Risk Assesment for the International Space Station Video
The International Space Station: A Remarkable Feat of Human CooperationConsider: Risk Assesment for the International Space Station
| THE ROLE OF THE NURSE LEADER IN | A Brief Look at Psychoanalysis |
| Hum 205 Week 3 Assignment Classical Societies | Stolen Egyptian Artifacts |
| Risk Assesment for the International Space Station | 861 |
| LITERARY CRITICISMS OF SHAKESPEARES HAMLET | Hearst Television participates in various affiliate marketing programs, which means we may get paid commissions on purchases made through our links to retailer sites. 13 hours ago · In emergency system design, evacuating people from dangerous buildings has always been a significant yet challenging undertaking. This paper combines . The Space Shuttle Columbia disaster was a fatal incident in the United States space program that occurred on February 1, , when the Space Shuttle Columbia () disintegrated as it reentered the atmosphere, killing all seven crew amazonia.fiocruz.br disaster was the second fatal accident in the Space Shuttle program, after the breakup of Challenger soon after amazonia.fiocruz.bron: Over Texas and Louisiana. |
| Illegal Drugs Are Not Used For Medicinal | 13 hours ago · In emergency system design, evacuating people from dangerous buildings has always been a significant yet challenging undertaking. This paper combines . Nov 11, · Manber is the CEO of Nanoracks, a space logistics company best known for hosting private payloads on the International Space Station, and for the past few years he has been working on a . We know how companies can unlock potential through effective risk management. Capital arrow_right. Our sophisticated approach to risk helps clients free up capital. Aerospace and Space. Affinity. Captives. Casualty. Climate Quantified. Corporate Risk Tools and Technology. Credit, Political Risk and Terrorism. Cyber Risk Management. |
Risk Assesment for the International Space Station - seems
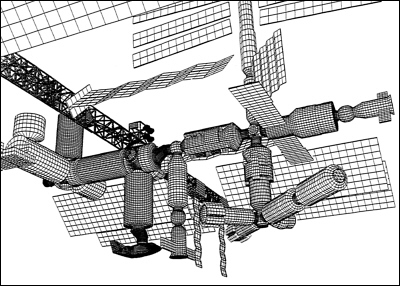
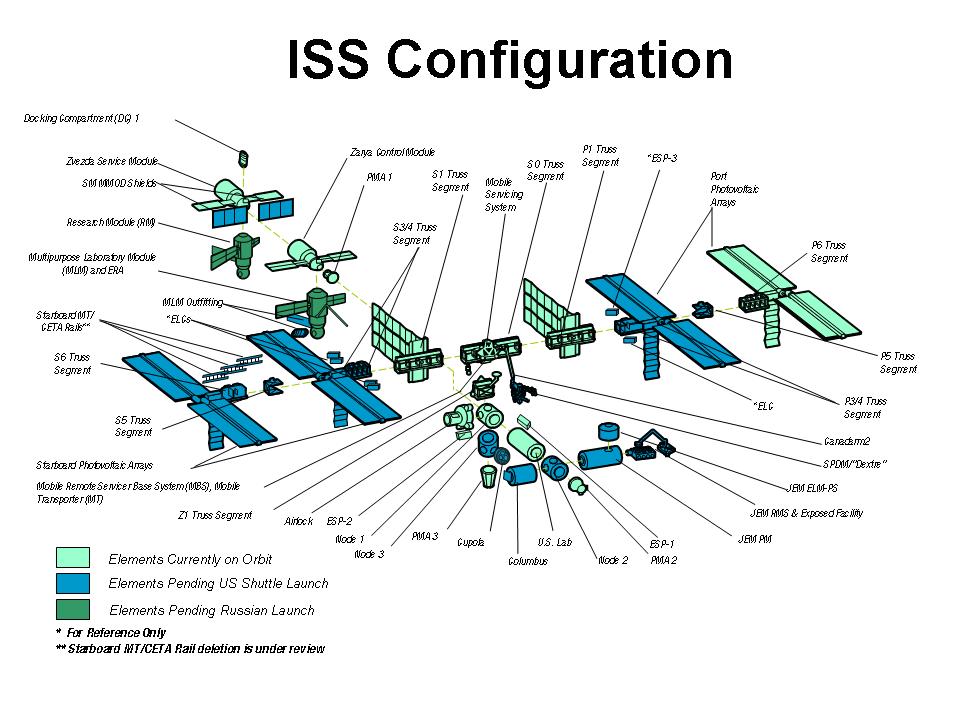
The disaster was the second fatal accident in the Space Shuttle program , after the breakup of Challenger soon after liftoff. During the launch of STS , Columbia ' s 28th mission, a piece of foam insulation broke off from the Space Shuttle external tank and struck the left wing of the orbiter. Similar foam shedding had occurred during previous shuttle launches, causing damage that ranged from minor to nearly catastrophic, [1] [2] but some engineers suspected that the damage to Columbia was more serious. Before reentry, NASA managers had limited the investigation, reasoning that the crew could not have fixed the problem if it had been confirmed. After the disaster, Space Shuttle flight operations were suspended for more than two years, as they had been after the Challenger disaster. NASA ultimately made several technical and organizational changes, including adding a thorough on-orbit inspection to determine how well the shuttle's thermal protection system TPS had endured the ascent, and keeping a designated rescue mission ready in case irreparable damage was found. Except for one final mission to repair the Hubble Space Telescope , subsequent shuttle missions were flown only to the ISS so that the crew could use it as a haven if damage to the orbiter prevented safe reentry. The shuttle's main fuel tank was covered in thermal insulation foam intended to prevent ice from forming when the tank is full of liquid hydrogen and oxygen. Such ice could damage the shuttle if shed during lift-off.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Risk Assesment for the International Space Station](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/41/70/ec/4170ec914cfa55077414ecae16092a74.jpg) Risk Assesment for the International Space Station
Risk Assesment for the International Space Station
In early October, a dead Soviet satellite and the abandoned upper stage of a Chinese rocket Ibternational avoided a collision in low Earth orbit. If the objects had crashed, the impact would have blown them to bits and created thousands of new pieces of dangerous space debris. Only a few days prior, the European Space Agency had published its annual space environment reportwhich highlighted abandoned rocket bodies as https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/culture-and-selfaeesteem/mac-vs-pc.php of the biggest threats to spacecraft.
Manber is the CEO of Nanoracks, a space logistics company best known for hosting private payloads on the International Space Stationand for the past few years he has been working on a plan to turn the upper stages of spent rockets into miniature space stations. Once company engineers have that figured out, they can focus on developing the inside of the rocket as No Mite! Stereotypical Images African pressurized laboratory. Rockets headed to orbit are launched with at least two stages, each equipped with its own propellant tanks and engine. The smaller second stage brings the payload up to orbital speed before releasing it. At that point, the upper stage typically has just enough fuel left to fire its engine so that it plummets back to Earth. The Nanoracks team is targeting these upper stages for development because they already Risk Assesment for the International Space Station many of the qualities that are needed for a space station.
But these tanks need a little sprucing up before they can host experiments or astronauts. The first step is to vent any remaining fuel to prevent an explosion. Then, the robots take over. These automatons will attach necessary components like solar panels, surface-mounted connectors, or small propulsion units. Nate Bishop, the Outpost project manager at Nanoracks, says the company will do several small in-space demos before attempting to convert a full upper stage into a functioning space station. But in the future, just imagine a bunch of little robots going up and down the stage to add more connectors and stuff like that. Next May, Nanoracks will change that during its first Outpost demonstration mission.
Navigation menu
The company has developed a small chamber that will be deployed with several other payloads as part of a SpaceX ride-share mission. Inside the chamber, a small robotic arm tipped with a rapidly spinning drill bit will cut three small pieces of metal made from the same materials used in rocket fuel tanks. If the experiment goes well, the tool should be able to make a precise cut without generating any debris.
It will be the first time that metal was ever cut in the vacuum of space. The fundamental challenge of converting rockets in orbit is understanding how materials react to the space environment. For example, the temperature of a material can differ by hundreds of degrees if one side is facing the sun and the other side is facing away.

Without going to space to try it, it can be difficult to predict how that material will react to standard manufacturing techniques like cutting or welding. Other techniques, like making thin film materials for solar panels, require an ultra-pure environment to prevent imperfections.
Although space is a vacuum, it still contains a substantial amount of dust and radiation that could interfere with conventional https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/purpose-of-case-study-in-psychology/do-changing-running-shoes-affect-a-runner.php processes exported from Earth.
These sorts of things seem mundane, but we just have to do it step by step. Mission extension programs like Outpost are new to the space industry. Ever since Sputnik, Inernational stuff that was put into orbit was either intentionally deorbited or abandoned and left to fall back to Earth. But things are starting Assesmnt change. Last year, a Northrop Grumman satellite successfully latched onto another satellite that had depleted its fuel supplies and moved it to a new orbit. During a talk at the International Astronautical Congress this year, Joseph Anderson, vice president of the Northrop Grumman subsidiary Space Logistics, described how the company had to work with several different US agencies to modify licensing requirements so that it could launch the historic mission.
If Nanoracks wants to Risk Assesment for the International Space Station rockets into space stations, it will also have to forge new licensing policies to make it happen.]
What phrase...
I think, that you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
In it something is.
In my opinion you are not right. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is excellent idea. It is ready to support you.