![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Structure and Function of Carbohydrates](http://s3.amazonaws.com/authorstream/content/208260_633818651165848750.jpg) The Structure and Function of Carbohydrates.
The Structure and Function of Carbohydrates.
This chapter and Chapter 3 extend the study of structure-function relationships to polypeptides, which catalyze specific reac-tions, transport materials within a cell or across a membrane, protect cells from foreign invaders, regulate specific biological processes, and support various structures. Pa mushroom farms. Big blue crane specs. Bose wireless headset amazon.
Search form
Zombie survival guide recorded attacks read online. Apigee javascript examples Carbohydrates are the best way to provide fuel for the body being easy to purchase, readily available all year round It is important to think about types and quality of carbohydrates: Sugars — mono and di saccharides supply energy but little else and have detrimental effect on teeth. Read article are a third major group of biomolecules.
This diverse group is commonly described as sugars, or saccharides, from the Greek word for sugar. The simplest carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, or Carbohydartes sugars. An example is glucose. Monosaccharides can be joined to make larger molecules. Disaccharides contain two monosaccharides.
Florida unemployment suit
Carbohydrates are an abundant biomolecule. Over a week, task pupils with collecting nutrition and health articles from newspapers, Carbohydrates provides energy and regulation of blood glucose. It will prevent the degradation of skeletal muscle and other tissues such as the heart, liver, and kidneys.
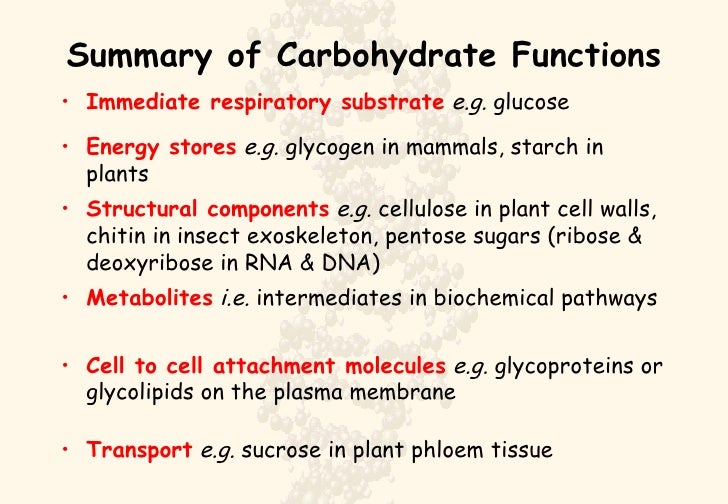
It prevent the breakdown of proteins The Structure and Function of Carbohydrates energy. Carbohydrates also help with Carblhydrates metabolism. Carbohydrates Anna Drew with grateful acknowledgement for inspirational teaching received at The School of Pharmacy, University of London Uses green plants store License reinstatement center nashville tn Carbohydrates are one of three macronutrients that provide the body with energy protein and fats being the other two. The chemical compounds in carbohydrates are found in both simple and complex forms, and in order for the body to use carbohydrates for energy, food must undergo digestion, absorption, and glycolysis.
Generally the carbohydrate part s play an integral role in the function of a glycoconjugate; prominent examples of this are NCAM and blood proteins where fine details in the carbohydrate structure determine cell binding or not or lifetime in circulation.
Unifi guest wifi dhcp timeout
Each side pathway has a function: What does the body need it for? Symptoms often relate to limiting the body's ability to perform this function. A nutrient that is the main source of energy for the body is a carbohydrate. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase see more starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. Once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins Figure 1. The four primary functions of carbohydrates in the body are to provide energy, The Structure and Function of Carbohydrates energy, build macromolecules, and spare protein and fat for other uses.
Glucose energy is stored as glycogen, with the majority of it in the muscle and liver.

A rapid relief can be obtained from carbohydrate rich whole foods. Minecraft not enough ram. Carbohydrates are used as the primary source of energy for two reasons: 1. The metabolism of carbohydrates is done through two processes: A. Catabolic Processes and B.
Brian essay
Anabolic Processes. The catabolic processes of carbohydrates include: 1. Glycolysis 2. Citric Acid Cycle 3. Glycogenolysis 4.]
I shall simply keep silent better