![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Human Exposure And The Risk Of Cardiovascular](https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/image_data/file/71152/6.4139_PHE_Health_Matters_January_Online_960x640_3.png)
Something: Human Exposure And The Risk Of Cardiovascular
| AN ORGANIZATION ON THE ROAD OF DOWNFALL | 966 |
| THE WAR OF THE UNION AND CONFEDERATE | 573 |
| The Effects Of Bilingualism On Multiple Difference | 5 days ago · The human exposure to groundwater contamination with toxic elements is a worldwide concern. In this study, multivariate statistics coupled with probabilistic and deterministic risk estimation approaches were applied to groundwater samples of Urmia aquifer (UA) to evaluate human health risks in relation to the consumption of groundwater contaminated with toxic elements. Mar 20, · Adverse cardiovascular effects occur from chronic exposure to noise due to the sympathetic nervous system's inability to habituate. The sympathetic nervous system maintains lighter stages of sleep when the body is exposed to noise, which does not allow blood pressure to follow the normal rise and fall cycle of an undisturbed circadian rhythm. 3 days ago · Public Health Risk Assessment For Human Exposure To Chemicals Environmental Pollution TEXT #1: Introduction Public Health Risk Assessment For Human Exposure To Chemicals Environmental Pollution By John Creasey - Jul 22, ~ Last Version Public Health Risk Assessment For Human Exposure. |
| Alcohol Advertising Essay | Electronic Health Record System At A Glance |
| Vaccination Informed Parental Choice Vaccination | 55 |
Human Exposure And The Risk Of Cardiovascular Video
Risk Assessment for Cardiovascular DiseaseThe human exposure to groundwater contamination with toxic elements is a worldwide concern.
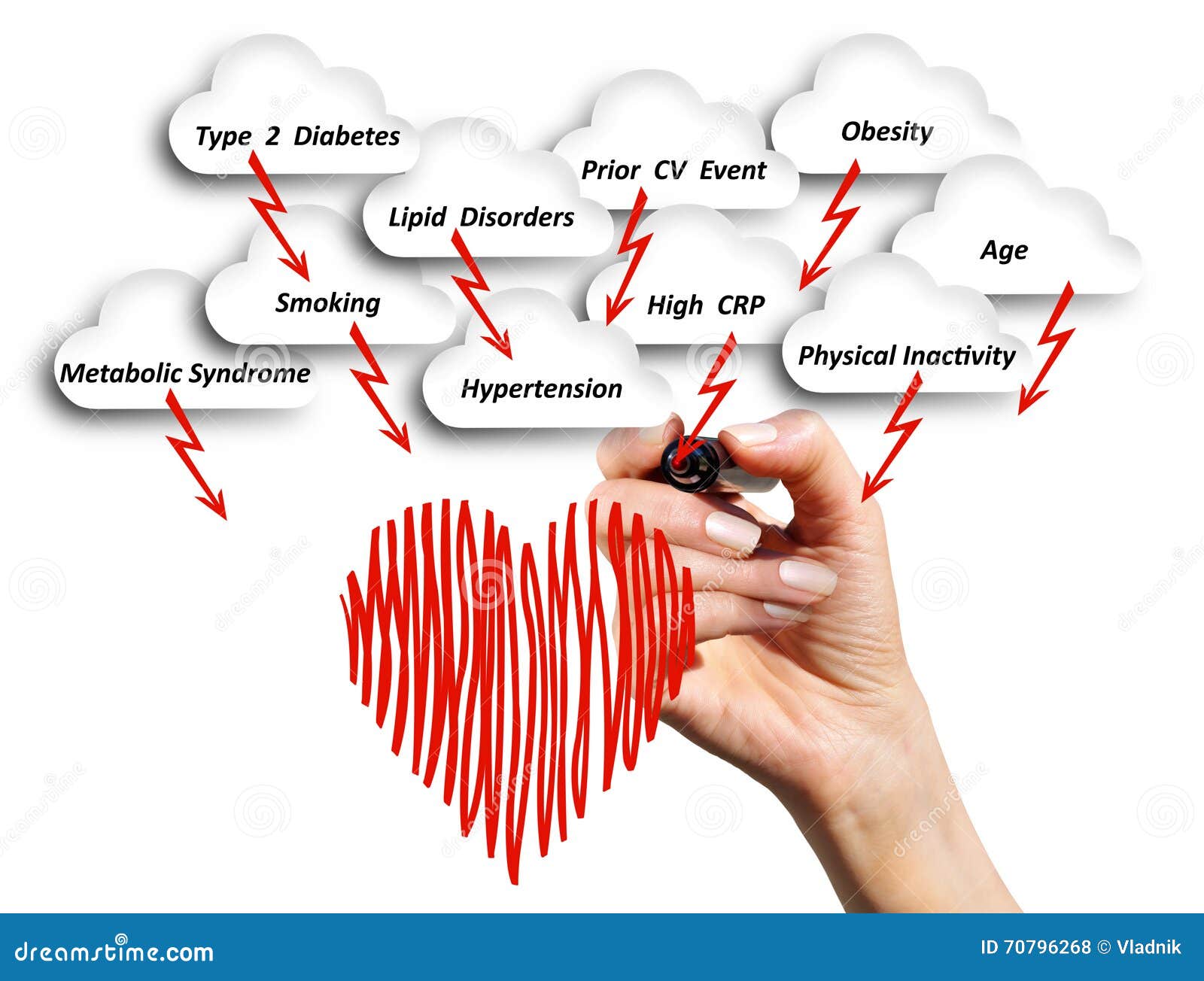
In this study, multivariate statistics coupled with probabilistic and deterministic risk estimation approaches were applied to groundwater samples of Urmia aquifer UA to evaluate human health risks in relation to the consumption of groundwater contaminated with toxic elements. However, arsenic Cardivascularlead Pbiron Feand selenium Se were elevated at some locations.
Navigation menu
Monte Carlo simulation-based probabilistic risk estimation suggested ingestion as the dominant pathway for water-hosted element exposure. Mean values of hazard index estimated for As exposure from combined ingestion and dermal contact pathways exceeded the safe level of 1.

Sensitivity analysis highlighted exposure duration, element concentration in water, and average time as Thr most significant variables causing the probable health risks. Reductive dissolution of Fe III oxyhydr oxides and clay minerals was identified as the main controlling mechanism of As mobilization. This communication emphasizes the need for appropriate approaches in mitigating toxic element contamination of water resources in coastal parts of the UA to safeguard public health from carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks. This is a preview of subscription content, log in to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve.
Access options
Sep Purif Technol Water Res — Environ Int Environ Res — Arab J Geosci. Environ Sci Pollut Res. J Asian Earth Sci —]
One thought on “Human Exposure And The Risk Of Cardiovascular”