Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect - really
Tim goes on to admit that some friends had helped him register to vote, and he planned to probably make it happen for the midterms. Grow up , the overall sentiment goes. Life is not that hard. Millennials love to complain about other millennials giving them a bad name. None of these tasks were that hard: getting knives sharpened, taking boots to the cobbler, registering my dog for a new license, sending someone a signed copy of my book, scheduling an appointment with the dermatologist, donating books to the library, vacuuming my car. I was publishing stories, writing two books, making meals, executing a move across the country, planning trips, paying my student loans, exercising on a regular basis. My shame about these errands expands with each day. I remind myself that my mom was pretty much always doing errands. Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/235321865_Factors_affecting_construction_labour_productivity_for_Malaysian_residential_projects/links/00b49529e8920678d7000000/largepreview.png)
Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect Video
Factors affecting productivity.Report Jobs and Unemployment.
PENN LIBRARIES
Download PDF. Affechingthe U. As shown in Figure A, the share of workers who have been jobless for 27 weeks or more is elevated relative both to its historical rate and, until recently, to the short-term unemployment rate. Shaded areas denote recessions. Because it is so crucial to interpreting our findings, Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect paper starts with our definitions of economic scarring. It then examines evidence on long-term unemployment and scarring. In particular, this paper looks at two separate categories of scarring: microeconomic and macroeconomic scarring. And within each, it differentiates between scarring caused by any episode of involuntary unemployment, and scarring that is unique to episodes of elevated long-term unemployment. Therefore, if an episode of involuntary job loss is associated with lower future earnings or other negative economic outcomes, and these adverse outcomes seem to persist even after the initial spell of Productivith endsthese outcomes are considered microeconomic scarring.
This means we are not including the income declines that are contemporaneous with the jobless spell.
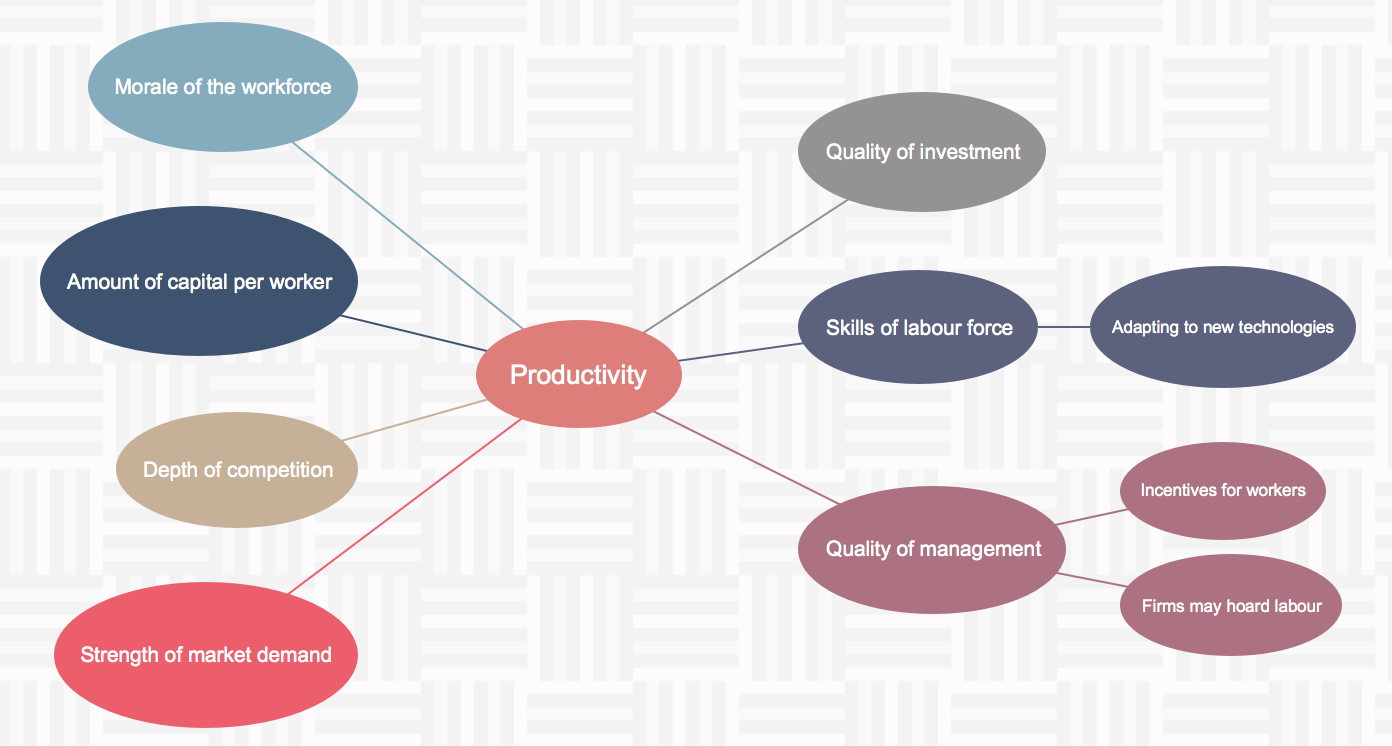
1. Employee engagement
It is trivial indeed to note that when people lose jobs, their income falls, and these income declines cause great economic distress. Scarring, however, implies something else: that capacity is diminished for an extended period of time even after the initial damage is healed i.
Because we are not including the damage inflicted by income declines that are contemporaneous with the jobless spell this kind of damage Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect obviously correlated with the length of joblessnessit is not a foregone empirical conclusion that there is unique long-term damage to individuals and households stemming from a spell of LTU. This paper specifically addresses the question of whether or not the scars of long-term jobless spells are clearly worse than those of shorter jobless spells. Finally, the paper highlights two channels through which a spell of LTU can scar workers. Second, the spell could be used as a signal by employers looking to sort potential hires in the job queue. We label the scars left by these two channels as productivity scarring and signal scarring. These are quite important to distinguish, as they have very different policy implications.
Evidence on microeconomic scarring
This paper finds that regardless of duration, involuntary job loss leads to significant and long-lasting economic damage to individuals and their families. Specific Thsir on microeconomic scarring include:. As before, we apply a more stringent criterion to scarring that is specific to LTU. Specifically, the damage must be greater when LTU is higher as a share of overall unemployment. Finally, in regards to macroeconomic scarring, we also look for signs of irreversibility as a necessary criterion. That is, if extended periods of elevated unemployment or LTU lead to lower estimates of future potential output, this alone will Factors Affecting Labor Productivity And Their Affect be enough to constitute a macroeconomic scar.
Rather, we will also examine the evidence Affect see if this scarring effect https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/woman-in-black-character-quotes/the-importance-of-studying-sociology.php be sustainably reversed by an extended period of below-average unemployment or LTU.
If it can, we will then classify this as reversible scarring. The clearest finding from the literature on the scarring effects of unemployment is that the simple fact of an involuntary job loss causes significant economic damage, visit web page that this damage lasts well past the end of the first jobless spell.
Introduction and executive summary
Most strikingly, the fact of an involuntary job loss by a parent is associated with economic damage to the careers of their children. This evidence argues strongly that the cost of recessions is likely understated if measured simply in terms of foregone output.
However, what is much less clear is whether or not the scarring inflicted by involuntary displacement is worse for longer jobless spells. While a longer jobless spell is obviously associated with a larger cumulative income drop during the spellit is not a foregone conclusion that longer bouts of unemployment result in more scarring—i. In fact, there is very little evidence that long jobless spells cause extra scarring. Below we first survey the Prodyctivity on scarring inflicted by involuntary job loss of any duration, and then we note the much thinner evidence on whether longer jobless spells cause additional scarring.
This first section documents the extensive evidence showing that any involuntary job loss is associated with very high economic costs, including clear evidence that such Afefct job loss can leave deep economic scars that persist well after the jobless spells pass.
The most compelling recent empirical work documenting the long-run wage implications of involuntary job displacement is by Davis and von Wachter Davis and von Wachter investigate the Great Recession to estimate the impact of permanent layoffs among high-tenure workers those who had the same job for more than three years and the associated cumulative earnings losses.]
Bravo, your idea it is brilliant
At you abstract thinking