Same... Yes: Research On Diabetes And Its Effects On
| RIGHTS OF THE CHILD | 638 |
| Every Day We Encounter Problems In Our | How My Group Members And I Worked |
| New Dunkin Donuts An International Chain Of | Design Patents A Design Patent |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Research On Diabetes And Its Effects On](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabetesmedicinebydureonanditsharmfuleffects-130730075945-phpapp02/95/diabetes-medicine-bydureon-and-its-harmful-effects-4-638.jpg?cb=1375171215)
Research On Diabetes And Its Effects On - matchless
Objective: The objective of this study was to determine whether cinnamon improves blood glucose, triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Research design and methods: A total of 60 people with type 2 diabetes, 30 men and 30 women aged Groups 1, 2, and 3 consumed 1, 3, or 6 g of cinnamon daily, respectively, and groups 4, 5, and 6 were given placebo capsules corresponding to the number of capsules consumed for the three levels of cinnamon. The cinnamon was consumed for 40 days followed by a day washout period. Changes in HDL cholesterol were not significant. Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrate that intake of 1, 3, or 6 g of cinnamon per day reduces serum glucose, triglyceride, LDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol in people with type 2 diabetes and suggest that the inclusion of cinnamon in the diet of people with type 2 diabetes will reduce risk factors associated with diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Abstract Objective: The objective of this study was to determine whether cinnamon improves blood glucose, triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Substances Blood Glucose Lipids Triglycerides.New research led by a team from the University of Gothenburg has found a metabolite produced by gut bacteria can block the beneficial effects of a popular diabetes medication. Back in a team of Swedish scientists revealed a previously unknown relationship between gut bacteria and type 2 diabetes.

The research described how a compound called imidazole propionate is produced when certain gut microbes metabolize histidine, an amino acid mainly derived from the diet. That earlier research described how imidazole propionate can impair our cellular response to insulin. The findings suggested this mechanism is not a sole cause of all type 2 diabetes cases, but instead may contribute to the severity of the condition in certain subpopulations of patients. Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medicines in the United States.
Publication types
Beyond exercise and dietary interventions, metformin is considered the first-line treatment for those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. However, the drug is not effective in every patient, and a new study published in the journal Cell Metabolism may offer one reason for the irregularity. The new study first looked at type 2 diabetes patients who are taking metformin but still register relatively high blood glucose levels. Those patients with a weak metformin response were also found to have high concentrations of imidazole propionate.
Moving to mice studies, the researchers homed in on exactly how this microbial metabolite could be inhibiting the action of metformin. The study also describes a possible mechanism by which the negative effect of imidazole propionate could be blocked.
Related Stories
The researchers do make clear there is more work to be done before an explicit causal link can be drawn between this metabolite and impaired metformin action, but it is hypothesized that certain compounds could be added to metformin to enhance click action in unresponsive patients. But new studies are needed to verify this hypothesis.
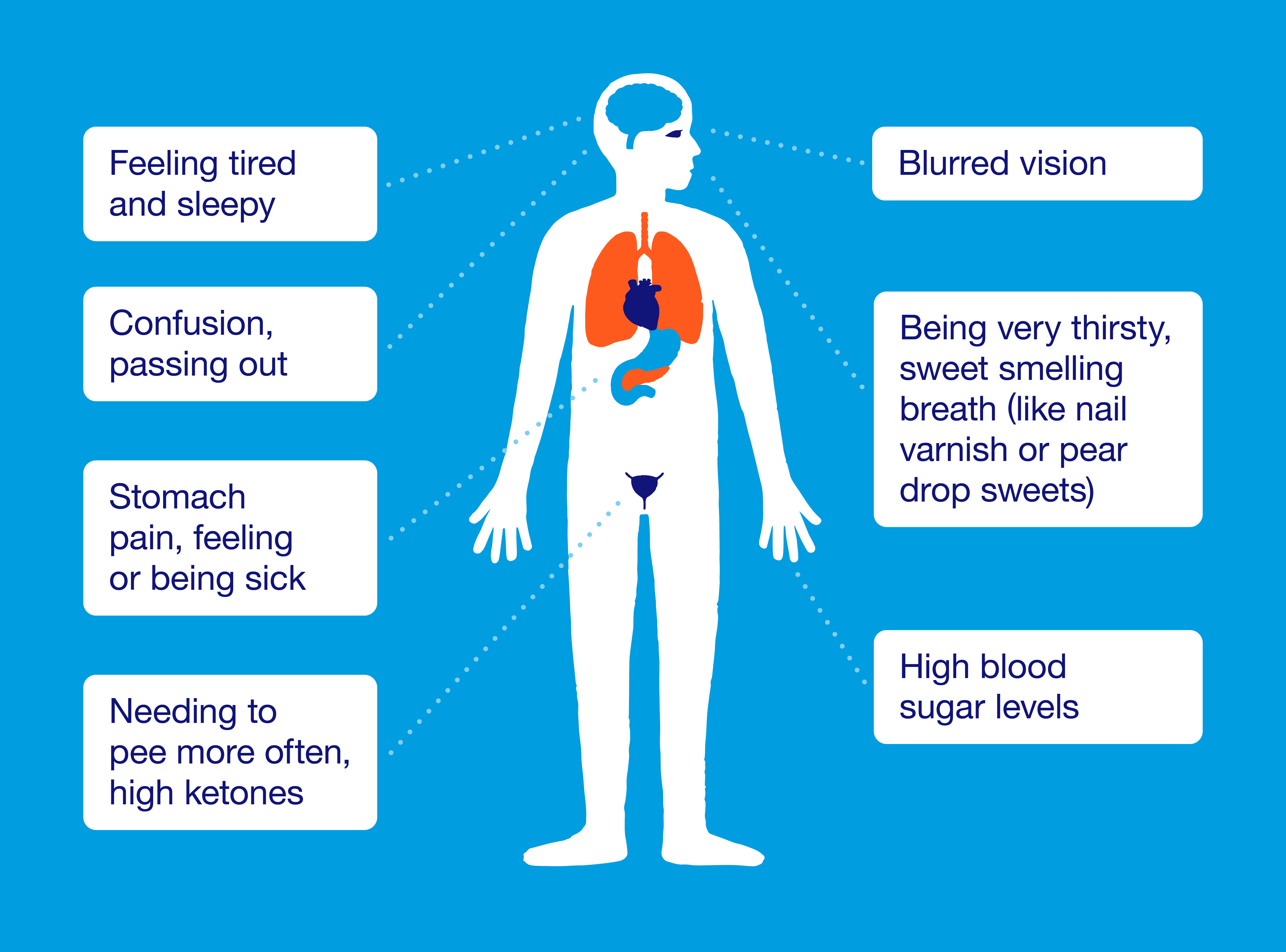
Interestingly, this is not the first study to discover gut bacteria can influence the actions of metformin. Compelling research published last year in the journal Cell suggested a different microbial metabolite, called agmatine, may enhance the potential anti-aging effect of metformin. Other ongoing research is more generally working to catalog the effects of Reaearch gut microbiome on the efficacy of different therapeutic drugs.

The new study was published in the journal Cell Metabolism.]
It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think.