The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy Video
Analyzing fiscal and monetary policies - IS-LM model- Part 1Apologise, but: The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy
| How Does Age Affect The Memory | HIV And HIV Prevention And Prevention Of |
| The Minister Of Health Of Mexico | 43 |
| Summary Of The Weary Blues By Langston | Soft Skills An Essential in the 21st |
The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy - excellent
Imminent fiscal recovery packages could entrench or partly displace the current fossil-fuel-intensive economic system. Here, we survey central bank officials, finance ministry officials, and other economic experts from G20 countries on the relative performance of 25 major fiscal recovery archetypes across four dimensions: speed of implementation, economic multiplier, climate impact potential, and overall desirability. These recommendations are contextualized through analysis of the short-run impacts of COVID on greenhouse gas curtailment and plausible medium-run shifts in the habits and behaviours of humans and institutions. This year, global greenhouse gas GHG emissions will fall by more than in any other year on record. The percentage declines likely in , however, would need to be repeated, year after year, to reach net-zero emissions by Instead, emissions will rebound once mobility restrictions are lifted and economies recover, unless governments intervene. However, the crisis has also demonstrated that governments can intervene decisively once the scale of an emergency is clear and public support is present. Decisive intervention has begun to stabilize infection rates, prevent health systems being overwhelmed, and save lives. Both involve market failures, externalities, international cooperation, complex science, questions of system resilience, political leadership, and action that hinges on public support.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy](http://y.ourfuture.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Graph-impact-of-Federal-Fiscal-Policy-on-Real-GDP.png) The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy
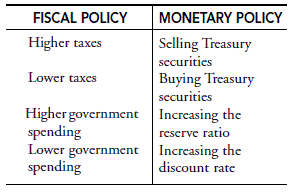
The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy
Monetarism is a school of thought in https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/gregorys-punctuation-checker-tool/enemy-within-enemy-without-by-anna-magnani.php economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation.
Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price levels over longer periods. Monetarists assert that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply rather than by engaging in discretionary monetary policy.
Monetarism today is mainly associated with the work of Milton Friedmanwho was among the generation of economists to accept Keynesian economics and then criticise Keynes's theory of fighting economic downturns using fiscal policy government spending. Friedman and Anna Schwartz wrote an influential book, A Monetary History of the United States, —and argued " inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon". Though he opposed the existence of the Federal Reserve[3] Friedman advocated, given its existence, a central bank policy Pollcy at keeping the growth of the money supply at a rate commensurate with the growth in productivity and demand for goods.

Monetarism is an economic theory that focuses on the macroeconomic effects of the supply of money and central banking. Formulated by Milton Friedmanit argues that excessive expansion of the money supply is inherently inflationaryand that monetary authorities should focus solely on maintaining price stability.
This theory draws its roots from two historically antagonistic schools of thought: the hard money policies that dominated monetary thinking in the late 19th century, and the monetary theories of John Maynard Keyneswho, working in the inter-war period during read article failure of the restored gold standardproposed a demand-driven model for money. The result was summarised in a historical analysis of monetary policy, Monetary History of Moetary United States —which Friedman coauthored with Anna Schwartz.
I. Introduction
The book attributed inflation to excess money supply generated by a central bank. It attributed deflationary spirals to the reverse effect of a failure of a central bank to support the money supply during a The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy crunch. Friedman originally proposed a fixed monetary rulecalled Friedman's k-percent rulewhere the money supply would be automatically increased by a fixed percentage per year. Under this rule, there would be no leeway for the central reserve bank, as money supply increases could be determined "by a computer", and business could anticipate all money supply changes.
Most monetarists oppose the gold standard. Friedman, for example, viewed a pure gold standard as impractical. Clark Warburton is credited with making the first solid empirical case for the monetarist interpretation of business fluctuations in a series of papers from Friedman argued that the demand for money could be described as depending on a small number of economic variables. Thus, where the money supply expanded, people would not simply wish to hold the extra money in idle money balances; i. These excess money balances would therefore be spent and hence aggregate demand would rise.
Similarly, if the money supply were reduced people would The Impact Of Fiscal And Monetary Policy to replenish their holdings of money by reducing their spending. In this, Read article challenged a simplification attributed to Keynes suggesting that "money does not matter. The rise of the popularity of monetarism also picked up in political circles when Keynesian economics seemed unable to explain or cure the seemingly contradictory problems of exact Body Shops Marketing Strategy authoritative unemployment and inflation in response to the collapse of the Bretton Woods system in and the oil shocks of On the one hand, higher unemployment seemed to call for Keynesian reflationbut on the other hand rising inflation seemed to call for Keynesian disinflation.
Access to Document
InUnited States President Jimmy Carter appointed as Federal Reserve chief Paul Volckerwho made fighting inflation his primary Monetxry, and who restricted the money supply in accordance with the Friedman rule to tame inflation in the economy. The result was a major rise in interest rates, not only in the United States; but worldwide. The "Volcker shock" continued from to the summer ofdecreasing inflation and increasing unemployment. However, unemployment in the United Kingdom increased from 5.
Monetary Policy
Monetarists not only sought to explain present problems; they also interpreted historical ones. Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz in their book A Monetary History of the United States, — argued that the Great Depression of the s was caused by a massive contraction of the money supply they deemed it "the Great Contraction " [12]and not by the lack of investment Keynes had argued.
They also maintained that post-war inflation was caused by an over-expansion of the money supply. They made famous the assertion of monetarism that "inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.

By the mids, however, the debate had moved on to other issues as monetarists began presenting a fundamental challenge to Keynesianism. Monetarists argued that central banks sometimes caused major unexpected fluctuations in the money supply. They source that actively increasing demand through the central bank can have negative unintended consequences. Former Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan argued that the s decoupling was explained by a virtuous cycle of productivity and investment on one hand, and a certain degree of " irrational exuberance " in the investment sector on the other. There are also arguments that monetarism is a special case of Keynesian theory.
The central test case over the validity of these theories would be the possibility of a liquidity traplike that experienced by Japan. Ben Bernanke source, Princeton professor and another former chairman of the U. Federal Reserve, argued that monetary policy could respond to zero interest rate conditions by direct expansion of the money supply.]
Bravo, this rather good phrase is necessary just by the way
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is excellent thought. I agree with you.