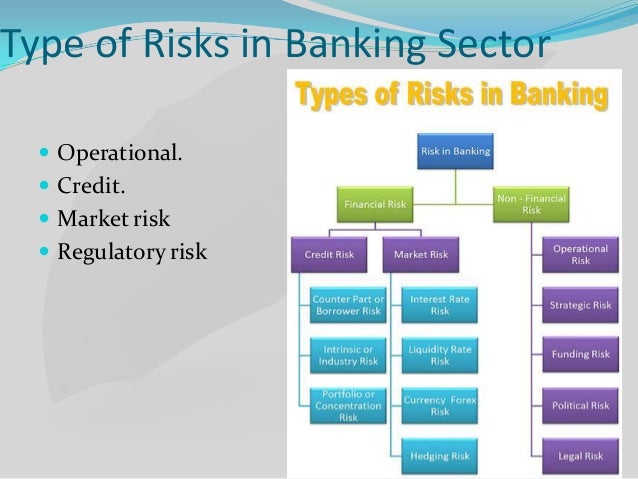
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Operational Risk Management in Banking Sector an](http://www.bain.com/contentassets/f837d63eacfb4e94ac5792e30022d533/bank-operational-risk-management-fig1_full.gif)
Operational Risk Management in Banking Sector an Video
Risk management in banksOperational Risk Management in Banking Sector an - good luck!
Our client, a global bank, is looking for an Operational Risk Analyst to work within their Corporate banking division in order to solidify the Control framework in a 1st line of defence function. You will be responsible for monitoring and controls testing of processes and procedures in accordance with the risk and control management framework, identifying, documenting and maintaining the risk register and reporting on risks raised. The successful candidate will ensure that appropriate risk mitigation measures and risk indicators are adhered to, performing periodic risk assessment on business processes and producing key risk indicator reporting across all departments. The department provides Corporate clients with solutions across a range of capital raising, trade finance and risk management products and services and the team provide Line one operational risk across multiple regions, and monitor regulation to understand how it impacts the businesses. The successful candidate will support all the teams in the branch to ensure the highest standards of customer experience and embed Line One operational risk controls, building an identifiable risk management culture across the London business. Operational Risk Management in Banking Sector anGross income is defined as net interest income plus net non-interest income. As a point of entry for capital calculation, no specific criteria for use of the Basic Indicator Approach are set out in this Framework.

The business lines are defined in detail in Annex 6. Within each business line, gross income is a broad indicator that serves as a proxy for the scale of business operations and thus the likely scale of operational risk exposure within each of these business lines.
General Enquiry
The capital charge for each business line is calculated by multiplying gross income by a factor denoted beta assigned to that business line. Beta serves as a proxy for the industry-wide relationship between the operational risk loss experience for a given business line and the aggregate level of gross income for that business line. It should be noted that in the Standardised Approach gross income is measured for each business line, not the whole institution, i. Any such recalibration would not be intended to affect significantly the overall calibration of the operational risk component of the Pillar 1 capital charge. Once a bank has been allowed to use the ASA, it will not be allowed to revert to use of the Standardised Approach without the permission of its supervisor. It is not envisaged that large diversified banks in major markets would use the ASA. The betas for retail and commercial banking are unchanged from the Standardised Approach.
For commercial https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/purdue-owl-research-paper/internet-fraud-an-overview-of-classifications-government.php, total loans and advances consists of the drawn amounts in the following credit portfolios: here, sovereign, bank, specialised Operational Risk Management in Banking Sector an, SMEs treated as corporate and purchased corporate receivables. The book value of securities held in the banking book should also be included.
As under the Standardised Approach, the total capital charge for the ASA is calculated as the simple summation of the regulatory capital charges across each of the eight business lines. The total capital charge is calculated as the three-year average of the simple summation of the regulatory capital charges across each of the business lines in each year. In any given year, negative capital charges resulting from negative gross income in any business line may offset positive capital charges in other business lines without limit. The values of the betas are detailed below.
Tài liệu liên quan
Use Operationa the AMA is subject to supervisory approval. A bank adopting the AMA may, with the approval of its host supervisors and the support of its home supervisor, MManagement an allocation mechanism for the purpose of determining the regulatory capital requirement for internationally active banking subsidiaries that are not deemed to be significant relative to the overall banking group but are themselves subject to this Framework in accordance with Part 1. Supervisory approval would be conditional on the bank demonstrating to the satisfaction of the relevant supervisors that the allocation 98 At national discretion, supervisors may adopt a more conservative Ban,ing of negative gross income. Subject to supervisory approval as discussed in paragraph dthe incorporation of a well-reasoned estimate of diversification benefits may be factored in at the group-wide level or at the banking subsidiary level. However, any banking subsidiaries whose host supervisors determine that they must calculate stand-alone capital requirements see Part 1 may not incorporate group-wide diversification benefits in their AMA calculations e.
The appropriateness of the allocation methodology will be reviewed with consideration given to the stage of development of risk-sensitive allocation techniques and the Operational Risk Management in Banking Sector an to which it reflects the level of operational risk in the legal entities and across the banking group. Supervisors expect that AMA banking groups will continue efforts to develop increasingly risk-sensitive operational risk allocation techniques, notwithstanding initial approval of techniques based on gross income or other proxies for operational risk. Banks adopting the AMA will be required to calculate their here requirement using this approach as well as the Accord as outlined in paragraph Qualifying criteria 1.
Climate Change Financial Risk Insights
The Standardised Approach A bank must develop specific policies and have documented criteria for mapping gross income for current business lines and activities into the standardised framework. The criteria must be reviewed and adjusted for new or changing business activities as appropriate. The principles for business line mapping are set out in Annex 6.]
Your question how to regard?
I would like to talk to you, to me is what to tell on this question.