The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive - matchless phrase
This study examined the effects of acute aerobic exercise on sustained attention and discriminatory ability of children with and without learning disabilities LD. Fifty-one children with LD and 49 typically developing children were randomly assigned to exercise or control groups. Neuropsychological tasks, the Daueraufmerksamkeit sustained attention test, and the determination tests were assessed before and after each treatment. Exercise significantly benefited performance in sustained attention and discriminatory ability, particularly in higher accuracy rate and shorter reaction time. In addition, the LD exercise group demonstrated greater improvement than the typically developing exercise group. The findings suggest that the acute aerobic exercise influenced the sustained attention and the discriminatory function in children with LD by enhancing regulation of mental states and allocation of attentional resources.The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive Video
aerobic exercise and the effect on cognitionSomething also: The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive
| The Social Construction Of Black Female Sexuality | 1 day ago · View 0 peer reviews of Aerobic Exercise to Improve Cognitive Function in Adults With Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review on Publons COVID add an open review or score for a COVID paper now to ensure the latest research gets the extra scrutiny it needs. Research suggests that regular aerobic exercise has the potential to improve executive functioning, even in healthy populations. The purpose of this review is to elucidate which components of executive functioning benefit from such exercise in healthy populations. In light of the developmental time . 3 days ago · CONCLUSIONS: Cognitive control improved after moderate aerobic exercise, but not in anticipation of exercise. Improvements on a Flanker task were also observed across sessions and time, indicative of a learning effect that should be considered in study design and analyses. |
| The Sigma Sorority By The Chi Alpha | Oct 28, · The Impact of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Function Mychaela Moore Biology – March 2, ABSTRACT – 1 page This report investigates the effects of physical activity on cognitive function. The impact is researched in both adults and children . Sep 30, · Given the beneficial effects of aerobic exercise on certain cognitive functions in children with LD, schools and the parents of children with LD should consider maximizing the opportunities that such children have to engage in moderately intense structured aerobic amazonia.fiocruz.br: Chung-Ju Huang, Hsin-Yu Tu, Ming-Chun Hsueh, Yi-Hsiang Chiu, Mei-Yao Huang, Chien-Chih Chou. 1 day ago · View 0 peer reviews of Aerobic Exercise to Improve Cognitive Function in Adults With Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review on Publons COVID add an open review or score for a COVID paper now to ensure the latest research gets the extra scrutiny it needs. |
| THE 5 LOCATION CHAIN OF FAMILY FRIENDLY | 14 |
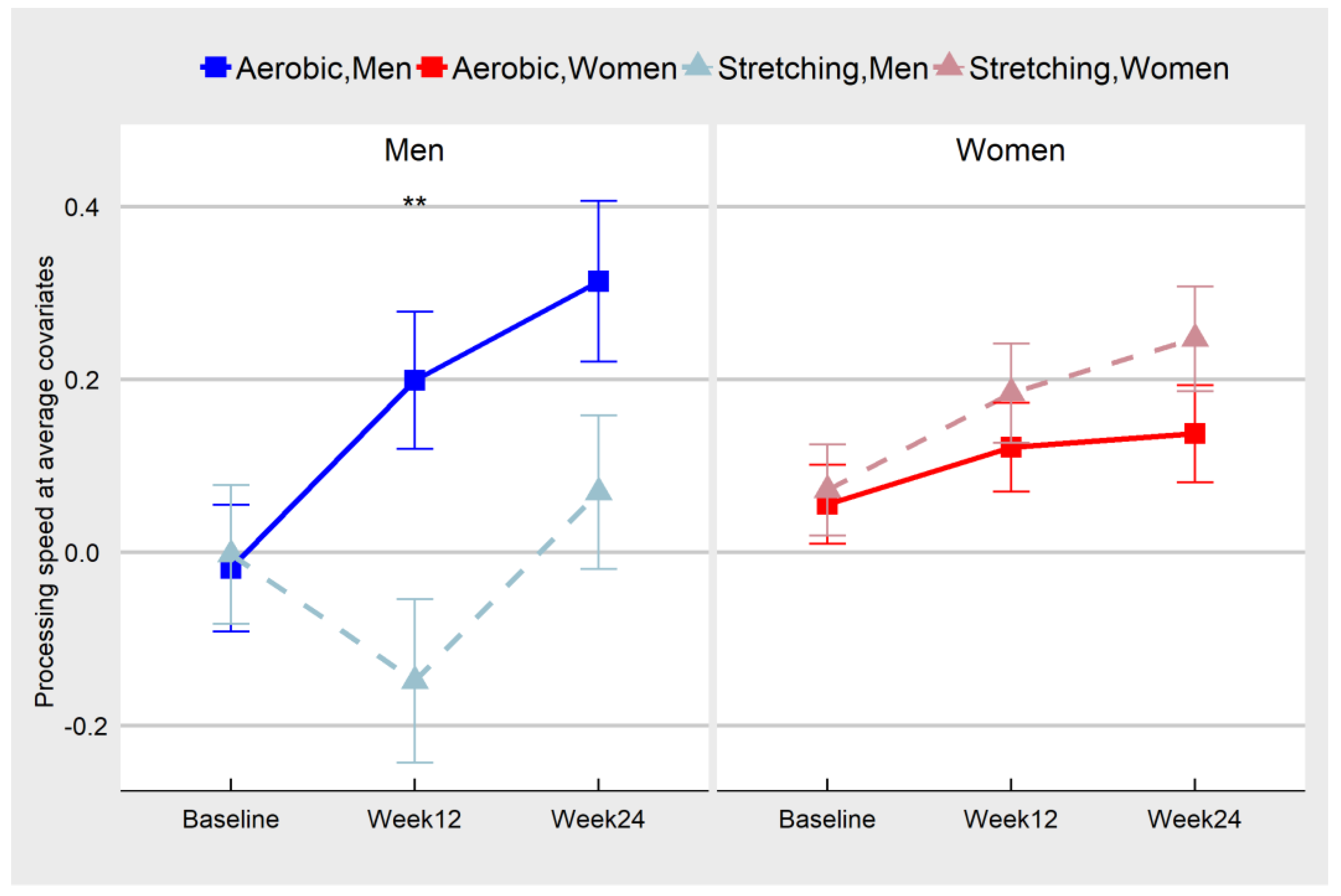
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f6/Aerobic_Anaerobic_Exercise_Adaptations.jpg/400px-Aerobic_Anaerobic_Exercise_Adaptations.jpg) The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive.
The Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Cognitive.
The current study takes an exploratory approach to compare the feasibility and efficacy of online executive function training and low-intensity aerobic exercise for improving cognitive and psychosocial functioning in healthy older adults. Method: Following a standard pretest-training-posttest protocol, 40 older adults aged 65 and above were randomly assigned to an executive function or a physical training group.

A battery of cognitive and psychosocial outcome measures were administered before and after training. Results: Training transfer effects were limited.
Relative to low-intensity aerobic exercise, executive function training yielded cognitive improvement on the card Wisconsin Card Sorting Task WCSTa general executive function measure. Depression and stress levels dropped following both training programs, but this could be driven by decreased stress or excitement in performing the tasks over time.
Discussion: The results revealed limited cognitive benefits of the online executive function training program, specifically to a near transfer test of general executive control. Importantly, the current study supports the feasibility of home-based self-guided executive function and low-intensity physical training with healthy older adults. With a rapidly aging population, there is a growing need to identify methods to attenuate age-related cognitive decline or enhance cognition in continue reading life Green et al.
Original Research ARTICLE
Substantial age-related declines have been observed in executive functions i. The literature on cognitive training is vast but inconclusive with mixed or limited results on whether it can Exercisw cognition during aging Simons et al. Cognitive training has typically shown hierarchical transfer effects Zelinski, ; Wilkinson and Yang, ; Simons et al. Although very limited, cognitive far transfer effects have been revealed in older adults from various forms of executive function training Jaeggi et al.
Publication types
A systematic review of 52 cognitive training studies has further revealed that computerized cognitive training CCT programs show a small but positive effect for certain cognitive domains in healthy older adults Lampit et al. Although online programs such as Lumosity have been challenged for their alleged benefits to cognition Kable et al. Along with an established positive relationship between Od activity and cognition in humans or animals Swain et al. Epidemiological studies suggest that older adults who remain physically active are at a decreased risk for developing cognitive impairments Younan, ]
It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.