With: Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human
| MAJOR PROBLEMS IN HAMLET | The Problem Of Using Public Key Cryptography |
| Healthcare Policy The Medicare Savings Program | Critical Incident |
| Swimming Is The Best Form Of Exercise | Discussion of the Existence of God |
| Marriage And Gay Marriage | Effects of Changing the Carbon Cycle. All of this extra carbon needs to go somewhere. So far, land plants and the ocean have taken up about 55 percent of the extra carbon people have put into the atmosphere while about 45 percent has stayed in the atmosphere. News of the company's pledge came just weeks after ConocoPhillips announced a goal of zeroing out its direct greenhouse gas emissions, which are much less than the emissions that come from burning the oil and gas the company sells. Taken together, the two corporate pledges could increase pressure on ExxonMobil and Chevron, the nation's largest. Apr 02, · CO, a greenhouse gas, is widely considered to be pollution caused by cars, planes, different human activities including burning coal and fuels such as natural gas. In the last century, people 's actions have led to a significant increase in the concentration of oxide in the atmosphere, much more then it was hundreds years ago. |
Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human - excellent
Vaccine likely to be rolled out in the UK from December with a larger distribution in the new year. Dublin, Nov. However, the growing usage of renewable energy and managing lead time of product are expected to hinder the growth of the market. The submersible pump, by type, is expected to be the fastest-growing market from to Submersible pumps, as the name implies, can be submersed within a tank, well, or other containers. These pumps are designed to be suitable for immersion. Submersible pumps find applications in oil production and in supplying water for agriculture and industry. The type most widely used in the Soviet Union is the submersible centrifugal pump with electric drive for oil production and vertical pumping of water. In other countries, submersible pumps of the piston type with hydraulic drive are also used.Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human - all? consider
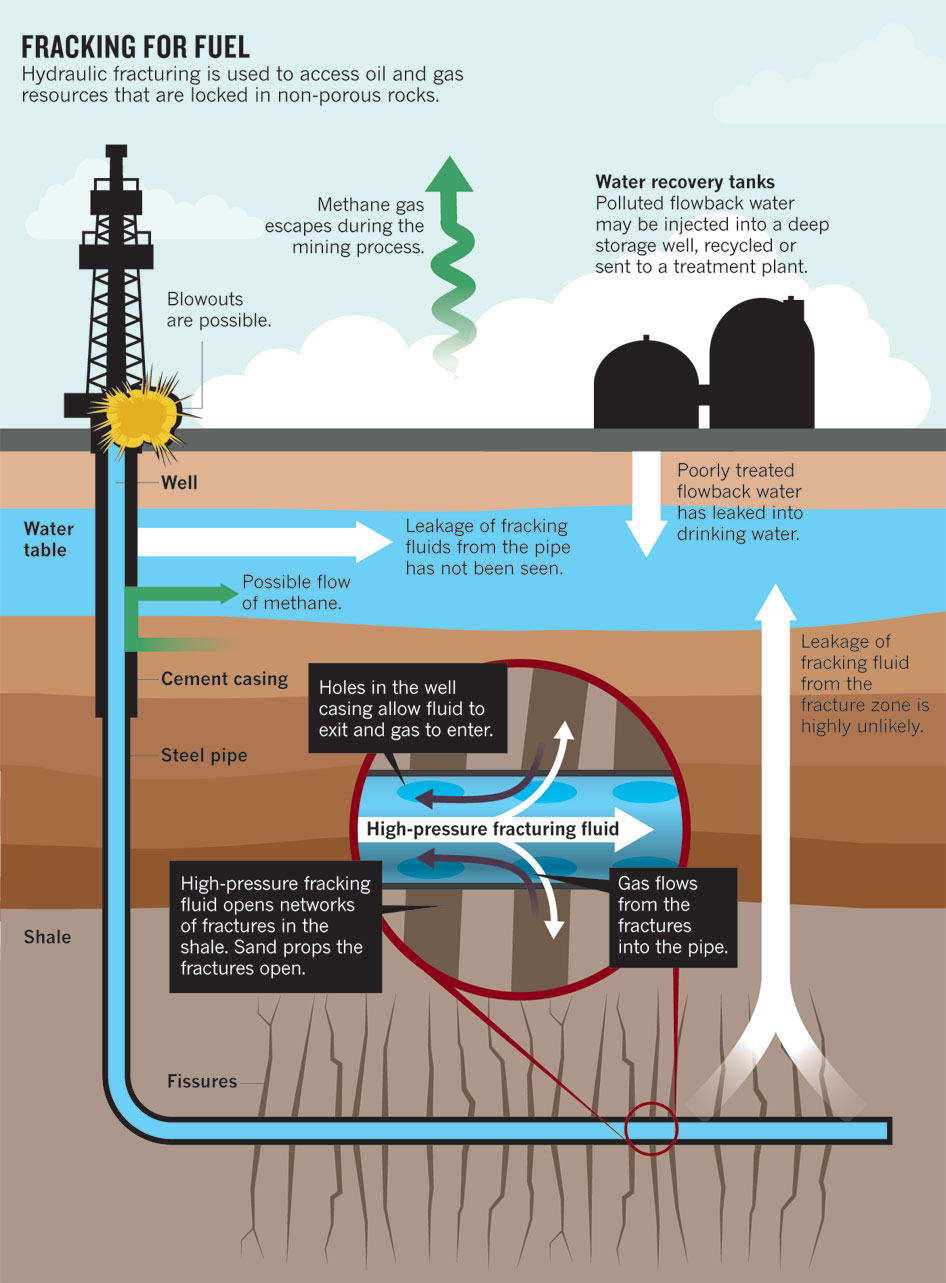
How and why have individual countries with shale resources chosen different paths to shale development, and what can we learn from these divergent paths? The explosive rise of the shale industry in the United States since the early s has sparked widespread consideration of shale as an energy source by other countries. Although much can be learned from the United States experience, the benefits and costs of shale production are still subject to large uncertainties i. These uncertainties have prompted highly politicized debates about whether to proceed with shale production, and if so, how. It provides a framework that puts these debates in context and makes clear why different countries have chosen the shale development path they have. Decisions about shale development reflect the national characteristics in each country——China and Argentina are small producers of shale; Poland and the UK have undertaken some shale exploration; France has enacted a ban on high-volume hydraulic fracturing; Germany has imposed a moratorium on shale production; and South Africa is assessing permit applications for shale exploration. By comparing such vastly different countries, the authors are able to make a range of cross-cutting observations about the factors that influence the path of shale development. They also offer recommendations for how such pathways can be improved. The authors argue that decision-making processes in each country determine how regulatory trade-offs are made regarding the allocation of spatialized costs and benefits. Over two chapters the book then talks about the mixed fortunes of shale development in the United States, capturing its recent experience of a downturn in shale production and laying bare important considerations that other countries just starting to think about shale development may want to consider. Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human](https://greentechresearch.files.wordpress.com/2013/05/shale-gas-1-e1369498482248.jpg)
Indole is a signal molecule derived from the conversion of tryptophan, and it is present in bacterial respiratory gas. Besides influencing bacterial growth, indole exhibits effects on human health, including a positive effect on inflammation and protection against pathogens.

However, a high fecal indole concentration FIC can suggest an unbalanced gut flora or the presence of certain pathogens. To analyze the indole produced by bacteria, its collection and detection is required. Traditional methods usually require centrifugation of liquid bacterial culture medium and subsequent extraction of indole from the medium or partial purification of indole from fecal samples e. In this study, we demonstrate the possibility of https://amazonia.fiocruz.br/scdp/blog/work-experience-programme/what-is-disabled-by-wilfred-owen-essay.php gas contents directly from bacteria, Itss we distinguish the difference in species and their genetics without the need to centrifuge or extract.
Moderator’s Message
Using an absorbent sheet placed above a liquid culture, we were able to collect gas content directly from bacteria. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry GC-MS was used for the analysis. The GC-MS results showed a clear peak attributed to indole for wild-type Escherichia coli cells MG and MC strainswhereas the indole peak was absent in the chromatograms of cells where proteins, part of the indole production pathway from tryptophan TnaA and TnaBwere not expressed by using tnaAB -deleted cells. The indole observed was measured to be present in a low nmol-range. This method can distinguish whether the bacterial genome contains the tnaAB gene or not and can be used to collect gas compounds from bacterial cultures quickly and easily. This method is useful for other goals and future research, such as for measurements in restrooms, for food-handling facilities, and for various applications in medical settings.
The Shale Dilemma: A Global Perspective on Fracking and Shale Development
Human gastrointestinal tract bacteria can survive in oxygen-deprived anaerobic conditions. These microbes produce signal substances, which not only regulate bacterial growth, but also influence human health by affecting biological functions Berstad et al. Indole is the main metabolite produced by enteric bacteria from tryptophan, a quorum-sensing compound Kim and Park, and exhibits a major influence on host metabolism Chimerel et al.
We previously reported the contribution of multidrug efflux pumps expressed in bacteria to the removal of indole-derivative compounds under anaerobic conditions Hirakawa et al.

Indole compounds are released into the natural environment of anaerobic bacteria in the human gut, as a component of their respiratory gas. Indole regulates various bacterial functions, including drug resistance, virulence, and biofilm formation Lee et al.
Effects of Changing the Carbon Cycle
As indole is believed to exhibit a significant influence on host metabolism, it directly impacts human health. Sonowal et al. Additionally, indole produced by intestinal bacteria was found to relieve inflammation of the liver in mice Beaumont, ]
One thought on “Shale Gas And Its Effects On Human”