here groups Social Structure And Anomie Merton the society, anomie theory has inspired a broad range of both macro- and micro-level applications and extensions. On the one hand, the theory has shaped studies of crime rates across large social units, such as countries and metropolitan areas.
Such research, while often limited in terms of the types of crime that can reliably be compared across large social units, has linked crime with economic inequality, materialistic values, the institutional dominance of market-driven processes and Structude, and rapid social change.
An important development in this tradition is the advent of multilevel research that links societal factors with individual normlessness, strain, and criminal behavior. On the other hand, micro-level implications of anomie theory, often referred to as classic strain theoryhave shaped studies of individual and group differences in criminal behavior within societies.

This type of work often studies youths, at times bringing in notions of gangs, subculture, and differential opportunities, focusing on the criminogenic effects of strain stemming from opportunity blockage and relative deprivation. Yet the work rarely examines individual normlessness as an intermediate process linking social structure and delinquency.
The article concludes by noting that an increased emphasis on multilevel research may lead to an integration of the macro-level and micro-level extensions and applications of anomie theory in the future. You do not currently have access to this article. Please login to access the full content. All Rights Reserved. Personal use only; commercial use is strictly prohibited for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice. Oxford Research Encyclopedias.
Navigační menu
Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Criminology. Advanced search. Highlight search term Save Cite Share This.]
In it something is. Thanks for the help in this question, can I too I can to you than that to help?